Ann Rehabil Med.
2016 Dec;40(6):1071-1081. 10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1071.
The Prognostic Value of Enhanced-MRI and Fluoroscopic Factors for Predicting the Effects of Transforaminal Steroid Injections on Lumbosacral Radiating Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jseok337@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2371340
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.6.1071
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the predictive value of enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluoroscopic factors regarding the effects of transforaminal epidural steroid injections (TFESIs) in low back pain (LBP) patients with lumbosacral radiating pain.
METHODS
A total of 51 patients who had LBP with radiating pain were recruited between January 2011 and December 2012. The patient data were classified into the two groups "˜favorable group' and "˜non-favorable group' after 2 weeks of follow-up results. The favorable group was defined as those with a 50%, or more, reduction of pain severity according to the visual analogue scale (VAS) for back or leg pain. The clinical and radiological data were collected for univariate and multivariate analyses to determine the predictors of the effectiveness of TFESIs between the two groups.
RESULTS
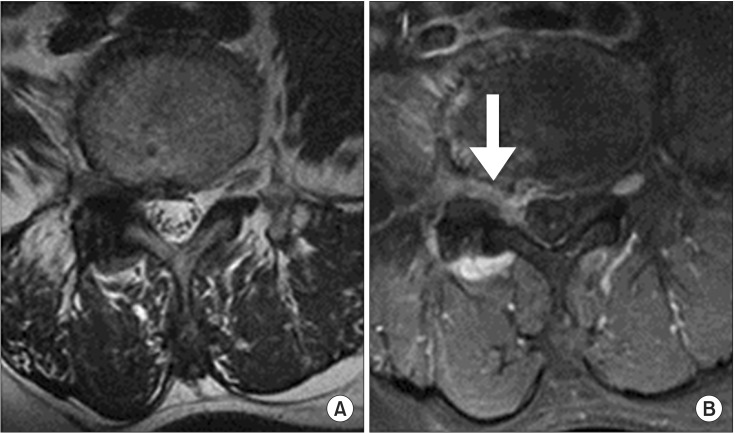
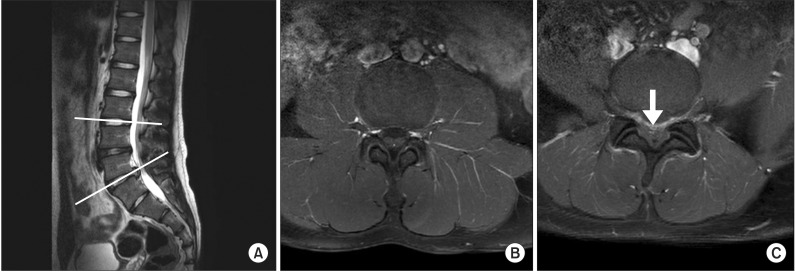
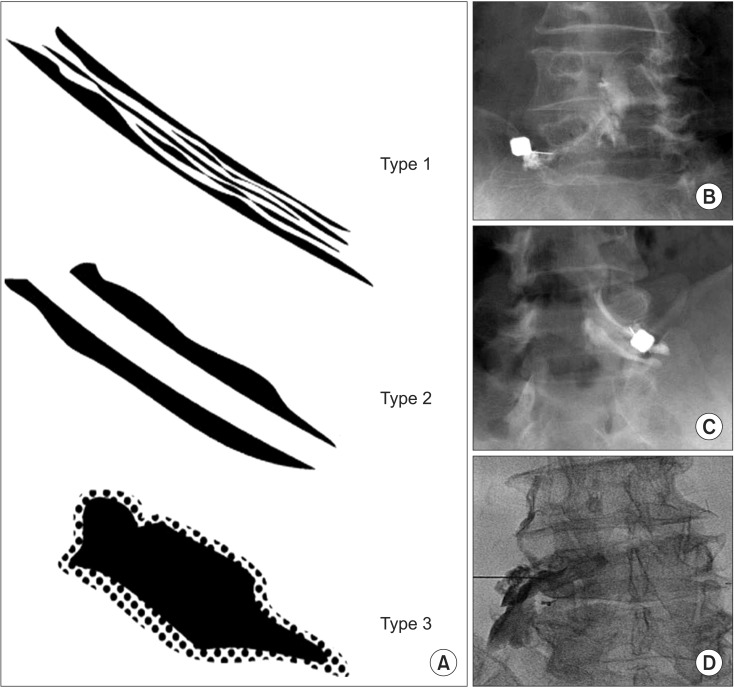
According to the back or the leg favorable-VAS group, the univariate analysis revealed that the corticosteroid approach for the enhanced nerve root, the proportion of the proximal flow, and the contrast dispersion of epidurography are respectively statistically significant relative to the other factors. Lastly, the multiple logistic regression analysis showed a significant association between the corticosteroid approach and the enhanced nerve root in the favorable VAS group.
CONCLUSION
Among the variables, MRI showed that the corticosteroid approach for the enhanced target root is the most important prognostic factor in the predicting of the clinical parameters of the favorable TFESIs group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Waddell G. 1987 Volvo award in clinical sciences: a new clinical model for the treatment of low-back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:632–644. PMID: 2961080.
Article2. Manchikanti L. Epidemiology of low back pain. Pain Physician. 2000; 3:167–192. PMID: 16906196.
Article3. Abdi S, Datta S, Trescot AM, Schultz DM, Adlaka R, Atluri SL, et al. Epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:185–212. PMID: 17256030.4. Koes BW, van Tulder M, Lin CW, Macedo LG, McAuley J, Maher C. An updated overview of clinical guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:2075–2094. PMID: 20602122.
Article5. Eckel TS, Bartynski WS. Epidural steroid injections and selective nerve root blocks. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 12:11–21. PMID: 19769903.
Article6. Ghahreman A, Ferch R, Bogduk N. The efficacy of transforaminal injection of steroids for the treatment of lumbar radicular pain. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1149–1168. PMID: 20704666.
Article7. Roberts ST, Willick SE, Rho ME, Rittenberg JD. Efficacy of lumbosacral transforaminal epidural steroid injections: a systematic review. PM R. 2009; 1:657–668. PMID: 19627959.
Article8. McCormick Z, Cushman D, Casey E, Garvan C, Kennedy DJ, Plastaras C. Factors associated with pain reduction after transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radicular pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95:2350–2356. PMID: 25108099.
Article9. Choi SJ, Song JS, Kim C, Shin MJ, Ryu DS, Ahn JH, et al. The use of magnetic resonance imaging to predict the clinical outcome of non-surgical treatment for lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Korean J Radiol. 2007; 8:156–163. PMID: 17420633.10. Fardon DF. Nomenclature and classification of lumbar disc pathology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:461–462. PMID: 11242371.
Article11. Lee S, Lee JW, Yeom JS, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Chung SK, et al. A practical MRI grading system for lumbar foraminal stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1095–1098. PMID: 20308517.
Article12. Attias N, Hayman A, Hipp JA, Noble P, Esses SI. Assessment of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of lumbar spine foraminal stenosis: a surgeon’s perspective. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006; 19:249–256. PMID: 16778658.13. Wildermuth S, Zanetti M, Duewell S, Schmid MR, Romanowski B, Benini A, et al. Lumbar spine: quantitative and qualitative assessment of positional (upright flexion and extension) MR imaging and myelography. Radiology. 1998; 207:391–398. PMID: 9577486.
Article14. Toyone T, Takahashi K, Kitahara H, Yamagata M, Murakami M, Moriya H. Visualisation of symptomatic nerve roots: prospective study of contrast-enhanced MRI in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:529–533. PMID: 8331104.
Article15. Paidin M, Hansen P, McFadden M, Kendall R. Contrast dispersal patterns as a predictor of clinical outcome with transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbar radiculopathy. PM R. 2011; 3:1022–1027. PMID: 21974903.
Article16. Pfirrmann CW, Oberholzer PA, Zanetti M, Boos N, Trudell DJ, Resnick D, et al. Selective nerve root blocks for the treatment of sciatica: evaluation of injection site and effectiveness: a study with patients and cadavers. Radiology. 2001; 221:704–711. PMID: 11719666.17. Haijiao W, Koti M, Smith FW, Wardlaw D. Diagnosis of lumbosacral nerve root anomalies by magnetic resonance imaging. J Spinal Disord. 2001; 14:143–149. PMID: 11285427.
Article18. Jinkins JR. MR of enhancing nerve roots in the unoperated lumbosacral spine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993; 14:193–202. PMID: 8427089.19. Bradley WG. Use of contrast in MR imaging of the lumbar spine. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1999; 7:439–457. viiPMID: 10494528.
Article20. Itoh R, Murata K, Kamata M, Mukubou N, Morita R. Lumbosacral nerve root enhancement with disk herniation on contrast-enhanced MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1619–1625. PMID: 8896611.21. Ross JS, Modic MT, Masaryk TJ, Carter J, Marcus RE, Bohlman H. Assessment of extradural degenerative disease with Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging: correlation with surgical and pathologic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989; 10:1243–1249. PMID: 2512790.
Article22. Vroomen PC, Van Hapert SJ, Van Acker RE, Beuls EA, Kessels AG, Wilmink JT. The clinical significance of gadolinium enhancement of lumbar disc herniations and nerve roots on preoperative MRI. Neuroradiology. 1998; 40:800–806. PMID: 9877135.
Article23. Bogduk N. Practice guidelines for spinal diagnostic and treatment procedures. San Francisco: International Spine Intervention Society;2004. p. 163–187.24. Tak HJ, Jones R, Cho YW, Kim EH, Ahn SH. Clinical evaluation of transforaminal epidural steroid injection in patients with gadolinium enhancing spinal nerves associated with disc herniation. Pain Physician. 2015; 18:E177–E185. PMID: 25794217.25. Lee JW, Kim SH, Lee IS, Choi JA, Choi JY, Hong SH, et al. Therapeutic effect and outcome predictors of sciatica treated using transforaminal epidural steroid injection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:1427–1431. PMID: 17114531.
Article26. Yeom JS, Lee JW, Park KW, Chang BS, Lee CK, Buchowski JM, et al. Value of diagnostic lumbar selective nerve root block: a prospective controlled study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1017–1023. PMID: 18272560.
Article27. Popescu A, Gupta A. Lumbar transforaminal epidural injections. In : Gupta A, editor. Interventional pain medicine. New York: Oxford University Press;2012. p. 106–111.28. Ploumis A, Transfeldt EE, Gilbert TJ, Mehbod AA, Pinto MR, Denis F. Radiculopathy in degenerative lumbar scoliosis: correlation of stenosis with relief from selective nerve root steroid injections. Pain Med. 2011; 12:45–50. PMID: 21087400.
Article29. Lee JH, Lee SH. Clinical effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis and predictive factors of treatment efficacy in patients with lumbosacral spinal stenosis. Pain Med. 2013; 14:1497–1504. PMID: 23802996.
Article30. Lee JH, An JH, Lee SH. Comparison of the effectiveness of interlaminar and bilateral transforaminal epidural steroid injections in treatment of patients with lumbosacral disc herniation and spinal stenosis. Clin J Pain. 2009; 25:206–210. PMID: 19333170.
Article31. Park Y, Lee WY, Ahn JK, Nam HS, Lee KH. Percutaneous adhesiolysis versus transforaminal epidural steroid injection for the treatment of chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar foraminal spinal stenosis: a retrospective comparative study. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:941–949. PMID: 26798608.
Article32. Delport EG, Cucuzzella AR, Marley JK, Pruitt CM, Fisher JR. Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with epidural steroid injections: a retrospective outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85:479–484. PMID: 15031837.
Article33. Campbell MJ, Carreon LY, Glassman SD, McGinnis MD, Elmlinger BS. Correlation of spinal canal dimensions to efficacy of epidural steroid injection in spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20:168–171. PMID: 17414988.
Article34. Jamison RN, VadeBoncouer T, Ferrante FM. Low back pain patients unresponsive to an epidural steroid injection: identifying predictive factors. Clin J Pain. 1991; 7:311–317. PMID: 1839719.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Combination of a Transforaminal Nerve Root Block and an Epidural Steroid Injection for Chronic Radiating Pain
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- Comparison of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection and Lumbar/Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Incidence of Intravascular Penetration during Transforaminal Lumbosacral Epidural Steroid Injection
- Efficacy of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injections According to Nerve Root Enhancement