Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2016 Dec;19(4):276-280. 10.5223/pghn.2016.19.4.276.
Three Year Old Male with Multiple Dieulafoy Lesions Treated with Epinephrine Injections via Therapeutic Endoscopy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, University of South Florida, Tampa, USA. clb09e@gmail.com
- 2Johns Hopkins All Children's Hospital, St. Petersburg, FL, USA.
- KMID: 2364769
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.4.276
Abstract
- Dieulafoy lesions, vascular anomalies typically found along the gastrointestinal tract, have been viewed as rare and obscure causes of sudden intestinal bleeding, especially in pediatric patients. Since their discovery in the late 19th century, the reported incidence has increased. This is due to an increased awareness of, and knowledge about, their presentation and to advanced endoscopic diagnosis and therapy. Our patient was a three-year-old male, without a complex medical history. He presented to the emergency department with acute hematemesis with blood clots and acute anemia requiring blood transfusion. Endoscopy revealed four isolated Dieulafoy lesions along the lesser curvature of the stomach, which were treated with an epinephrine injection. The Dieulafoy lesion, although thought to be rare, should be considered when investigating an acute gastrointestinal bleed. These lesions have been successfully treated endoscopically. Appropriate anticipation and preparation for diagnosis and therapy can lead to optimal outcomes for the pediatric patient.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
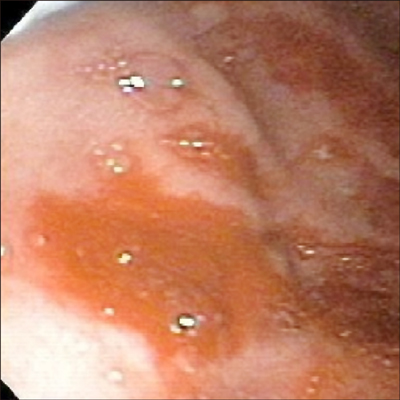
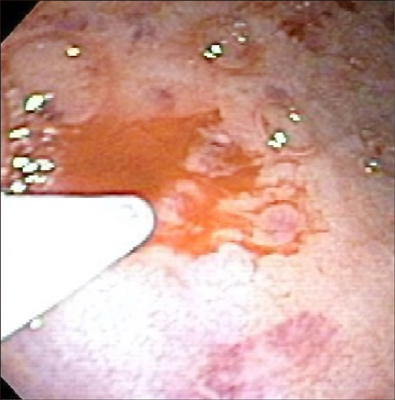
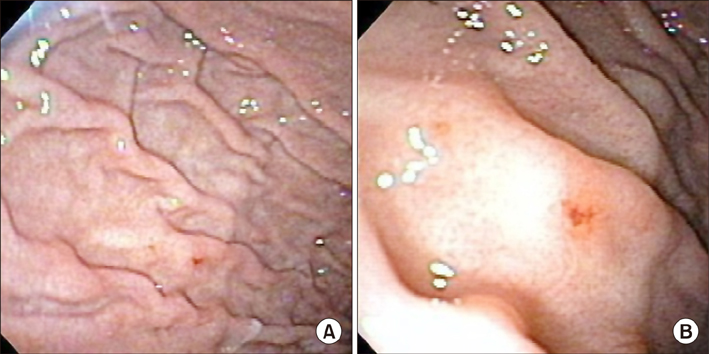
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ünal F, Çakır M, Baran M, Duygulu Ş, Aydoğdu S. Application of endoscopic hemoclips for nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding in children. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014; 25:147–151.
Article2. Baxter M, Aly EH. Dieulafoy's lesion: current trends in diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:548–554.
Article3. Senger JL, Kanthan R. The Evolution of Dieulafoy's Lesion Since 1897: then and now-a journey through the lens of a pediatric lesion with literature review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; 2012:432517.
Article4. Chaer RA, Helton WS. Dieulafoy's disease. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 196:290–296.
Article5. Alshumrani G, Almuaikeel M. Angiographic findings and endovascular embolization in Dieulafoy disease: a case report and literature review. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006; 12:151–154.6. Löschhorn C, Nierhoff N, Mayer R, Zaunbauer W, Neuweiler J, Knoblauch A. Dieulafoy's disease of the lung: a potential disaster for the bronchoscopist. Respiration. 2006; 73:562–565.
Article7. Ajay G, Mohnish C. Anorectal Dieulafoy's lesion. Indian J Surg. 2006; 68:325–327.8. Apiratpracha W, Ho JK, Powell JJ, Yoshida EM. Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding from a dieulafoy lesion proximal to the anorectal junction post-orthotopic liver transplant. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:7547–7548.
Article9. Dieulafoy G. Exulceratio simplex: lecons 1-3. In : Dieulafoy G, editor. Clinique medicale de l'hotel Dieu de Paris. Paris: Masson et Cie;1898. p. 1–38.10. Driver CP, Bruce J. An unusual cause of massive gastric bleeding in a child. J Pediatr Surg. 1997; 32:1749–1750.
Article11. Arain Z, Rossi TM. Gastrointestinal bleeding in children: an overview of conditions requiring nonoperative management. Semin Pediatr Surg. 1999; 8:172–180.
Article12. Kapetanos D, Beltsis A, Chatzimavroudis G, Katsinelos P. The use of endoclips in the treatment of non-variceal gastrointestinal bleeding. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2009; 19:2–10.
Article13. British Society of Gastroenterology Endoscopy Committee. Non-variceal upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage: guidelines. Gut. 2002; 51:Suppl 4. iv1–iv6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Dieulafoy's Lesion of the Rectum Treated by Endoscopic Band Ligation: A case report
- A Case of a Dieulafoy Lesion Treated usingCoil Embolization in a Child
- Endoscopic Management with Ethanol Injection in a Child with Gastric Dieulafoy Lesion
- A Case of Rectal Dieulafoy's Lesion Treated by Endoscopic Band Ligation
- Endoscopic Band Ligation in Bleeding Dieulafoy's Lesions