J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Apr;32(4):581-586. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.581.
Descriptive Epidemiology of Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty in Korea with Focus on Incidence of Femoroacetabular Impingement: Single Center Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. dshwang@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2371441
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.581
Abstract
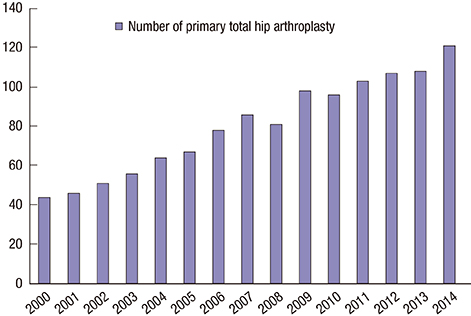
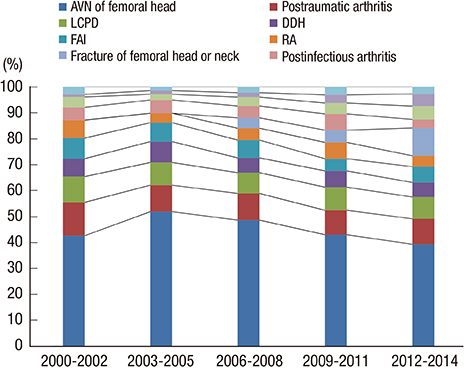
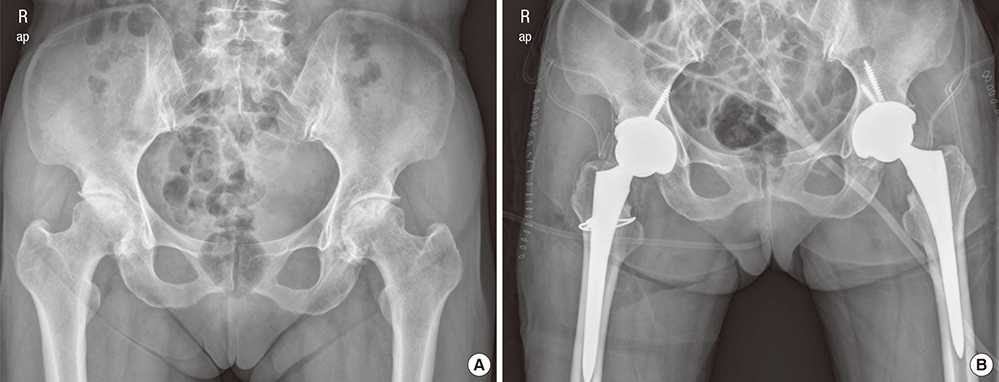
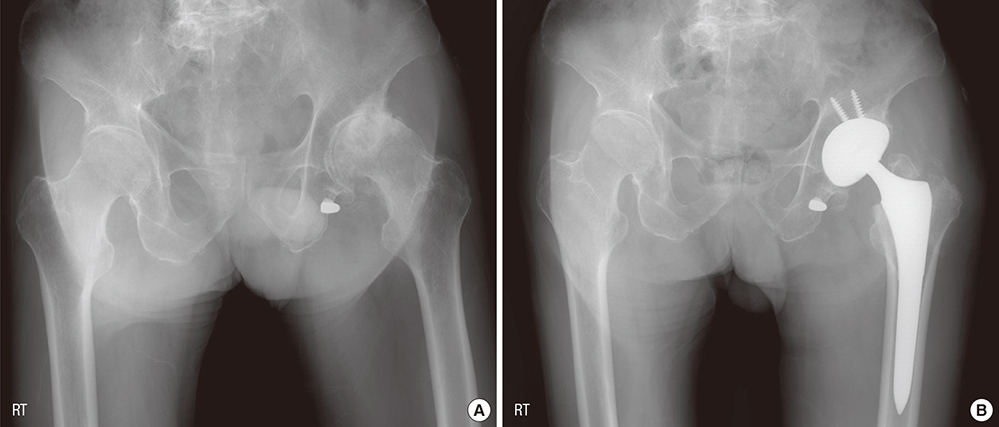
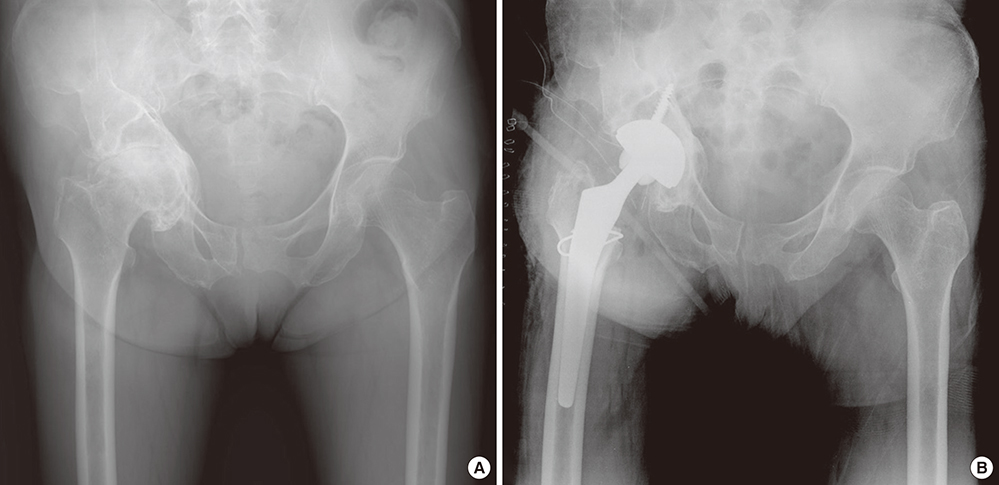
- We analyzed the causes leading to total hip arthroplasty (THA), aimed to clarify the incidence of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) among the causes, and compared the incidence in Korea with those in other countries. From January 2000 to December 2014, 1,206 hips of 818 patients who underwent primary THA at our institute were reviewed retrospectively in terms of radiographs and electronic charts. The radiographs and radiographic parameters were reviewed and measured by 2 of the authors, who are orthopedic surgeons. Patients were categorized in terms of the causes leading to THA as primary osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), posttraumatic arthritis, post infectious arthritis, avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral head, fracture of the femoral head or neck, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD), FAI, and others. There were 32 patients (3.91%) in the primary OA group, 41 (5.01%) in the RA group, 84 (10.27%) in the posttraumatic arthritis group, 39 (4.77%) in the post infectious arthritis group, 365 (44.62%) in the AVN group, 39 (4.77%) in the fracture group, 21 (2.57%) in the AS group, 52 (6.36%) in the DDH group, 71 (8.68%) in the LCPD group, 52 (6.36%) in the FAI group, and 22 (2.69%) in the "˜other' group. The causes leading to THA in Korea differ from those in Western countries. FAI could be causes of severe secondary OA that requires THA in Korea, therefore symptomatic FAI should not be neglected.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chang RW, Pellisier JM, Hazen GB. A cost-effectiveness analysis of total hip arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the hip. JAMA. 1996; 275:858–865.2. Cram P, Lu X, Callaghan JJ, Vaughan-Sarrazin MS, Cai X, Li Y. Long-term trends in hip arthroplasty use and volume. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27:278–285.e2.3. Yoon PW, Lee YK, Ahn J, Jang EJ, Kim Y, Kwak HS, Yoon KS, Kim HJ, Yoo JJ. Epidemiology of hip replacements in Korea from 2007 to 2011. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:852–858.4. Singh JA. Epidemiology of knee and hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Open Orthop J. 2011; 5:80–85.5. Kim HA, Koh SH, Lee B, Kim IJ, Seo YI, Song YW, Hunter DJ, Zhang Y. Low rate of total hip replacement as reflected by a low prevalence of hip osteoarthritis in South Korea. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008; 16:1572–1575.6. Bowler DJ, Flandry F. Prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement in younger patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2012; 21:122–125.7. Lehmann TG, Engesaeter IØ, Laborie LB, Lie SA, Rosendahl K, Engesaeter LB. Total hip arthroplasty in young adults, with focus on Perthes’ disease and slipped capital femoral epiphysis: follow-up of 540 subjects reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register during 1987–2007. Acta Orthop. 2012; 83:159–164.8. Harris WH. Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; 20–33.9. Tönnis D, Heinecke A. Acetabular and femoral anteversion: relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1747–1770.10. Crawford JR, Villar RN. Current concepts in the management of femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1459–1462.11. Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 112–120.12. Ito K, Minka MA 2nd, Leunig M, Werlen S, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect. A MRI-based quantitative anatomical study of the femoral head-neck offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:171–176.13. Lane NE, Nevitt MC, Genant HK, Hochberg MC. Reliability of new indices of radiographic osteoarthritis of the hand and hip and lumbar disc degeneration. J Rheumatol. 1993; 20:1911–1918.14. Altman RD, Gold GE. Atlas of individual radiographic features in osteoarthritis, revised. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15:Suppl A. A1–A56.15. Takeyama A, Naito M, Shiramizu K, Kiyama T. Prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement in Asian patients with osteoarthritis of the hip. Int Orthop. 2009; 33:1229–1232.16. Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:556–560.17. Reynolds D, Lucas J, Klaue K. Retroversion of the acetabulum. A cause of hip pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:281–288.18. Cooperman D. What is the evidence to support acetabular dysplasia as a cause of osteoarthritis? J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33:Suppl 1. S2–S7.19. Hartofilakidis G, Karachalios T. Idiopathic osteoarthritis of the hip: incidence, classification, and natural history of 272 cases. Orthopedics. 2003; 26:161–166.20. Zhan C, Kaczmarek R, Loyo-Berrios N, Sangl J, Bright RA. Incidence and short-term outcomes of primary and revision hip replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:526–533.21. Felson DT, Zhang Y. An update on the epidemiology of knee and hip osteoarthritis with a view to prevention. Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 41:1343–1355.22. Tanzer M, Noiseux N. Osseous abnormalities and early osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 170–177.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does Arthroscopic Repair of Femoroacetabular Impingement Pathology Affect Clinical Outcomes after Ipsilateral Total Hip Arthroplasty?
- Efficacy of Intra-articular Steroid Injection in Patients with Femoroacetabular Impingement
- Descriptive Epidemiology of Symptomatic Femoroacetabular Impingement in Young Athlete: Single Center Study
- Controversial Issues in Arthroscopic Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement
- Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome