Restor Dent Endod.
2017 Feb;42(1):60-64. 10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.60.
Maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health, School of Dentistry, Feira de Santana State University, Bahia, Brazil.
- 2Department of Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Faculdades Unidas do Norte de Minas (FUNORTE), Bahia, Brazil.
- 3Department of Endodontics, School of Dentistry, Rio de Janeiro State University and Grande Rio University, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. nogueiraemmanuel@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2367323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.1.60
Abstract
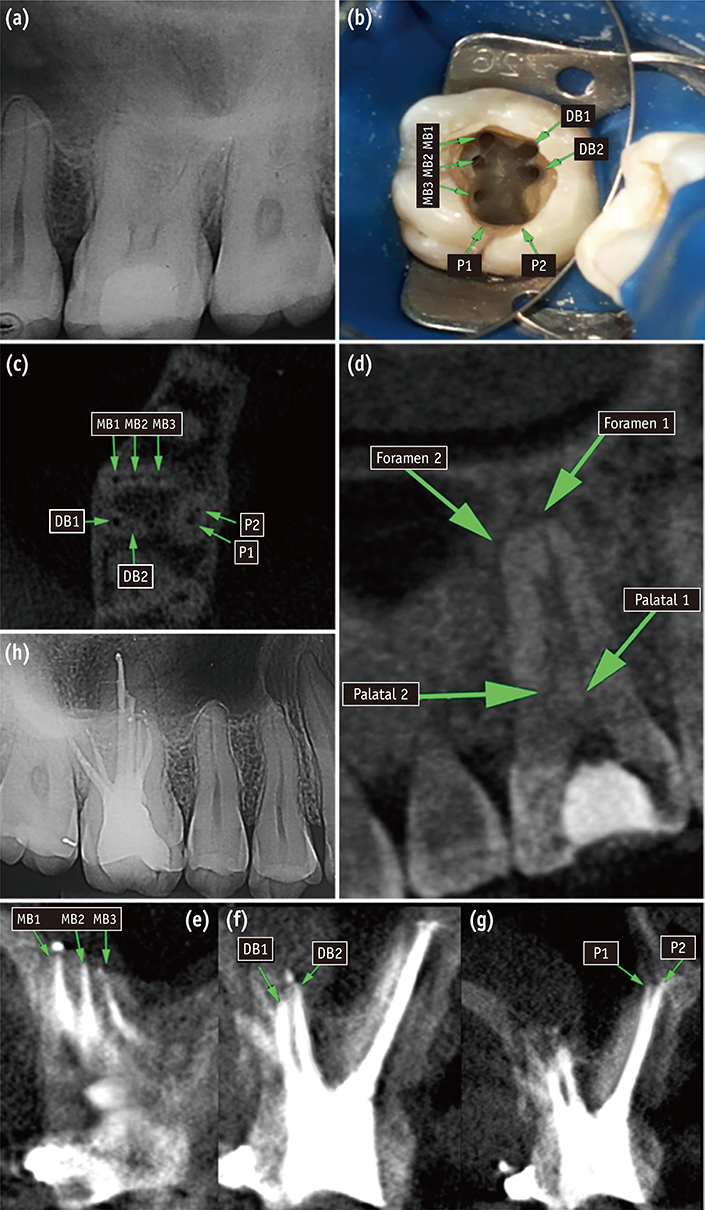
- Root canal anatomy is complex, and the recognition of anatomic variations could be a challenge for clinicians. This case report describes the importance of cone beam computed tomographyic (CBCT) imaging during endodontic treatment. A 23 year old woman was referred by her general dental practitioner with the chief complaint of spontaneous pain in her right posterior maxilla. From the clinical and radiographic findings, a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis was made and endodontic treatment was suggested to the patient. The patient underwent CBCT examination, and CBCT scan slices revealed seven canals: three mesiobuccal (MB1, MB2, and MB3), two distobuccal (DB1 and DB2), and two palatal (P1 and P2). Canals were successfully treated with reciprocating files and filled using single-cone filling technique. Precise knowledge of root canal morphology and its variation is important during root canal treatment. CBCT examination is an excellent tool for identifying and managing these complex root canal systems.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
Prateeksha Chowdhry, Pallavi Reddy, Mamta Kaushik
Restor Dent Endod. 2018;43(3):. doi: 10.5395/rde.2018.43.e35.
Reference
-
1. Ida RD, Gutmann JL. Importance of anatomic variables in endodontic treatment outcomes: case report. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1995; 11:199–203.
Article2. Lin LM, Pascon EA, Skribner J, Gängler P, Langeland K. Clinical, radiographic, and histologic study of endodontic treatment failures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1991; 71:603–611.
Article3. Jain D, Reddy S, Vanigalla BS, Kamishetty S. Endodontic management of a mandibular first molar with six root canal systems. J Conserv Dent. 2015; 18:419–422.
Article4. Neelakantan P, Subbarao C, Ahuja R, Subbarao CV, Gutmann JL. Cone-beam computed tomography study of root and canal morphology of maxillary first and second molars in an Indian population. J Endod. 2010; 36:1622–1627.
Article5. Lee JH, Kim KD, Lee JK, Park W, Jeong JS, Lee Y, Gu Y, Chang SW, Son WJ, Lee WC, Baek SH, Bae KS, Kum KY. Mesiobuccal root canal anatomy of Korean maxillary first and second molars by cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011; 111:785–791.
Article6. Silva EJ, Nejaim Y, Silva AI, Haiter-Neto F, Zaia AA, Cohenca N. Evaluation of root canal configuration of maxillary molars in a Brazilian population using cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: an in vivo study. J Endod. 2014; 40:173–176.
Article7. Kottoor J, Velmurugan N, Sudha R, Hemamalathi S. Maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed with cone-beam computed tomography scanning: a case report. J Endod. 2010; 36:915–921.
Article8. Kottoor J, Velmurugan N, Surendran S. Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with eight root canal systems evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: a case report. J Endod. 2011; 37:715–719.
Article9. Badole GP, Warhadpande MM, Shenoi PR, Lachure C, Badole SG. A rare root canal configuration of bilateral maxillary first molar with 7 root canals diagnosed using cone-beam computed tomographic scanning: a case report. J Endod. 2014; 40:296–301.
Article10. Raghavendra SS, Hindlekar AN, Desai NN, Vyavahare NK, Napte BD. Endodontic management of maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed using cone beam computed tomography scanning. Indian J Dent. 2014; 5:152–156.
Article11. Martins JN. Endodontic treatment of a maxillary first molar with seven root canals confirmed with cone beam computer tomography - case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZD13–ZD15.12. Kumar R. Report of a rare case: a maxillary first molar with seven canals confirmed with cone-beam computed tomography. Iran Endod J. 2014; 9:153–157.13. Almeida G, Machado R, Sanches Cunha R, Vansan LP, Neelakantan P. Maxillary first molar with 8 root canals detected by CBCT scanning: a case report. Gen Dent. 2015; 63:68–70.14. Nayak G, Singh KK, Shekhar R. Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography. Restor Dent Endod. 2015; 40:241–248.
Article15. Munavalli A, Kambale S, Bandekar S, Ajgaonkar N. Maxillary first molar with seven root canals diagnosed with cone-beam computed tomography scanning. Indian J Dent Res. 2015; 26:82–85.
Article16. Vertucci FJ. Root canal anatomy of the human permanent teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984; 58:589–599.
Article17. Ball RL, Barbizam JV, Cohenca N. Intraoperative endodontic applications of cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2013; 39:548–557.
Article18. Wu MK, van der Sluis LW, Wesselink PR. A 1-year follow-up study on leakage of single-cone fillings with RoekoRSA sealer. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:662–667.
Article19. Wu MK, Bud MG, Wesselink PR. The quality of single cone and laterally compacted gutta-percha fillings in small and curved root canals as evidenced by bidirectional radiographs and fluid transport measurements. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108:946–951.
Article20. Yilmaz Z, Tuncel B, Ozdemir HO, Serper A. Microleakage evaluation of roots filled with differene obturation techniques and sealers. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108:124–128.
Article21. Barton DJ, Clark SJ, Eleazer PD, Scheetz JP, Farman AG. Tuned-aperture computed tomography versus parallax analog and digital radiographic images in detecting second mesiobuccal canals in maxillary first molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003; 96:223–228.
Article22. Kersten HW, Wesselink PR, Thoden Van Velzen SK. The diagnostic reliability of the buccal radiograph after root canal filling. Int Endod J. 1987; 20:20–24.
Article23. Special Committee to revise the Joint AAE/AAOMR position statement on use of CBCT in Endodontics. AAE and AAOMR Joint position statement: Use of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontics 2015 Update. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2015; 120:508–512.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of C-shaped root canal configuration in maxillary molars in a Korean population using cone-beam computed tomography
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- A cone-beam computed tomographic study of C-shaped root and root canal in maxillary molars
- Endodontic management of a C-shaped maxillary first molar with three independent buccal root canals by using cone-beam computed tomography