J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2017 Feb;58(2):192-196. 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.2.192.
Relationship between Palpebral Fissure Height and Corneal Astigmatism of Epiblepharon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. kimleejy@hallym.or.kr
- 2Korea Doctor Lee's Eye Clinic, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2369467
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2017.58.2.192
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To study the effect of plapebral fissure height on astigmatism in epiblepharon patients.
METHODS
The study consisted of 68 eyes of 34 patients who were diagnosed with epiblepharon and 88 eyes of 44 patients who had normal eyelids from September 2012 to July 2013. Data on palpebral fissure height and refractive errors were compared between the epiblepharon group and the control group. Epiblepharon patients were further divided into two subgroups depending on the degree of preoperative corneal erosion in order to study the effects of corneal erosion on corneal astigmatism.
RESULTS
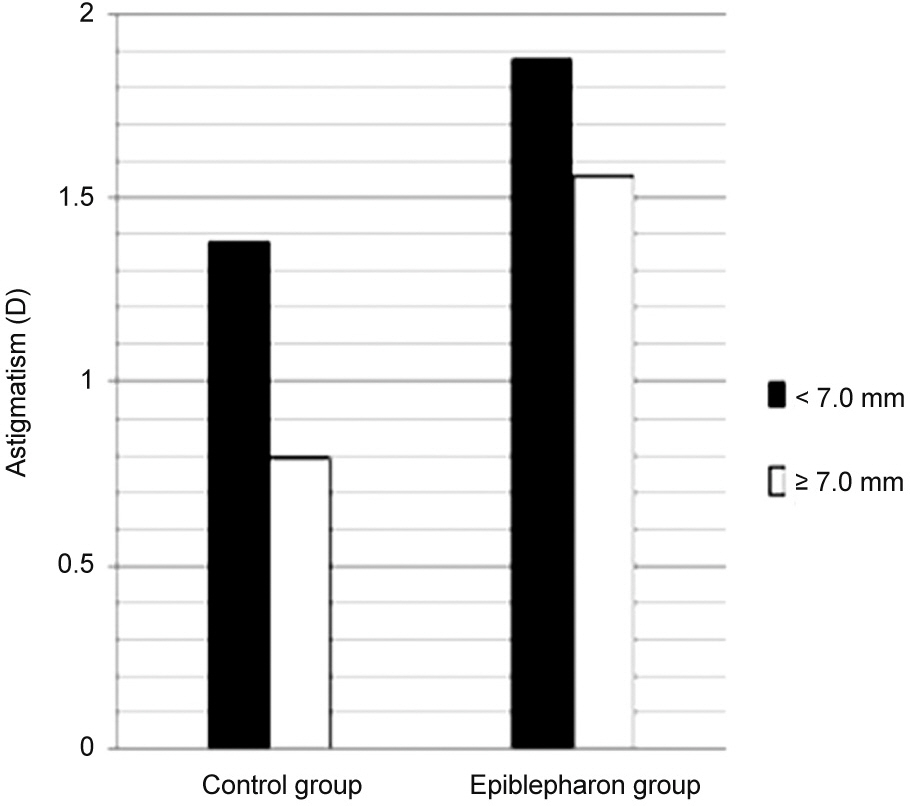
The mean age was 5.6 ± 2.2 years in the epiblepharon group and 6.1 ± 1.5 years in the control group (p = 0.339). The mean astigmatism was 2.28 ± 1.54 D in the epiblepharon group and 0.91 ± 1.07 D in the control group. The epiblepharon group showed higher astigmatism than the control group (p < 0.001). The mean palepebral fissure height was 6.70 ± 1.19 mm in the epiblepharon group and 7.63 ± 1.06 mm in the control group. The epiblepharon group exhibited smaller palpebral fissure height than the control group (p < 0.001). In the palpebral fissure height subgroups of the epiblepharon group, the <7.0 mm group showed higher astigmatism than the ≥7.0 mm group (p = 0.026). Higher astigmatism was associated with smaller palpebral fissure height (p = 0.022).
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with epiblepharon had significantly higher corneal astigmatism, and higher astigmatism was associated with smaller palpebral fissure height.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Preechawai P, Amrith S, Wong I, Sundar G. Refractive changes in epiblepharon. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:835–9.
Article2. Noda S, Hayasaka S, Setogawa T. Epiblepharon with inverted eye-lashes in Japanese children. I. Incidence and symptoms. Br J Ophthalmol. 1989; 73:126–7.
Article3. Kim NM, Jung JH, Choi HY. The effect of epiblepharon surgery on visual acuity and with-the-rule astigmatism in children. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010; 24:325–30.
Article4. Lee DP, Kim SD, Hu YJ. Change of visual acuity and astigmatism after operation in epiblepharon children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001; 42:223–7.5. Baek SH, Heo NH, Lee KS. Corneal topographic changes after sur-gery in epiblepharon children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2002; 43:1841–6.6. Hyun DW, Jeon CY, Jin SY, Ha MS. Visual acuity and astigmatism after simultaneous surgery for upper and lower eyelid epiblepharon in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:272–6.
Article7. Jeoung JW, Kim NJ, Choung HK, Khwarg SI. Changes in astigma-tism after surgical repair of epiblepharon or ptosis: a vectorial-ana-lytic approach. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1429–34.8. Khwarg SI, Lee YJ. Epiblepharon of the lower eyelid: classi-fication and association with astigmatism. Korean J Ophthalmol. 1997; 11:111–7.
Article9. Garcia ML, Huang D, Crowe S, Traboulsi EI. Relationship be-tween the axis and degree of high astigmatism and obliquity of pal-pebral fissure. J AAPOS. 2003; 7:14–22.
Article10. Read SA, Collins MJ, Carney LG. The influence of eyelid morphol-ogy on normal corneal shape. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:112–9.
Article11. Kang WS, Ahn M. The Effects of epiblepharon surgery on the im-provement of astigmatism. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:343–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparing Changes in Corneal Astigmatism Using Scheimpflug Camera after Epiblepharon Correction Surgery
- Epiblepharon of the lower eyelid: classification and association with astigmatism
- Corneal Topographic Changes after Surgery in Epiblepharon Children
- Change of Visual Acuity and Astigmatism after Operation in Epiblepharon Children
- The Effects of Epiblepharon Surgery on the Improvement of Astigmatism