J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2016 Dec;23(4):251-261. 10.4184/jkss.2016.23.4.251.
Surgical Strategies for Successful Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Korea. yungspine@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongguk University International Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2365087
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2016.23.4.251
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Literature review.
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to demonstrate surgical strategies for successful minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF). SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Although many studies have reported the benefits and disadvantages of minimally invasive TLIF, few have described surgical strategies to improve the success rate or to reduce complications.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We searched for studies reporting the clinical and radiological outcomes of minimally invasive TLIF, and analyzed the optimal indications, technical pitfalls, and tips for successful surgical outcomes.
RESULTS
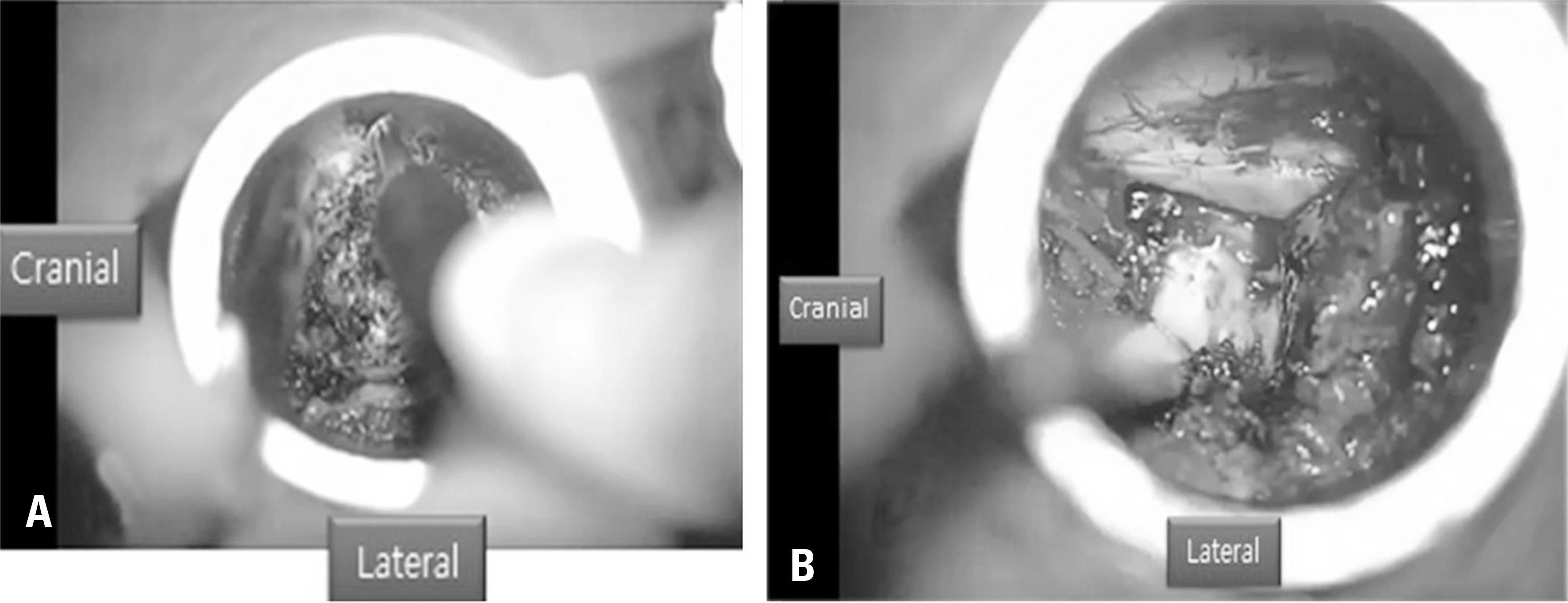
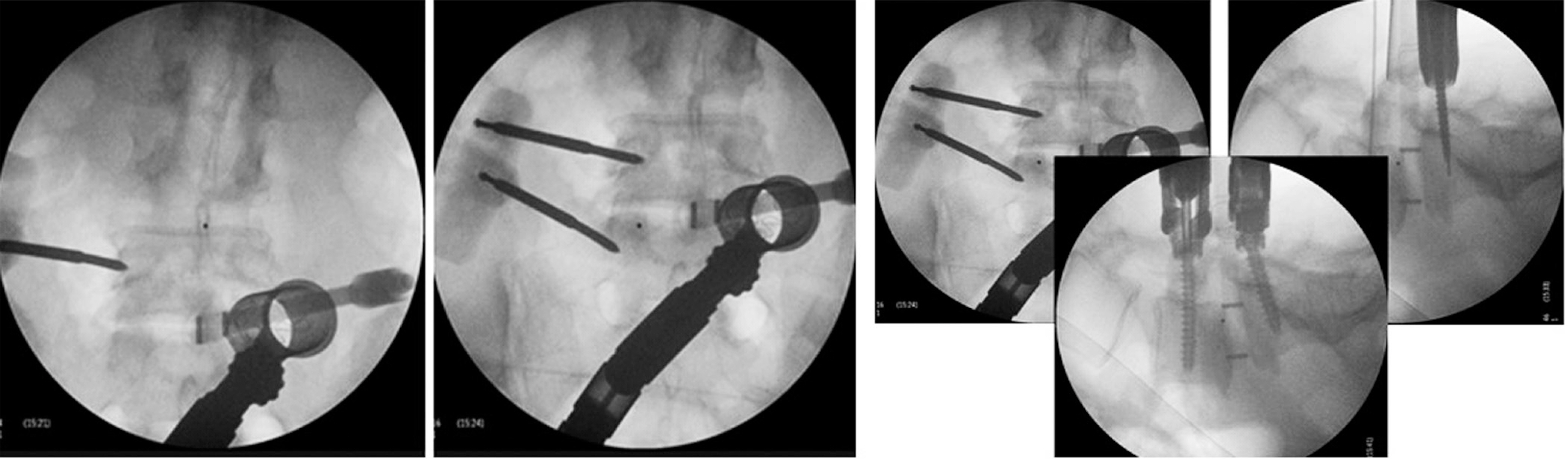
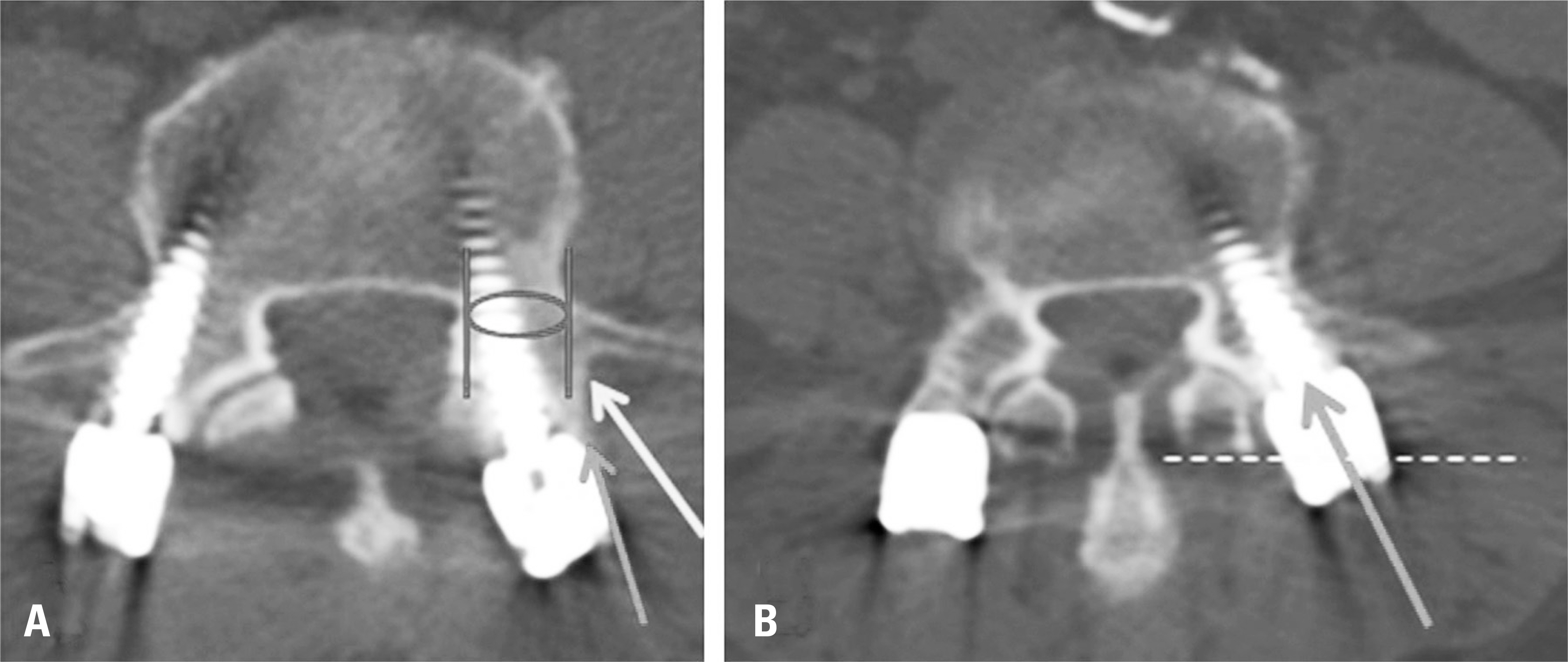
The ideal candidate for minimally invasive TLIF is a patient with single or 2-level low-grade adult degenerative or isthmic spondylolisthesis. Incomplete decompression, dura tearing, nerve root injury, and implant-related complications were found to be the most commonly reported adverse events, especially in the early periods of a surgeon's experience. Precise positioning for skin incision and tube insertion, complete neural decompression, proper interbody preparation for bone graft and cage insertion, and the correct placement of percutaneous pedicle screws are critical strategies for successful surgical outcomes. Fully understanding the surgical pitfalls and tips described in this review is also important to avoid potential complications.
CONCLUSIONS
It is imperative not only to carry out a comprehensive preoperative evaluation and proper patient selection, but also to perform meticulous surgical procedures with thoughtful considerations of potential pitfalls, in order to improve the success rate and to reduce the complications of minimally invasive TLIF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Foley KT, Holly LT, Schwender JD. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine. 2003; 28(Suppl):26–35.
Article2. Brodano GB, Martikos K, Lolli F, et al. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Degenerative Disk Disease and Spondylolisthesis Grade I: Minimally Invasive Versus Open Surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015; 28:E559–64.3. Seng C, Siddiqui MA, Wong KP, et al. Five-year outcomes of minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a matched-pair comparison study. Spine. 2013; 38:2049–55.4. Sclafani JA, Kim CW. Complications associated with the initial learning curve of minimally invasive spine surgery: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:1711–7.
Article5. Park Y, Ha JW, Lee YT, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis and degenerative spondylosis: 5-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472:1813–23.
Article6. Phan K, Rao PJ, Kam AC, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24:1017–30.
Article7. Khan NR, Clark AJ, Lee SL, et al. Surgical Outcomes for Minimally Invasive vs Open Transforaminal Lumbar Inter-body Fusion: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2015; 77:847–74.8. Isaacs RE, Podichetty VK, Santiago P, et al. Minimally invasive microendoscopy-assisted transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with instrumentation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005; 3:98–105.
Article9. Schwender JD, Holly LT, Rouben DP, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF): technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005; 18(Suppl):1–6.10. Selznick LA, Shamji MF, Isaacs RE. Minimally invasive interbody fusion for revision lumbar surgery: technical feasibility and safety. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009; 22:207–13.11. Holly LT, Schwender JD, Rouben DP, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: indications, technique, and complications. Neurosurg Focus. 2006; 20:E6.
Article12. Park Y, Lee SB, Seok SO, et al. Perioperative surgical complications and learning curve associated with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a single-institute experience. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015; 7:91–6.
Article13. Wang J, Zhou Y. Perioperative complications related to minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar fusion: evaluation of 204 operations on lumbar instability at single center. Spine J. 2014; 14:2078–84.
Article14. Karikari IO, Isaacs RE. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a review of techniques and outcomes. Spine. 2010; 35(Suppl):294–301.15. Rahman M, Summers LE, Richter B, et al. Comparison of techniques for decompressive lumbar laminectomy: the minimally invasive versus the “classic” open approach. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2008; 51:100–5.
Article16. Benzel EC, Shedid D, Gonugunta V. Neurological Com-plications of Spinal Surgery in the Spine. Fifth ed. Saunders Elsevier. Philadelphia;2006. 1441-53.17. Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Sangani PK, et al. Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine. 2000; 25:2663–7.
Article18. Campbell PG, Hanna A, Harrop JS. Spinal Dural Inju-ries in the Spine. Sixth ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2011. 1720-7.19. Tian NF, Wu YS, Zhang XL, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis based on the current evidence. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:1741–9.
Article20. Antonacci MD, Eismont FJ. Neurologic complications after lumbar spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001; 9:137–45.
Article21. Strothman D, Schwender JD. Minimally Invasive Posterior Lumbar Fusion Techniques. The Spine. 6th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co:;2011. 1020-40.22. Lee JC, Jang HD, Shin BJ. Learning curve and clinical outcomes of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: our experience in 86 consecutive cases. Spine. 2012; 37:1548–57.23. Ringel F, Stoffel M, Stü er C, et al. Minimally invasive trans-muscular pedicle screw fixation of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59(Suppl):361–6.
Article24. O'Driscoll SW, Horii E, Carmichael SW, et al. The cu-bital tunnel and ulnar neuropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:613–7.25. Jutte PC, Castelein RM. Complications of pedicle screws in lumbar and lumbosacral fusions in 105 consecutive primary operations. Eur Spine J. 2002; 11:594–8.
Article26. Kreppel D, Antoniadis G, Seeling W. Spinal hematoma: a literature survey with meta-analysis of 613 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2003; 26:1–49.
Article27. Kou J, Fischgrund J, Biddinger A, et al. Risk factors for spinal epidural hematoma after spinal surgery. Spine. 2002; 27:1670–3.
Article28. Amiri AR, Fouyas IP, Cro S, et al. Postoperative spinal epidural hematoma (SEH): incidence, risk factors, onset, and management. Spine J. 2013; 13:134–40.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications
- Mini-invasive unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation
- History and Evolution of the Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- The Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Single Level Fusion
- Technique of Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion