Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2016 Sep;19(3):207-209. 10.5223/pghn.2016.19.3.207.
Corrosive Esophagitis with Benzalkonium Chloride in a Two Days Old Neonate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition, Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul, Turkey. hasretayyildiz@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2364780
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.3.207
Abstract
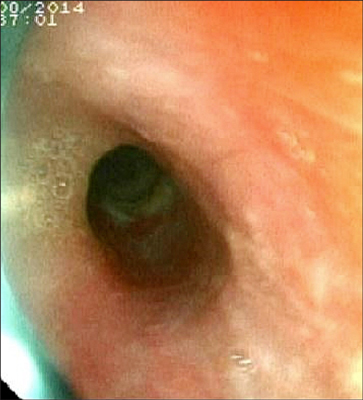
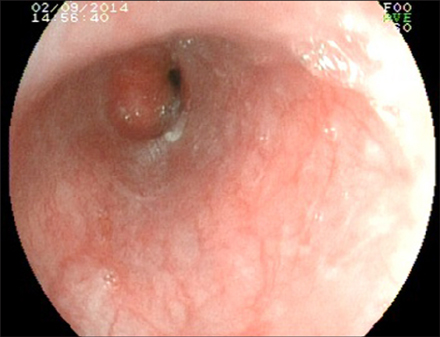
- Benzalkonium chloride (BAC) is a caustic agent which is used in farms, homes and hospitals for cleaning skin and wounds as an antiseptic solution. It may lead to digestive system injuries in case of ingestion. We present a two-days-old newborn case which was carried to the emergency unit with complaints of poor breastfeeding, uneasiness and crying for 4-6 hours. Her mom confessed that she had given a spoon of 10% BAC solution for her cough. Initial laboratory tests were in normal ranges. A gastroscopy performed in the second hour of her admission revealed an hyperemic and edematous mucosa in the middle third of esophagus and a circumferential ulceration followed in the distal portion. Hereupon, a conservative treatment for 10 days was administered and the control gastroscopy demonstrated that the damage was almost totally improved. She was the youngest case with this etiology and successfully treated with conservative approach.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haller JA, Andrews HG, White JJ, Tamer MA, Cleveland WW. Pathophysiology and management of acute corrosive burns of the esophagus: results and treatment in 258 children. J Pediatr Surg. 1971; 6:578–584.2. Okan F, Coban A, Ince Z, Can G. A rare and preventable cause of respiratory insufficiency ingestion of benzalkonium chloride. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2007; 23:404–406.3. Kushimo T, Ekanem MM. Acid ingestion in a 2-day old baby. West Afr J Med. 1997; 16:121–123.4. Turan C, Ozkan U, Ozokutan BH, Ozdemir M, Okur H, Küçükaydin M. Corrosive injuries of the esophagus in newborns. Pediatr Surg Int. 2000; 16:483–484.
Article5. Altuntaş N, Sarıcı D, Çelebi TA, Kışlal FM, Karadağ F, Özkan B, et al. Benzalkonyum klorür: yenidoğanın nadir bir kimyasal perine yanğı nedeni. Pam med J. 2014; 7:159–162.6. Hardwicke J, Azad S. Temporary henna tattooing in siblings-an unusual chemical burn. Burns. 2006; 32:1064–1065.
Article7. Estrera A, Taylor W, Mills LJ, Platt MR. Corrosive burns of esophagus and stomach: a recommendation for an aggressive surgical approach. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986; 41:276–283.
Article8. Wilson JT, Burr IM. Benzalkonium chloride poisoning in infant twins. Am J Dis Child. 1975; 129:1208–1209.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis Induced by Benzalkonium Chloride (Zephanon®)
- Corrosive Esophagitis after Ingestion of Chinese Squill
- Comparison of Skin Responses for Irritation Produced by Benzalkonium Chloride and Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
- Acute toxicity of benzalkonium chloride in Balb/c mice following intratracheal instillation and oral administration
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis due to EDTA and Benzalkonium Chloride in Eyedrops