Korean J Ophthalmol.
2017 Feb;31(1):88-89. 10.3341/kjo.2017.31.1.88.
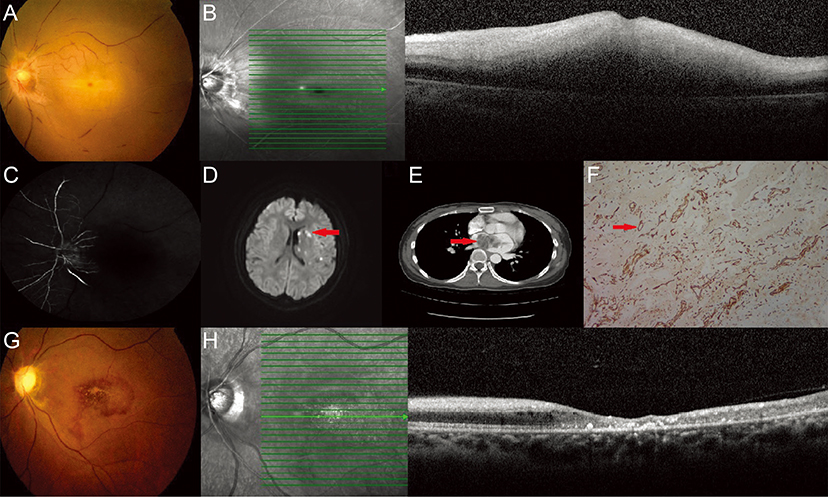
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion by Left Atrial Myxoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. itkim@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2368684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2017.31.1.88
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Varma DD, Cugati S, Lee AW, Chen CS. A review of central retinal artery occlusion: clinical presentation and management. Eye (Lond). 2013; 27:688–697.2. O'Rourke F, Dean N, Mouradian MS, et al. Atrial myxoma as a cause of stroke: case report and discussion. CMAJ. 2003; 169:1049–1051.3. Pucci A, Gagliardotto P, Zanini C, et al. Histopathologic and clinical characterization of cardiac myxoma: review of 53 cases from a single institution. Am Heart J. 2000; 140:134–138.4. Rafuse PE, Nicolle DA, Hutnik CM, Pringle CE. Left atrial myxoma causing ophthalmic artery occlusion. Eye (Lond). 1997; 11(Pt 1):25–29.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incomplete Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion after Cervical Spine Surgery in Prone Position: A Case Report
- The Successful Treatment of a Case of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
- A Case Report of Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Caused by Cardiac Myxoma
- Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Masquerading as Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion