J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2017 Feb;52(1):92-96. 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.1.92.
Treatment of Spinal Infection Following Bilateral Total Knee Replacement Postoperative Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. bumjinshim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2369576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.1.92
Abstract
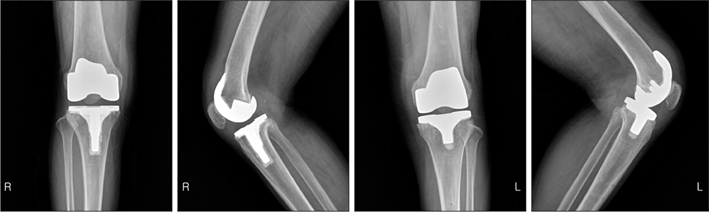
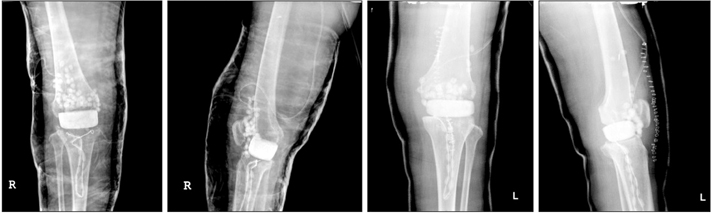
- Postoperative infection from total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an issue drawing great attention, which can manifest as a local or general infection. Its development into sepsis has also occasionally been reported. Such sepsis is a critical complication that can spread to various parts of the body, which can ultimately lead to mortality. However, the cases where infection has spread to the spine do not have clear clinical signs, making diagnosis difficult. These cases are not found in the literature. Therefore, this is a case study on both postoperative infection from TKA that has developed into sepsis and spread to the spine.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee SH, Lee WH, Heo JW, et al. A case of prosthetic knee joint infection caused by streptococcus agalactiae. J Rheum Dis. 2012; 19:295–298.2. Bae DK, Kim HS. Deep infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2003; 38:23–28.
Article3. Lee BJ, Kyung HS, Yoon SD. Two-stage revision for infected total knee arthroplasty: based on autoclaving the recycled femoral component and intraoperative molding using antibiotic-impregnated cement on the tibial side. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015; 7:310–317.
Article4. Ha CW, Na SE, Lee SH. Treatment of infected total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Knee Soc. 2010; 22:141–146.
Article5. Kyung HS, Mun JU. Treatment of infections after total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2010; 45:335–341.
Article6. Poultsides LA, Memtsoudis SG, Vasilakakos T, et al. Infection following simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28:8 Suppl. 92–95.
Article7. Park SH, Yim SJ. Complication rate and clinical result of oneweek interval staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty: compared to simultaneous and several-months interval staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2015; 50:1–7.
Article8. Lee CS. Pyogenic infection of the spine. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999; 6:247–255.9. Hwang JK, Oh CW, Lee HJ, Kyung HS. An articulating versus non-articulating spacer for 2-stage reimplantation patients who undergo in infected total kKnee arthroplasty. J Korean Knee Soc. 2009; 21:150–157.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Perioperative Changes in C-Reactive Protein Levels after Unilateral and Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Replacement
- Total Knee Replacement in Gonarthrosis
- Candida Infection After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Infection Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Bilateral Total Knee Replacement: A Case Report