J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Jan;76(1):10-13. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.1.10.
Preoperative Embolization of a Giant Neurofibroma of the Chest in a Patient with Neurofibromatosis Type II: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. sjsy7942@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2365046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.1.10
Abstract
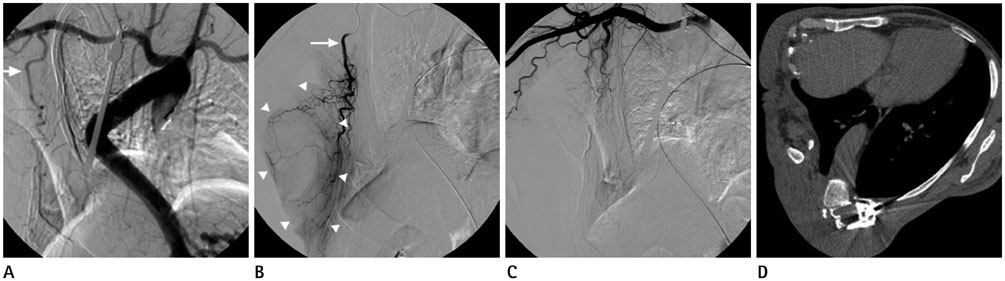
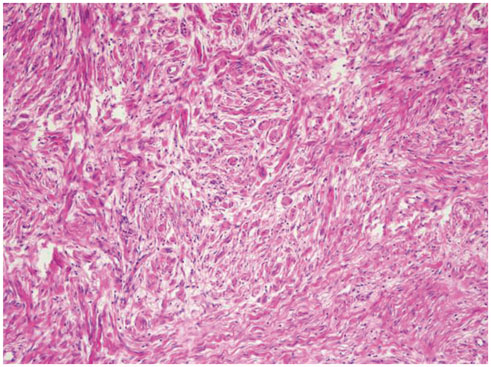
- Giant plexiform neurofibromas, which are rare in patients with neurofibromatosis type II (NFII), are difficult to manage surgically, as they are extensively infiltrative and highly vascularized. Preoperative embolization is performed to reduce intraoperative blood loss and operative time, increase resectability of lesions, and improve visualization of the operative field during surgery of hypervascular tumors such as renal cell carcinoma and intracranial meningioma. Preoperative intravascular embolization of a giant chest wall neurofibroma has not been reported in the English literature. We report successful treatment of a giant chest wall neurofibroma in a 45-year-old male with NFII by preoperative intravascular embolization followed by surgical resection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jones RG, Kiatisevi P, Morris DC, Munk PL, Clarkson PW, Masri BA. Intravascular embolisation and surgical resection of a giant neurofibroma with intratumoural haemorrhage. Br J Radiol. 2010; 83:e225–e229.2. Vélez R, Barrera-Ochoa S, Barastegui D, Pérez-Lafuente M, Romagosa C, Pérez M. Multidisciplinary management of a giant plexiform neurofibroma by double sequential preoperative embolization and surgical resection. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2013; 2013:987623.3. Ji Y, Xu B, Wang X, Liu W, Chen S. Surgical treatment of giant plexiform neurofibroma associated with pectus excavatum. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 6:119.4. Kashyap RR, Gogineni SB. Hypervascular neurofibromas in a case of neurofibromatosis type 1 - a case report. J Clin Exp Dent. 2011; 3:Suppl 1. e356–e359.5. Shah AH, Patel N, Raper DM, Bregy A, Ashour R, Elhammady MS, et al. The role of preoperative embolization for intracranial meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2013; 119:364–372.6. Cihangiroglu M, Yilmaz S, Topsakal C, Gok U, Altinsoy B, Cobanoglu B. Laryngeal neurofibroma associated with neurofibromatosis type 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1637–1639.7. Pendse NA, Menghani V. Neurofibromatosis 2 - a case report. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2003; 13:99–101.8. Hourani R, Rizk T, Kung S, Boudghène F. Elephantiasis neuromatosa in neurofibromatis type I. MRI findings with review of the literature. J Neuroradiol. 2006; 33:62–66.9. Shakir M, Blossom G, Lippert J. Anterior mediastinal paraganglioma: a case for preoperative embolization. World J Surg Oncol. 2012; 10:134.10. Nair S, Gobin YP, Leng LZ, Marcus JD, Bilsky M, Laufer I, et al. Preoperative embolization of hypervascular thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spinal column tumors: technique and outcomes from a single center. Interv Neuroradiol. 2013; 19:377–385.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Orbital Neurilemoma Associated with Neurofibroma tosis
- A Case of Cutaneous Neurofibroma Intimately Contacted with Intrathoracic and Chest Wall Plexiform Neurofibroma in Von Recklinghausen's Disease
- Malignant Schwannoma of the Scalp in Type I Neurofibromatosis: Case Report
- A Giant Retroperitoneal Neurofibroma
- Mediastinal Neurofibroma in a the Patient with Type 1 Neurofibromatosis: A case report