Ann Lab Med.
2015 Sep;35(5):544-547. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.544.
Immature Teratoma and Subsequent Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia in a Pediatric Patient With XYY Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea. mgshin@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea.
- 3Environmental Health Center for Childhood Leukemia and Cancer, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea.
- 4Brain Korea 21 Plus Project, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2369774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.544
Abstract
- No abstract available.
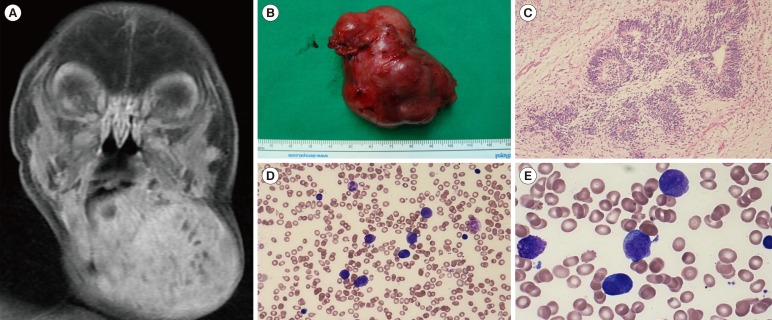
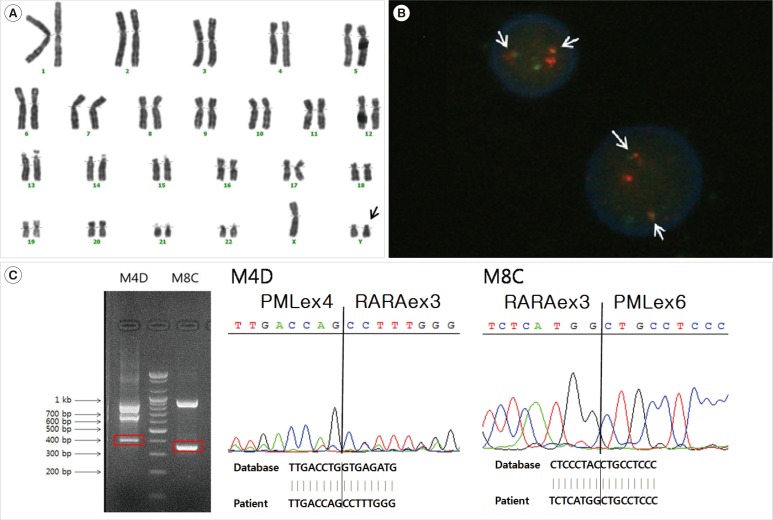
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stochholm K, Juul S, Gravholt CH. Diagnosis and mortality in 47,XYY persons: a registry study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010; 5:15. PMID: 20509956.
Article2. Jacobs PA, Brunton M, Melville MM, Brittain RP, McClemont WF. Aggressive behavior, mental sub-normality and the XYY male. Nature. 1965; 208:1351–1352. PMID: 5870205.3. Côté GB, Tsomi K, Papadakou-Lagoyanni S, Petmezaki S. Oligohydramnios syndrome and XYY karyotype. Ann Genet. 1978; 21:226–228. PMID: 314260.4. Higgins CD, Swerdlow AJ, Schoemaker MJ, Wright AF, Jacobs PA. UK Clinical Cytogenetics Group. Mortality and cancer incidence in males with Y polysomy in Britain: a cohort study. Hum Genet. 2007; 121:691–696. PMID: 17457613.
Article5. Limacher JM, Girard-Lemaire F, Jeandidier E, Chenard-Neu MP, Kassem M, Flori E, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor in an XYY/XY male. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002; 133:152–155. PMID: 11943343.
Article6. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. WHO Classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2008. p. 127–129.7. Schneider DT, Hilgenfeld E, Schwabe D, Behnisch W, Zoubek A, Wessalowski R, et al. Acute myelogenous leukemia after treatment for malignant germ cell tumors in children. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:3226–3233. PMID: 10506623.
Article8. Harms D, Zahn S, Göbel U, Schneider DT. Pathology and molecular biology of teratomas in childhood and adolescence. Klin Padiatr. 2006; 218:296–302. PMID: 17080330.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia with a 47,XYY Karyotype
- Overview of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
- Transient spontaneous remission in acute promyelocytic leukemia: two case reports
- Sweet Syndrome Developed in a Patient of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia During Remission Induction Therapy with All-trans Retinoic Acid
- A case of microgranular acute promyelocytic leukemia