J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2016 Dec;21(4):181-188. 10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.4.181.
Latissimus Dorsi Tendon Transfer for the Treatment of Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. csjwillow@gmail.com
- KMID: 2364208
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.4.181
Abstract
- PURPOSE
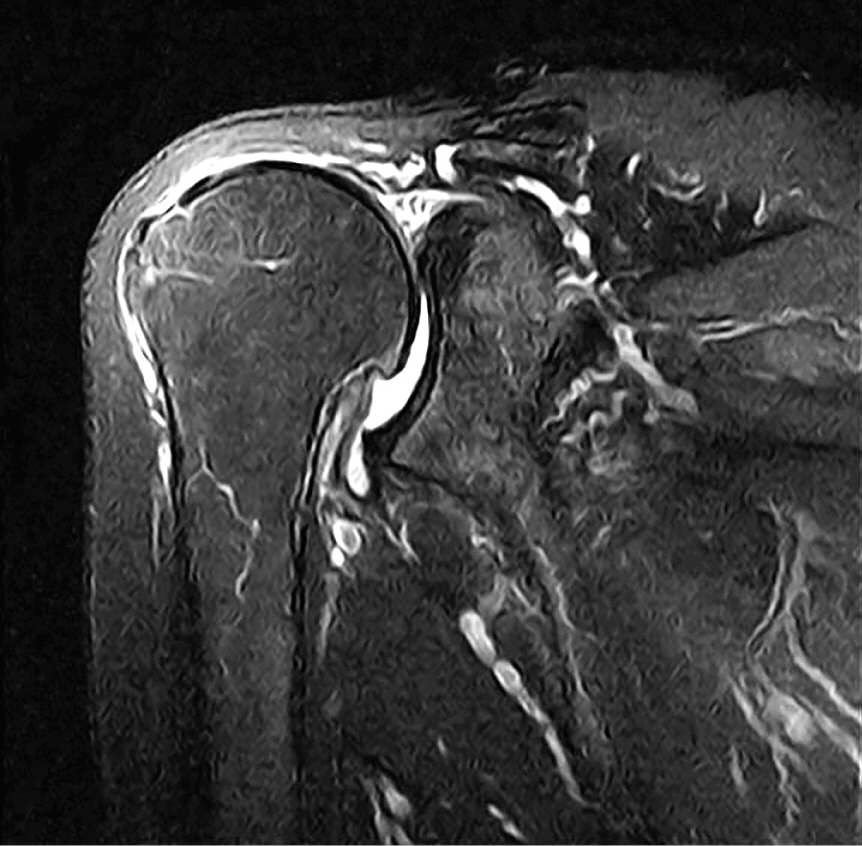
Massive and irreparable rotator cuff tears present a difficult treatment problem, and if further progressed, then cuff tear arthropaty may develop. We treated seven cases of massive rotator cuff tears with latissimus dorsi tendon transfer and report their clinical results.
METHODS
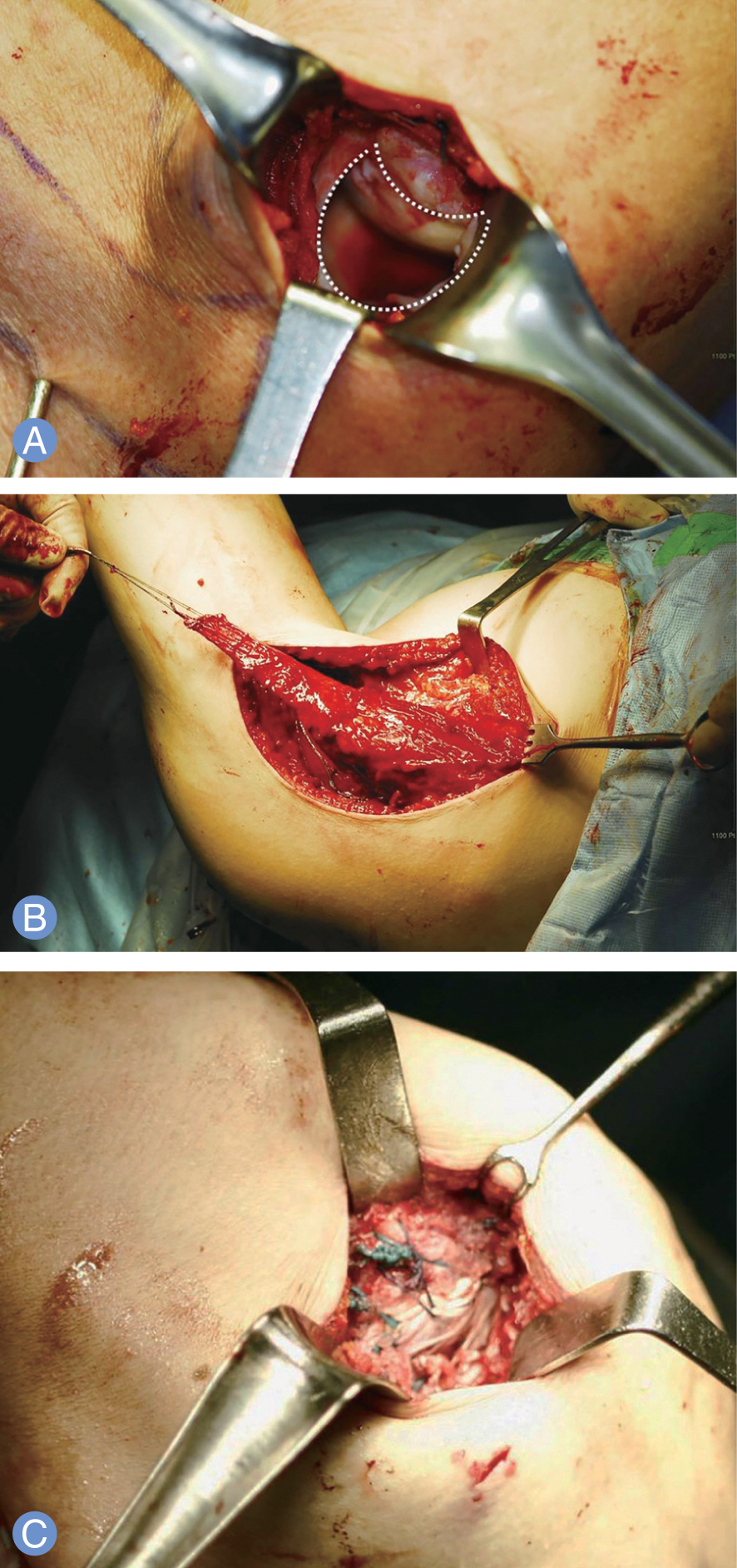
Seven patients of mean age of 64 years (range, 51-70 years) with irreparable massive rotator cuff tears were treated using latissimus dorsi tendon transfer. The latissimus dorsi flap was harvested through an axillary approach and reattached on the greater tuberosity, using transosseous suture with non-absorbable sutures. Outcomes were assessed clinically and radiographically after an average of 48 months (range, 28-68 months).
RESULTS
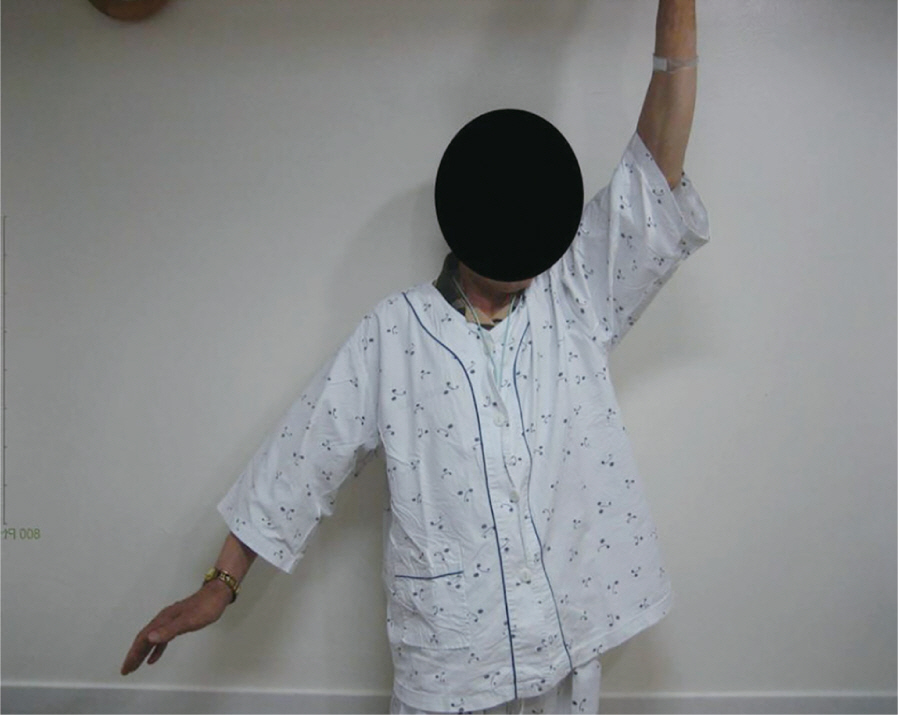
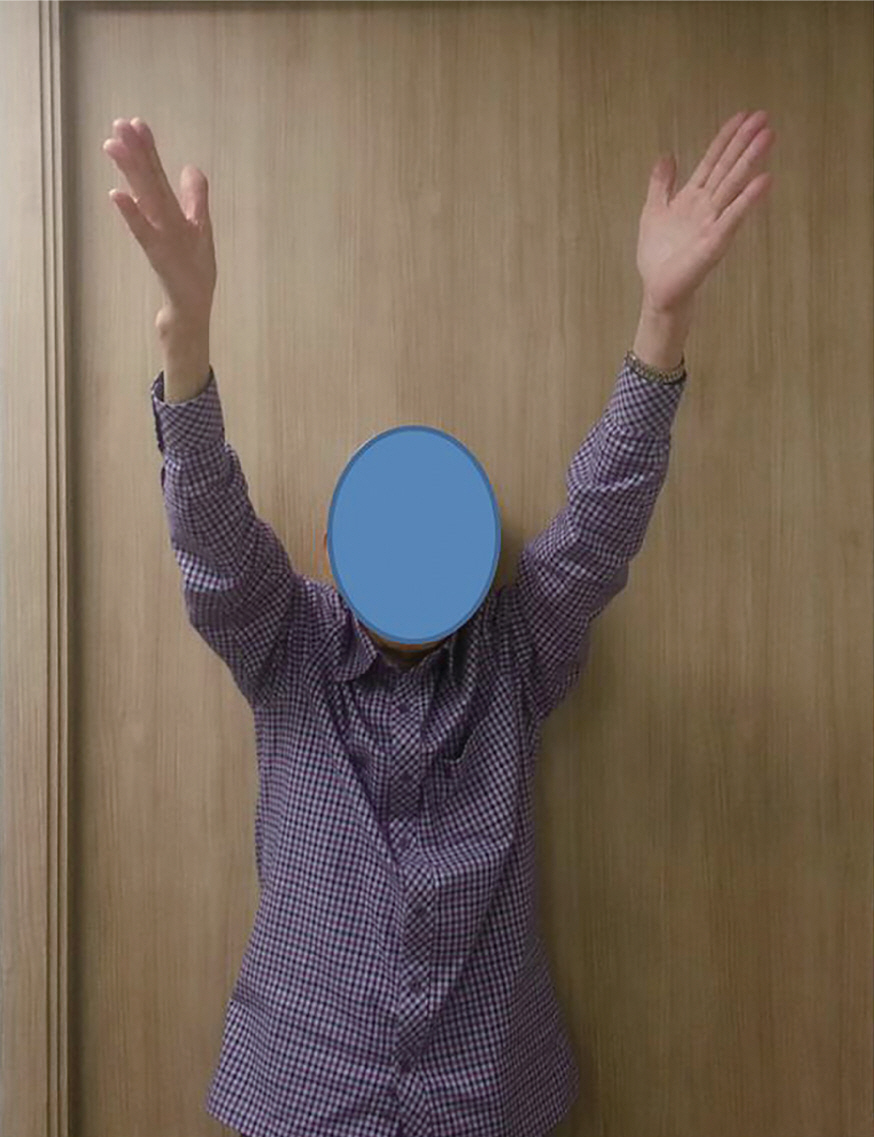
The VAS pain scores improved from 6.3 to 3.3 points (p=0.019). Forward flexion increased from 62° to 105°, abduction increased from 49° to 94°, and external rotation increased from 15° to 34°. Postoperative antero-posterior radiography revealed a mean 0.1 mm depression of the humeral head, without statistical the mean American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons score improved from 44 to 76. The acromiohumeral distance showed slight increase in amount of 0.1 mm without statistical significance. There was no complication.
CONCLUSION
Latissimus dorsi transfer is a useful surgical option for treating irreparable massive rotator cuff tears.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hamada K, Fukuda H, Mikasa M, Kobayashi Y. Roentgenographic findings in massive rotator cuff tears: a long-term observation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (254):92–6.
Article2. Feeney MS, O'Dowd J, Kay EW, Colville J. Glenohumeral articular cartilage changes in rotator cuff disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003; 12:20–3.
Article3. Neer CS 2nd, Craig EV, Fukuda H. Cuff-tear arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65:1232–44.
Article4. Namdari S, Voleti P, Baldwin K, Glaser D, Huffman GR. Latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for irreparable rotator cuff tears: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94:891–8.5. Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC. Fatty infiltration of disrupted rotator cuff muscles. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1995; 62:415–22.6. Gerber C, Maquieira G, Espinosa N. Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:113–20.
Article7. Gartsman GM. Arthroscopic treatment of rotator cuff disease. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1995; 4:228–41.
Article8. Burkhart SS. Arthroscopic treatment of massive rotator cuff tears: clinical results and biomechanical rationale. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (267):45–56.9. Rockwood CA Jr, Williams GR Jr, Burkhead WZ Jr. Debridement of degenerative, irreparable lesions of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:857–66.10. Pill SG, Walch G, Hawkins RJ, Kissenberth MJ. The role of the biceps tendon in massive rotator cuff tears. Instr Course Lect. 2012; 61:113–20.11. Fenlin JM Jr, Chase JM, Rushton SA, Frieman BG. Tuberoplasty: creation of an acromiohumeral articulation-a treatment option for massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002; 11:136–42.
Article12. Gerber C, Vinh TS, Hertel R, Hess CW. Latissimus dorsi transfer for the treatment of massive tears of the rotator cuff: a reliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (232):51–61.13. Aoki M, Okamura K, Fukushima S, Takahashi T, Ogino T. Transfer of latissimus dorsi for irreparable rotator-cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:761–6.
Article14. Warner JJ, Parsons IM 4th. Latissimus dorsi tendon transfer: a comparative analysis of primary and salvage reconstruction of massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001; 10:514–21.
Article15. Vandenbussche E, Bensaida M, Mutschler C, Dart T, Augereau B. Massive tears of the rotator cuff treated with a deltoid flap. Int Orthop. 2004; 28:226–30.
Article16. Baumfeld JA, van Riet RP, Zobitz ME, Eygendaal D, An KN, Steinmann SP. Triceps tendon properties and its potential as an autograft. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19:697–9.
Article17. Ramirez MA, Ramirez J, Murthi AM. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for irreparable rotator cuff tears and cuff tear arthropathy. Clin Sports Med. 2012; 31:749–59.
Article18. Warner JJ. Management of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears: the role of tendon transfer. Instr Course Lect. 2001; 50:63–71.19. Nishijma N, Yamamuro T, Fujio K, Ohba M. The swallow-tail sign: a test of deltoid function. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:152–3.
Article20. Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bernageau J, Lavau L, Voisin MC. Fatty muscle degeneration in cuff ruptures: pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (304):78–83.21. Richards RR, An KN, Bigliani LU, et al. A standardized method for the assessment of shoulder function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1994; 3:347–52.
Article22. Chun JM, Kim SY, Kim EG, Kim KH. Anatomical repair of massive rotator cuff tear. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2002; 37:453–8.
Article23. Apoil A, Augereau B. Deltoid flap repair of large losses of substance of the shoulder rotator cuff. Chirurgie. 1985; 111:287–90.24. Birmingham PM, Neviaser RJ. Outcome of latissimus dorsi transfer as a salvage procedure for failed rotator cuff repair with loss of elevation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008; 17:871–4.
Article25. Miniaci A, MacLeod M. Transfer of the latissimus dorsi muscle after failed repair of a massive tear of the rotator cuff: a two to five-year review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81:1120–7.26. Neri BR, Chan KW, Kwon YW. Management of massive and irreparable rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009; 18:808–18.
Article27. Aldridge JM 3rd, Atkinson TS, Mallon WJ. Combined pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi tendon transfer for massive rotator cuff deficiency. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2004; 13:621–9.
Article28. Yamaguchi K, Sher JS, Andersen WK, et al. Glenohumeral motion in patients with rotator cuff tears: a comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2000; 9:6–11.
Article29. Boileau P. Complications and revision of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016; 102:S33–43.
Article30. Churchill JL, Garrigues GE. Current controversies in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. JBJS Rev. 2016; 4:pii:01874474-201606000-00002.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterolateral Mini-open Fixation with a Patch Augmentation for Latissimus Dorsi Tendon Transfer in Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears: Technical Note
- Tendon Transfer for Irreparable Massive Rotator Cuff Tear
- Arthroscopic-assisted Latissimus Dorsi Tendon Transfer for the Management of Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears in Middle-aged Physically Active Patients
- Mid-term Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Latissimus Dorsi Tendon Transfer in Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
- Tendon Transfer in Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear