J Clin Neurol.
2016 Jan;12(1):117-118. 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.117.
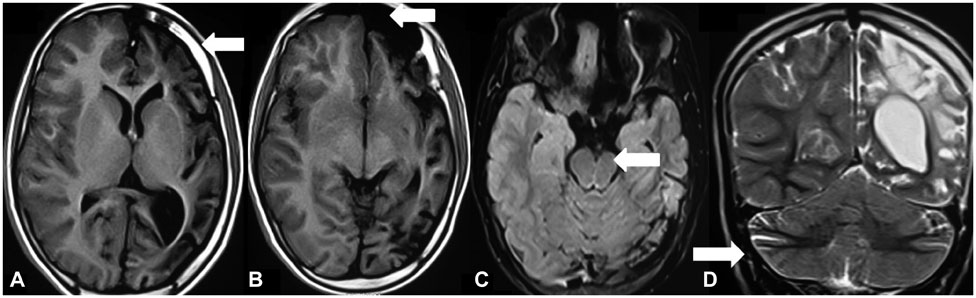
Early Transneuronal Degeneration in Dyke-Davidoff-Masson Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, PGIMER, Chandigarh, India. dr.anusingla82@gmail.com
- KMID: 2364929
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.117
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dyke CG, Davidoff LM, Masson LB. Cerebral hemiatrophy with homolateral hypertrophy of the skull and sinuses. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1933; 57:588–600.
Article2. Carrazana EJ, Liu GT, Holmes GL. Crossed cerebellar atrophy in the Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome. Neuroradiology. 1992; 34:326–327.
Article3. Cowan WM. Anterograde and Retrograde Transneuronal Degeneration in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. New York: Springer;1970. p. 217–251.4. Winkler DT, Probst A, Wegmann W, Tolnay M. Dyke Davidoff Masson syndrome with crossed cerebellar atrophy: an old disease in a new millenium. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2001; 27:403–405.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Dyke-Davidoff-Masson Syndrome with Infantile Spasm
- Craniofacial Deformity in a Patient with Dyke-Davidoff-Masson Syndrome: A Case Report
- Two cases of Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome
- Incidentally Detected Acquired Cerebral Hemiatrophy in Old Age: Dyke-Davidoff-Masson Syndrome
- Classical oral manifestations of Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome: a case report with review of the literature