Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Mar;8(1):49-56. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.49.
Quantification of the Effect of Vertical Bone Resection of the Medial Proximal Tibia for Achieving Soft Tissue Balancing in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. drsky71@duih.org
- KMID: 2363945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.49
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
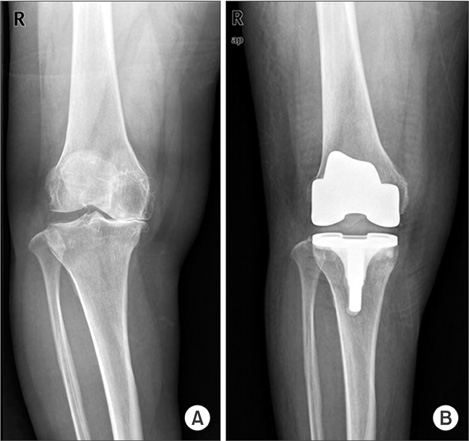
Degenerative osteoarthritis of the knee usually shows arthritic change in the medial tibiofemoral joint with severe varus deformity. In total knee arthroplasty (TKA), the medial release technique is often used for achieving mediolateral balancing. But, in a more severe varus knee, there are more difficult technical problems. Bony resection of the medial proximal tibia (MPT) as an alternative technique for achieving soft tissue balancing was assessed in terms of its effectiveness and possibility of quantification.
METHODS
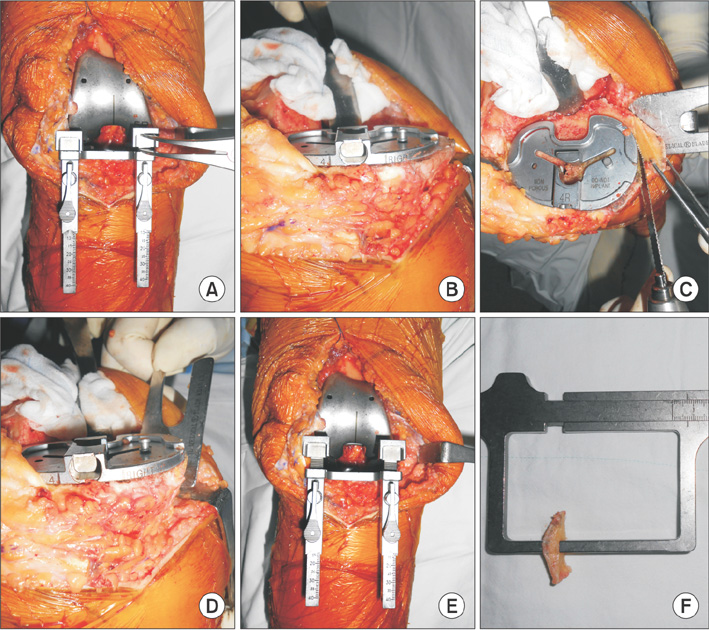
TKAs were performed in 78 knees (60 patients) with vertical bone resection of the MPT for soft tissue balancing from September 2011 to March 2013. During operation, the medial and lateral gaps were measured before and after the bony resection technique. First, the correlation between the measured thickness of the resected bone and the change in medial and lateral gaps was analyzed. Second, the possibility of quantification of each parameter was evaluated by linear regression and the coefficient ratio was obtained.
RESULTS
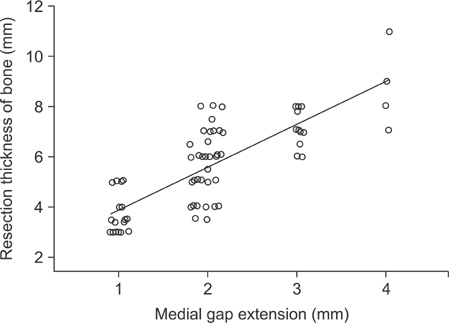
A significant correlation was identified between alteration in the medial gap change in extension and the measured thickness of the vertically resected MPT (r = 0.695, p = 0.000). In the medial gap change in flexion, there was no statistical significance (r = 0.214, p = 0.059). When the MPT was resected at an average thickness of 8.25 +/- 1.92 mm, the medial gap in extension was increased by 2.94 +/- 0.87 mm. In simple linear regression, it was predictable that MPT resection at a thickness of 2.80 mm was required to increase the medial gap by 1.00 mm in knee extension.
CONCLUSIONS
The method of bone resection of the MPT can be considered effective with a predictable result for achieving soft tissue balancing in terms of quantification during TKA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heyse TJ, Decking R, Davis J, Boettner F, Laskin RS. Varus gonarthrosis predisposes to varus malalignment in TKA. HSS J. 2009; 5(2):143–148.
Article2. Matsuda Y, Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Ishii R. Varus-valgus balance and range of movement after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(6):804–808.
Article3. Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; (192):13–22.
Article4. Teeny SM, Krackow KA, Hungerford DS, Jones M. Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with severe varus deformity: a comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (273):19–31.5. Laskin RS, Schob CJ. Medial capsular recession for severe varus deformities. J Arthroplasty. 1987; 2(4):313–316.6. Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Instability following total knee arthroplasty. HSS J. 2011; 7(3):273–278.
Article7. Yasgur DJ, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Medial release for fixed-varus deformity. In : Scuderi GR, Tria AJ, editors. Surgical technique in total knee arthroplasty. New York: Springer;2002. p. 189–196.8. Dixon MC, Parsch D, Brown RR, Scott RD. The correction of severe varus deformity in total knee arthroplasty by tibial component downsizing and resection of uncapped proximal medial bone. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19(1):19–22.
Article9. Verdonk PC, Pernin J, Pinaroli A, Ait Si Selmi T, Neyret P. Soft tissue balancing in varus total knee arthroplasty: an algorithmic approach. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17(6):660–666.
Article10. Babazadeh S, Stoney JD, Lim K, Choong PF. The relevance of ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty: how important is it? A systematic review of the literature. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2009; 1(2):e26.
Article11. Krackow KA, Mihalko WM. The effect of medial release on flexion and extension gaps in cadaveric knees: implications for soft-tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Am J Knee Surg. 1999; 12(4):222–228.12. Heesterbeek PJ, Wymenga AB. Correction of axial and rotational alignment after medial and lateral releases during balanced gap TKA: a clinical study of 54 patients. Acta Orthop. 2010; 81(3):347–353.
Article13. Sekiya H, Takatoku K, Takada H, Sasanuma H, Sugimoto N. Postoperative lateral ligamentous laxity diminishes with time after TKA in the varus knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467(6):1582–1586.
Article14. Chen W, Nagamine R, Kondo K, Todo M. Effect of medial soft-tissue releases during posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011; 19(2):230–233.
Article15. Whiteside LA, Saeki K, Mihalko WM. Functional medical ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (380):45–57.16. Sim JA, Kwak JH, Yang SH, Moon SH, Lee BK, Kim JY. Utility of preoperative distractive stress radiograph for beginners to extent of medial release in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009; 1(2):110–113.
Article17. Sugama R, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Takaoka K. Preparation of the flexion gap affects the extension gap in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(5):602–607.
Article18. Mihalko WM, Saleh KJ, Krackow KA, Whiteside LA. Soft-tissue balancing during total knee arthroplasty in the varus knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009; 17(12):766–774.
Article19. Asano H, Muneta T, Sekiya I. Soft tissue tension in extension in total knee arthroplasty affects postoperative knee extension and stability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16(11):999–1003.
Article20. Siston RA, Goodman SB, Delp SL, Giori NJ. Coronal plane stability before and after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 463:43–49.
Article21. Peters CL. Soft-tissue balancing in primary total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2006; 55:413–417.22. Engh GA. The difficult knee: severe varus and valgus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (416):58–63.23. Heesterbeek PJ, Keijsers NL, Wymenga AB. Ligament releases do not lead to increased postoperative varus-valgus laxity in flexion and extension: a prospective clinical study in 49 TKR patients. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(2):187–193.
Article24. Vince KG. Diagnosis and management of patients with instability of the knee. Instr Course Lect. 2012; 61:515–524.25. Wang JW, Wang CJ. Total knee arthroplasty for arthritis of the knee with extra-articular deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(10):1769–1774.
Article26. Meftah M, Blum YC, Raja D, Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS. Correcting fixed varus deformity with flexion contracture during total knee arthroplasty: the "inside-out" technique. AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(10):e66.27. Moon YW, Kim JG, Woo KJ, Lim SJ, Seo JG. Analysis of medial flexion gap after medial release for varus deformity by navigation-guided TKA. Orthopedics. 2011; 34(5):355.
Article28. Bellemans J. Multiple needle puncturing: balancing the varus knee. Orthopedics. 2011; 34(9):e510–e512.
Article29. Engh GA, Ammeen D. Results of total knee arthroplasty with medial epicondylar osteotomy to correct varus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; (367):141–148.
Article30. Pottenger LA, Phillips FM, Draganich LF. The effect of marginal osteophytes on reduction of varus-valgus instability in osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33(6):853–858.
Article31. Ahn JH, Back YW. Comparative study of two techniques for ligament balancing in total knee arthroplasty for severe varus knee: medial soft tissue release vs. bony resection of proximal medial tibia. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25(1):13–18.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Study of Two Techniques for Ligament Balancing in Total Knee Arthroplasty for Severe Varus Knee: Medial Soft Tissue Release vs. Bony Resection of Proximal Medial Tibia
- The Bone Mineral Density of the Proximal Tibia, Lumbar Spine and Proximal Femur and Its Correlation with the Alignment of the Lower Extremity in Knee Osteoarthritic Patients
- Autogenous Bone Graft for Medial Tibial Bone Defect in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Extramedullary Tibial Bone Cutting Using Medial Cortical Line in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Radiographic Analysis of the Tibial Axis on the Antero-posterior and Lateral view of Knee