Tuberc Respir Dis.
2016 Oct;79(4):295-301. 10.4046/trd.2016.79.4.295.
Association of Specific Immunoglobulin E to Staphylococcal Enterotoxin with Airway Hyperresponsiveness in Asthma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. craft7820@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Kunkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy and Immunology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2365322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2016.79.4.295
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization to staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) has been recently considered to be related to allergic disease, including asthma. Despite studies on specific IgE (sIgE) to SE and its relationship to asthma diagnosis and severity, the association of sIgE to SE with airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) remains unclear.
METHODS
We enrolled 81 asthma patients admitted to the Severance Hospital in Korea from March 1, 2013, to February 28, 2015 and retrospectively reviewed the electronic medical records of the enrolled subjects. The serum levels of sIgE to SE (A/B) of all subjects was measured using the ImmunoCAP 250 (Phadia) system with SE-sIgE positive defined as >0.10 kU/mL.
RESULTS
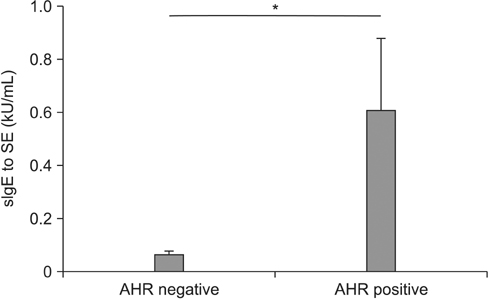
The SE-sIgE level was not significantly correlated with asthma severity (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEVâ‚], FEVâ‚/forced vital capacity, sputum eosinophils, and serum eosinophils), whereas the SE-sIgE level in patients with positive AHR (mean±standard error of the mean, 0.606±0.273 kU/mL) was significantly higher than that in patients with negative AHR (0.062±0.015 kU/mL, p=0.034). In regression analysis, SE sensitization (sIgE to SE ≥0.010 kU/mL) was a significant risk factor for AHR, after adjustment for age, sex, FEVâ‚, and sputum eosinophils (odds ratio, 7.090; 95% confidence interval, 1.180-42.600; p=0.032). Prevalence of SE sensitization was higher in patients with allergic rhinitis and non-atopic asthma patients, as compared to patients without allergic rhinitis and atopic asthma patients, respectively, but without statistical significance.
CONCLUSION
SE sensitization is significantly associated with AHR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prevalence of Self-reported Allergic Diseases and IgE Levels: A 2010 KNHANES Analysis
Hye Jung Park, Eun-Jin Kim, Dankyu Yoon, Jeom Kyu Lee, Woo-Sung Chang, Yoen-Mi Lim, Jung-Won Park, Joo-Shil Lee
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(4):329-339. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.329.
Reference
-
1. Bachert C, Zhang N. Chronic rhinosinusitis and asthma: novel understanding of the role of IgE 'above atopy'. J Intern Med. 2012; 272:133–143.2. Pastacaldi C, Lewis P, Howarth P. Staphylococci and staphylococcal superantigens in asthma and rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Allergy. 2011; 66:549–555.3. Bachert C, Zhang N, Patou J, van Zele T, Gevaert P. Role of staphylococcal superantigens in upper airway disease. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 8:34–38.4. Bachert C, van Steen K, Zhang N, Holtappels G, Cattaert T, Maus B, et al. Specific IgE against Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins: an independent risk factor for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 130:376–381.5. Breuer K, Wittmann M, Bosche B, Kapp A, Werfel T. Severe atopic dermatitis is associated with sensitization to staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). Allergy. 2000; 55:551–555.6. Zhang N, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Patou J, Dhaliwal B, Gould H, et al. Mucosal tissue polyclonal IgE is functional in response to allergen and SEB. Allergy. 2011; 66:141–148.7. Bacigaluppi JE, Negroni R, de Severino HM. Bacterial allergy in allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy. 1979; 42:95–98.8. Tomassen P, Jarvis D, Newson R, Van Ree R, Forsberg B, Howarth P, et al. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin-specific IgE is associated with asthma in the general population: a GA(2) LEN study. Allergy. 2013; 68:1289–1297.9. Song WJ, Chang YS, Lim MK, Yun EH, Kim SH, Kang HR, et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin sensitization in a community-based population: a potential role in adult-onset asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014; 44:553–562.10. Song WJ, Sintobin I, Sohn KH, Kang MG, Park HK, Jo EJ, et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin IgE sensitization in late-onset severe eosinophilic asthma in the elderly. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016; 46:411–421.11. Liang Z, Zhang Q, Thomas CM, Chana KK, Gibeon D, Barnes PJ, et al. Impaired macrophage phagocytosis of bacteria in severe asthma. Respir Res. 2014; 15:72.12. Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Reddel HK. The revised 2014 GINA strategy report: opportunities for change. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2015; 21:1–7.13. Lee JH, Park KH, Park JW, Hong CS. YKL-40 in induced sputum after allergen bronchial provocation in atopic asthma. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2012; 22:501–507.14. Bousquet J, Reid J, van Weel C, Baena Cagnani C, Canonica GW, Demoly P, et al. Allergic rhinitis management pocket reference 2008. Allergy. 2008; 63:990–996.15. Park HJ, Lee JH, Park KH, Kim KR, Han MJ, Choe H, et al. A six-year study on the changes in airborne pollen counts and skin positivity rates in Korea: 2008-2013. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:714–720.16. Huvenne W, Callebaut I, Plantinga M, Vanoirbeek JA, Krysko O, Bullens DM, et al. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B facilitates allergic sensitization in experimental asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:1079–1090.17. Herz U, Ruckert R, Wollenhaupt K, Tschernig T, Neuhaus-Steinmetz U, Pabst R, et al. Airway exposure to bacterial superantigen (SEB) induces lymphocyte-dependent airway inflammation associated with increased airway responsiveness: a model for non-allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29:1021–1031.18. Bachert C, Gevaert P, Howarth P, Holtappels G, van Cauwen-berge P, Johansson SG. IgE to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins in serum is related to severity of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:1131–1132.19. Kowalski ML, Cieslak M, Perez-Novo CA, Makowska JS, Bachert C. Clinical and immunological determinants of severe/refractory asthma (SRA): association with staphylococcal superantigen-specific IgE antibodies. Allergy. 2011; 66:32–38.20. Lee JY, Kim HM, Ye YM, Bahn JW, Suh CH, Nahm D, et al. Role of staphylococcal superantigen-specific IgE antibodies in aspirin-intolerant asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2006; 27:341–346.21. Lee JH, Lin YT, Yang YH, Wang LC, Chiang BL. Increased levels of serum-specific immunoglobulin e to staphylococcal enterotoxin a and B in patients with allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005; 138:305–311.22. Rossi RE, Monasterolo G. Prevalence of serum IgE antibodies to the Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins (SAE, SEB, SEC, SED, TSST-1) in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2004; 133:261–266.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IL-5 Promoter Polymorphism Enhances IgE Responses to Staphylococcal Superantigens in Adult Asthmatics
- Staphylococcal enterotoxin specific IgE and asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Relationship Between Atopy and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
- Effects of CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides in Chronic Inflammation and Remodeling of Airway in a Murine Model of Bronchial Asthma
- Association between specific IgE to staphylococcal enterotoxin B and the eosinophilic phenotype of asthma