J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2015 Aug;41(4):213-216. 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.4.213.
Oral cavity lipoma: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jsjolly@naver.com
- KMID: 2364020
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.4.213
Abstract
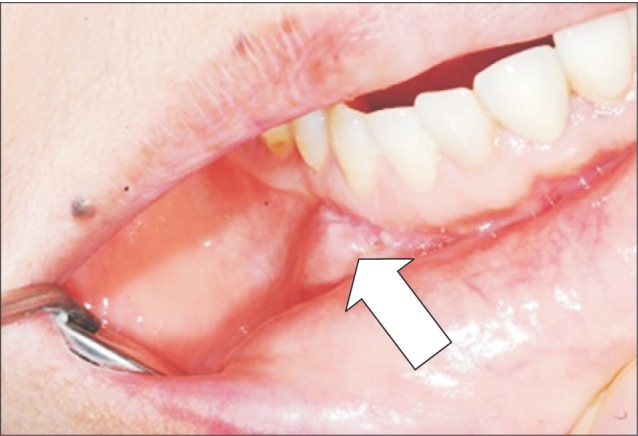
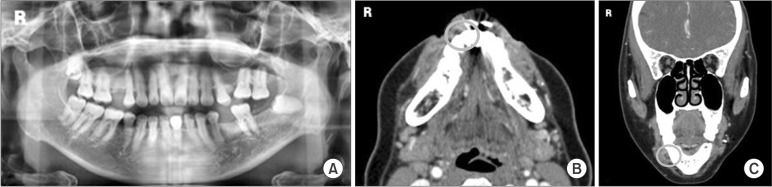
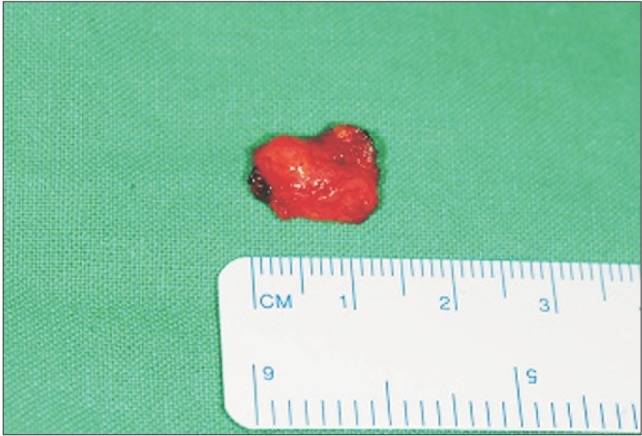
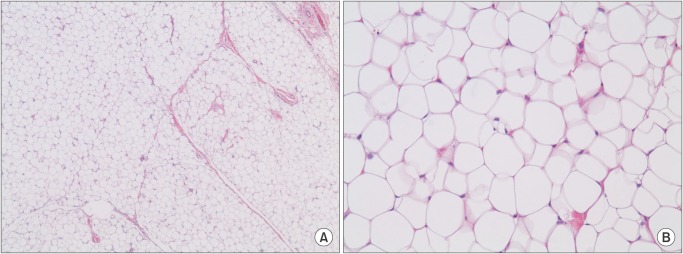
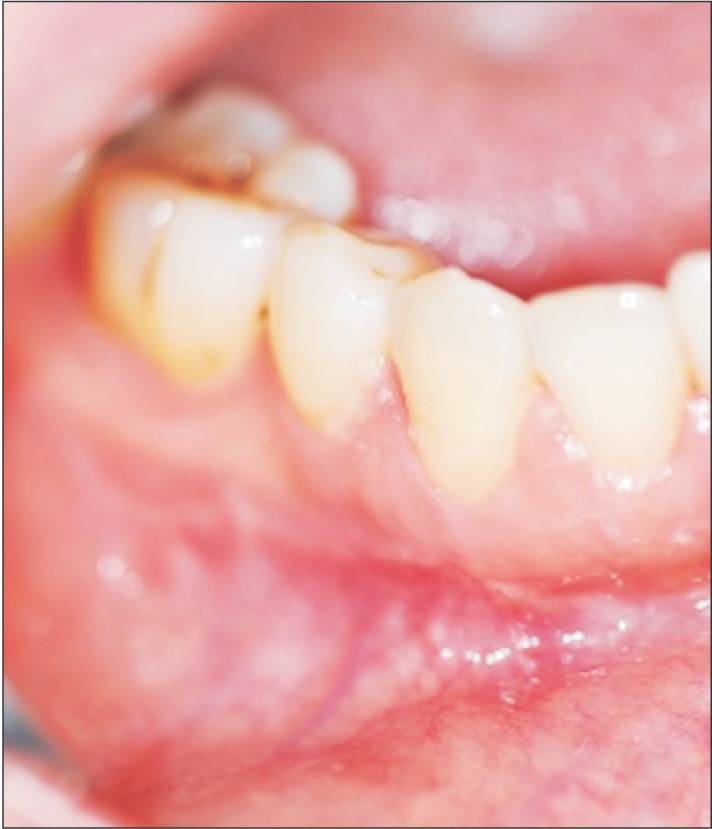
- Intraoral lipomas are a rare clinical entity, comprising only 0.1% to 5% of all benign tumors in the intraoral cavity. A 56-year-old woman suffering from diabetes presented with this relatively rare intraoral lipoma and was treated by surgical excision under general anesthesia. Because the mass was located adjacent to the mental foramen, a precise dissection was necessary to ensure minimal nerve damage. No abnormalities or recurrence was noted at 1-year follow-up and the patient did not complain of numbness. We studied the occurrence of oral lipoma in this diabetic patient and reviewed the relationship between oral lipoma and diabetes in the literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fregnani ER, Pires FR, Falzoni R, Lopes MA, Vargas PA. Lipomas of the oral cavity: clinical findings, histological classification and proliferative activity of 46 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 32:49–53. PMID: 12653233.
Article2. Guillou L, Dehon A, Charlin B, Madarnas P. Pleomorphic lipoma of the tongue: case report and literature review. J Otolaryngol. 1986; 15:313–316. PMID: 3773049.3. de Visscher JG. Lipomas and fibrolipomas of the oral cavity. J Maxillofac Surg. 1982; 10:177–181. PMID: 6957523.
Article4. Pass B, Guttenberg S, Childers EL, Emery RW. Soft tissue lipoma with the radiographic appearance of a neoplasm within the mandibular canal. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006; 35:299–302. PMID: 16798930.
Article5. Han CH, Kook MS, Park HJ, Oh HK, Ryu SY, Cho JH. Infiltrating lipoma of the cervical and parotid area: report of a case. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 32:598–602.6. Debnath SC, Saikia A. Lipoma of the parotid gland extending from the superficial to the deep lobe: a rarity. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 48:203–204. PMID: 19910088.
Article7. Malave DA, Ziccardi VB, Greco R, Patterson GT. Lipoma of the parotid gland: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994; 52:408–411. PMID: 8133376.
Article8. Hatziotis JC. Lipoma of the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1971; 31:511–524. PMID: 4926907.
Article9. Horton JE. Lipomas of the tongue: report of a fibrolipoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1968; 25:914–918. PMID: 5239745.10. Greer RO, Richardson JF. The nature of lipomas and their significance in the oral cavity: a review and report of cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973; 36:551–557. PMID: 4580925.11. Neville BW. Clinical review of oral and maxillofacial surgery. 3rd ed. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier;2008.12. Kacker A, Taskin M. Atypical intramuscular lipoma of the tongue. J Laryngol Otol. 1996; 110:189–191. PMID: 8729513.
Article13. Pisanty S. Bilateral lipomas of the tongue. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1976; 42:451–453. PMID: 1067545.
Article14. Das Gupta TK. Tumors and tumor-like conditions of the adipose tissue. Curr Probl Surg. 1970; 7:3–60.
Article15. Suzuki Y, Tsukuda K, Atsumi Y, Goto Y, Hosokawa K, Asahina T, et al. Clinical picture of a case of diabetes with mitochondrial tRNA mutation at position 3271. Diabetes Care. 1996; 19:1304–1305. PMID: 8908402.
Article16. Low PA, Nickander KK, Tritschler HJ. The roles of oxidative stress and antioxidant treatment in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1997; 46(Suppl 2):S38–S42. PMID: 9285497.
Article17. Berkovic SF, Andermann F, Shoubridge EA, Carpenter S, Robitaille Y, Andermann E, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in multiple symmetrical lipomatosis. Ann Neurol. 1991; 29:566–569. PMID: 1650162.
Article18. Holme E, Larsson NG, Oldfors A, Tulinius M, Sahlin P, Stenman G. Multiple symmetric lipomas with high levels of mtDNA with the tRNA(Lys) A-->G(8344) mutation as the only manifestation of disease in a carrier of myoclonus epilepsy and ragged-red fibers (MERRF) syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993; 52:551–556. PMID: 8447321.