J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2009 Aug;44(4):442-448.
Perioperative Changes in C-Reactive Protein Levels after Unilateral and Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Replacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Mok-Dong Himchan Hospital, Seoul, Korea. changcape@naver.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Mok-Dong Himchan Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
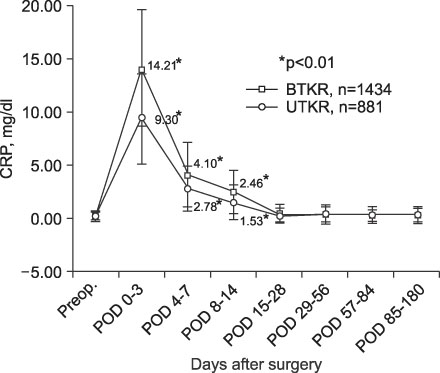
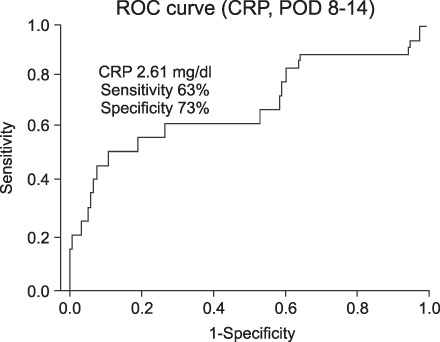
The objective of this study was to determine the patterns of C-reactive protein (CRP) changes during the postoperative period after total knee replacement (TKR), and to determine the CRP changes associated with infection after TKR. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective analysis of the pattern of CRP changes during the first 6 postoperative months was conducted on 2,315 patients who underwent unilateral or simultaneous bilateral TKR. This data was also compared with the pattern of CRP changes which occurred in 19 patients with a deep prosthesis infection who were not enrolled in the main study. RESULTS: The CRP levels peaked 3 days postoperatively, and then decreased to baseline levels at 15-28 days postoperatively. Within 14 days postoperatively, the CRP levels were significantly higher in the simultaneous bilateral TKA group than in the unilateral group (p<0.01). Thereafter, no significant difference in CRP levels existed between two groups. After the 8th postoperative day, a significant difference in CRP level existed between patients with and without deep prosthesis infections. CONCLUSION: CRP changes post-TKR provide an effective means of monitoring of infections. In cases of non-inflammatory arthritis in which the CRP levels are significantly difference after the 8th postoperative day or are elevated after the 4th postoperative week, an infection should be suspected.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haidar SG, Charity RM, Bassi RS, Nicolai P, Singh BK. Knee skin temperature following uncomplicated total knee replacement. Knee. 2006. 13:422–426.
Article2. Mehra A, Langkamer VG, Day A, Harris S, Spencer RF. C reactive protein and skin temperature post total knee replacement. Knee. 2005. 12:297–300.
Article3. Bernard L, Lübbeke A, Stern R, et al. Value of preoperative investigations in diagnosing prosthetic joint infection: retrospective cohort study and literature review. Scand J Infect Dis. 2004. 36:410–416.
Article4. Fischer CL, Gill C, Forrester MG, Nakamura R. Quantitation of "acute-phase proteins" postoperatively. Value in detection and monitoring of complications. Am J Clin Pathol. 1976. 66:840–846.
Article5. Greidanus NV, Masri BA, Garbuz DS, et al. Use of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level to diagnose infection before revision total knee arthroplasty. A prospective evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. 89:1409–1416.6. Peltola H, Laipio ML, Siimes MA. Quantitative C-reactive protein (CRP) determined by an immunoturbidimetric method in rapid differential diagnosis of acute bacterial and viral diseases of children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1984. 73:273–274.
Article7. Lee DC, Kim SD, Jung KA, Baek SH. Changes of ESR and CRP after total knee and hip arthroplasty. J Korean Knee Society. 2001. 12:23–29.8. Parvizi J, Ghanem E, Sharkey P, Aggarwal A, Burnett RS, Barrack RL. Diagnosis of infected total knee: findings of a multicenter database. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466:2628–2633.
Article9. Mok JM, Pekmezci M, Piper SL, et al. Use of C-reactive protein after spinal surgery: comparison with erythrocyte sedimentation rate as predictor of early postoperative infectious complications. Spine. 2008. 33:415–421.10. Osei-Bimpong A, Meek JH, Lewis SM. ESR or CRP? A comparison of their clinical utility. Hematology. 2007. 12:353–357.
Article11. Shih LY, Wu JJ, Yang DJ. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein values in patients with total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. 225:238–246.
Article12. Agrawal A. CRP after 2004. Mol Immunol. 2005. 42:927–930.
Article13. Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med. 2005. 340:448–454.
Article14. Marnell L, Mold C, Du Clos TW. C-reactive protein: ligands, receptors and role in inflammation. Clin Immunol. 2005. 117:104–111.
Article15. Andres BM, Taub DD, Gurkan I, Wenz JF. Postoperative fever after total knee arthroplasty: the role of cytokines. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. 415:221–231.
Article16. Di Cesare PE, Chang E, Preston CF, Liu CJ. Serum interleukin-6 as a marker of periprosthetic infection following total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1921–1927.
Article17. Pearle AD, Scanzello CR, George S, et al. Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels are associated with local inflammatory findings in patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007. 15:516–523.
Article18. Aalto K, Osterman K, Peltola H, Räsänen J. Changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984. 184:118–120.
Article19. White J, Kelly M, Dunsmuir R. C-reactive protein level after total hip and total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998. 80:909–911.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral total knee replacement, a simultaneous procedure
- C-reactive protein course after classical complication free total knee arthroplasty using navigation
- Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Windswept deformities of the knee are challenging to manage
- Complication Rate and Clinical Result of One-Week Interval Staged Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: Compared to Simultaneous and Several-Months Interval Staged Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty