Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2017 Jan;19(1):34-39. 10.14253/acn.2017.19.1.34.
Normal data on axonal excitability in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsb_res@hotmail.co.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Headong Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2367992
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.2017.19.1.34
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
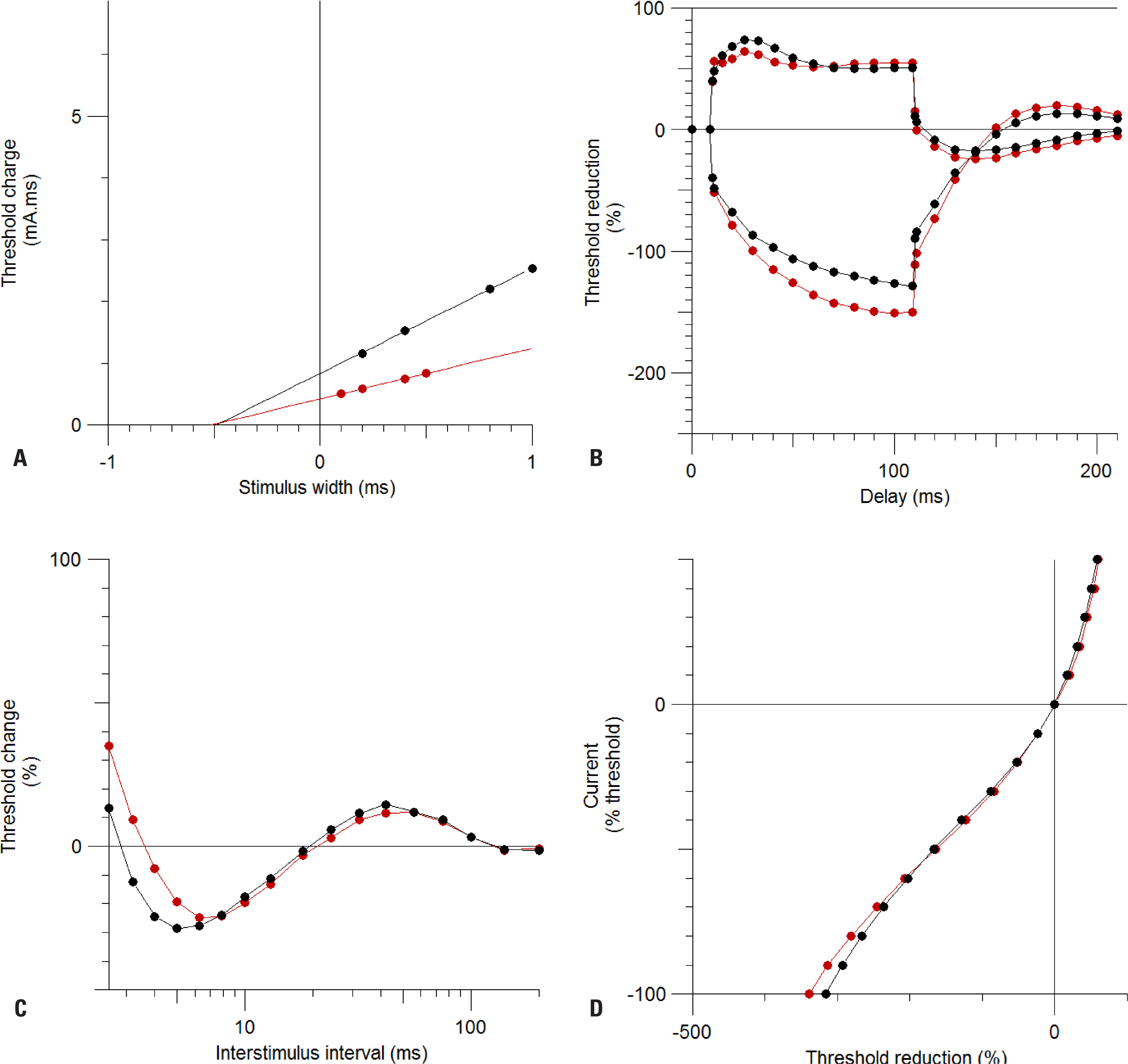
Automated nerve excitability testing is used to assess various peripheral neuropathies and motor neuron diseases. Comparing these excitability parameters with normal data provides information regarding the axonal excitability properties and ion biophysics in diseased axons. This study measured and compared normal values of axonal excitability parameters in both the distal motor and sensory axons of normal Koreans.
METHODS
The axonal excitability properties of 50 distal median motor axons and 30 distal median sensory axons were measured. An automated nerve excitability test was performed using the QTRACW threshold-tracking software (Institute of Neurology, University College London, London, UK) with the TRONDF multiple excitability recording protocol. Each parameter of stimulus-response curves, threshold electrotonus, current-voltage relationship, and recovery cycle was measured and calculated.
RESULTS
Our Korean normal data on axonal excitability showed ranges of values and characteristics similar to previous reports from other countries. We also reaffirmed that there exist characteristic differences in excitability properties between motor and sensory axons: compared to motor axons, sensory axons showed an increased strength-duration time constant, more prominent changes in threshold to hyperpolarizing threshold electrotonus (TE) and less prominent changes in threshold to depolarizing TE, and more prominent refractoriness and less prominent subexcitability and superexcitability.
CONCLUSIONS
We report normal data on axonal excitability in Koreans. These data can be used to compare various pathological conditions in peripheral nerve axons such as peripheral neuropathies and motor neuron disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Bae JS., Kim BJ. Subclinical diabetic neuropathy with normal con-ventional electrophysiological study. J Neurol. 2007. 254:53–59.
Article2.Kuwabara S., Misawa S. Axonal ionic pathophysiology in human peripheral neuropathy and motor neuron disease. Curr Neuro-vasc Res. 2004. 1:373–379.
Article3.Nodera H., Kaji R. Nerve excitability testing and its clinical application to neuromuscular diseases. Clin Neurophysiol. 2006. 117:1902–1916.
Article4.Kiernan MC., Burke D., Andersen KV., Bostock H. Multiple measures of axonal excitability: a new approach in clinical testing. Muscle Nerve. 2000. 23:399–409.
Article5.Burke D., Kiernan MC., Bostock H. Excitability of human axons. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001. 112:1575–1585.
Article6.Jankelowitz SK., McNulty PA., Burke D. Changes in measures of motor axon excitability with age. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. 118:1397–1404.
Article7.Bae JS., Sawai S., Misawa S., Kanai K., Isose S., Shibuya K, et al. Effects of age on excitability properties in human motor axons. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008. 119:2282–2286.
Article8.Paeing SH., Kang MR., Ahn SH., Lee MW., Pyun SY., Bostock H, et al. Relative sparing of the second lumbrical muscle in carpal tunnel syndrome is not associated with regional differences in axonal membrane potential. Clin Neurophysiol. 2016. 127:905–910.
Article9.Bae JS., Kim OK., Kim JM. Altered nerve excitability in subclinical/early diabetic neuropathy: evidence for early neurovascular pro-cess in diabetes mellitus? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011. 91:183–189.
Article10.Mogyoros I., Kiernan MC., Burke D. Strength-duration properties of human peripheral nerve. Brain. 1996. 119(Pt 2):439–447.
Article11.Z'Graggen WJ., Lin CS., Howard RS., Beale RJ., Bostock H. Nerve excitability changes in critical illness polyneuropathy. Brain. 2006. 129(Pt 9):2461–2470.12.Murray JE., Jankelowitz SK. A comparison of the excitability of motor axons innervating the APB and ADM muscles. Clin Neurophysiol. 2011. 122:2290–2293.
Article13.Jankelowitz SK., Burke D. Axonal excitability in the forearm: normal data and differences along the median nerve. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009. 120:167–173.
Article14.Kiernan MC., Cikurel K., Bostock H. Effects of temperature on the excitability properties of human motor axons. Brain. 2001. 124(Pt 4):816–825.
Article15.Mogyoros I., Kiernan MC., Burke D., Bostock H. Excitability changes in human sensory and motor axons during hyperventilation and ischaemia. Brain. 1997. 120(Pt 2):317–325.
Article16.Krishnan AV., Phoon RK., Pussell BA., Charlesworth JA., Bostock H., Kiernan MC. Altered motor nerve excitability in end-stage kidney disease. Brain. 2005. 128(Pt 9):2164–2174.
Article17.Bostock H., Cikurel K., Burke D. Threshold tracking techniques in the study of human peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve. 1998. 21:137–158.
Article18.Kiernan MC., Lin CS., Andersen KV., Murray NM., Bostock H. Clinical evaluation of excitability measures in sensory nerve. Muscle Nerve. 2001. 24:883–892.
Article19.Kuwabara S. Physiological differences in excitability among human axons. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009. 120:1–2.
Article20.Lin CS., Mogyoros I., Kuwabara S., Cappelen-Smith C., Burke D. Accommodation to depolarizing and hyperpolarizing currents in cutaneous afferents of the human median and sural nerves. J Physiol. 2000. 529(Pt 2):483–492.
Article21.Bae JS. Automated nerve excitability test by utilizing threshold tracking technique. Korean J Clin Neurophysiol. 2014. 16(Suppl 1):82–86.22.Krishnan AV., Lin CS., Kiernan MC. Nerve excitability properties in lower-limb motor axons: evidence for a length-dependent gra-dient. Muscle Nerve. 2004. 29:645–655.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Peripheral Nerve Axon Involvement in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1, Measured Using the Automated Nerve Excitability Test
- Altered Peripheral Nerve Excitability Properties in Acute and Subacute Supratentorial Ischemic Stroke
- Excitability scores of goats administered ascorbic acid and transported during hot-dry conditions
- Chronic Hypoxemia Triggers a Neuropathic Process in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Insight From In Vivo Neurophysiological Assessments
- A Case of Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy