J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(Suppl 1):S45-S54. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S1.S45.
Patient Dose Management: Focus on Practical Actions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. sejung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2363380
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S1.S45
Abstract
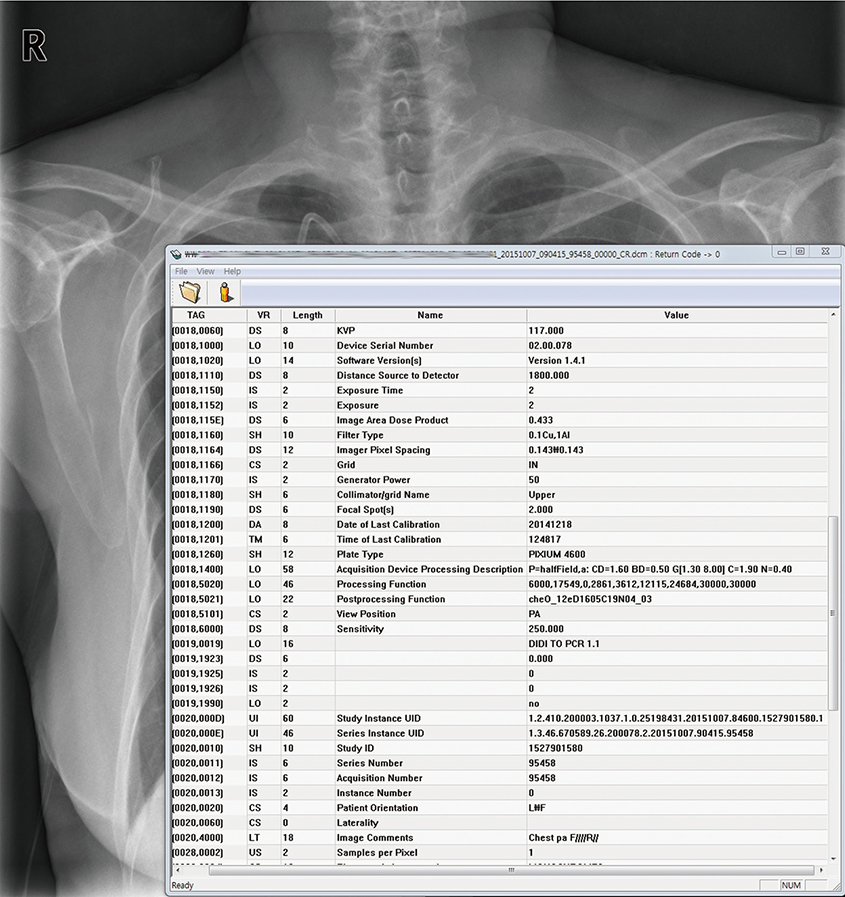
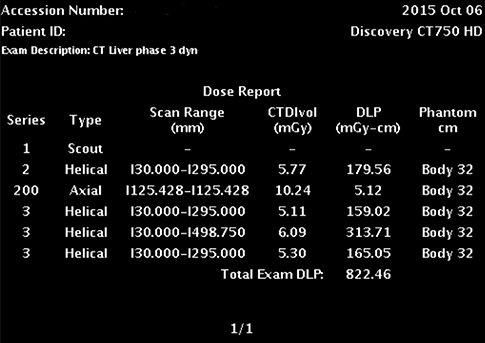
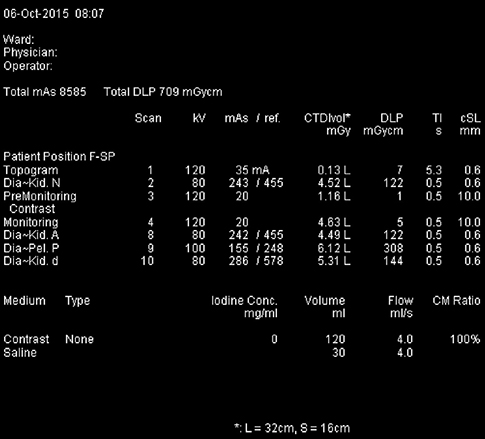
- Medical radiation is a very important part of modern medicine, and should be only used when needed and optimized. Justification and optimization of radiation examinations must be performed. The first step of reduction of medical exposure is to know the radiation dose in currently performed examinations. This review covers radiation units, how various imaging modalities report dose, and the current status of radiation dose reports and legislation. Also, practical tips that can be applied to clinical practice are introduced. Afterwards, the importance of radiology exposure related education is emphasized and the current status of education for medical personal and the public is explained, and appropriate education strategies are suggested. Commonly asked radiation dose related example questions and answers are provided in detail to allow medical personnel to answer patients. Lastly, we talk about computerized programs that can be used in medical facilities for managing patient dose. While patient dose monitoring and management should be used to decrease and optimize overall radiation dose, it should not be used to assess individual cancer risk. One must always remember that medically justified examinations should always be performed, and unneeded examinations should be avoided in the first place.
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (KR). Effects of radiation on the human body: in view of the impact of the Japanese nuclear accident. 2011. 07. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.dbpia.co.kr/Article/NODE02308340.2. 1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann ICRP. 1991; 21:1–201.3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Radiation quantities and units. 2015. 10. 02. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.fda.gov/Radiation-EmittingProducts/RadiationEmittingProductsandProcedures/MedicalImaging/MedicalX-rays/ucm115335.htm.4. The 2007 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP. 2007; 37:1–332.5. Nickoloff EL, Lu ZF, Dutta AK, So JC. Radiation dose descriptors: BERT, COD, DAP, and other strange creatures. Radiographics. 2008; 28:1439–1450.6. Sung DW. A study of strategies for patient dose management. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea;2012.7. Rickwood P. Media perspective: a good story. In : Justification of medical exposure in diagnostic imaging: proceedings of an International Workshop Brussels; 2-4 September 2009; Brussels. Brussels: International Atomic Energy Agency;2009. p. 73–102. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at: http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/Pub1532_web.pdf.8. Lee CI, Haims AH, Monico EP, Brink JA, Forman HP. Diagnostic CT scans: assessment of patient, physician, and radiologist awareness of radiation dose and possible risks. Radiology. 2004; 231:393–398.9. Krille L, Hammer GP, Merzenich H, Zeeb H. Systematic review on physician’s knowledge about radiation doses and radiation risks of computed tomography. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 76:36–41.10. O’Sullivan J, O’Connor OJ, O’Regan K, Clarke B, Burgoyne LN, Ryan MF, Maher MM. An assessment of medical students’ awareness of radiation exposures associated with diagnostic imaging investigations. Insights Imaging. 2010; 1:86–92.11. 25 Texas administrative code §289.227. Use of radiation machines in the healing arts. 2013. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at www.dshs.state.tx.us/radiation/pdffiles/Rules/227_fn_-5_-2013.12. Borgen L, Stranden E, Espeland A. Clinicians’ justification of imaging: do radiation issues play a role? Insights Imaging. 2010; 1:193–200.13. Lee S, Jung SE, Rha SE, Byun JY. Reducing radiation in CT urography for hematuria: Effect of using 100 kilovoltage protocol. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:e830–4.14. International Atomic Energy Agency (AT). Radiation protection and safety of radiation sources: international basic safety standards. 2014. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/Pub1578_web-57265295.pdf.15. Mettler FA Jr, Huda W, Yoshizumi TT, Mahesh M. Effective doses in radiology and diagnostic nuclear medicine: a catalog. Radiology. 2008; 248:254–263.16. Larke FJ, Kruger RL, Cagnon CH, Flynn MJ, McNitt-Gray MM, Wu X, Judy PF, Cody DD. Estimated radiation dose associated with low-dose chest CT of average-size participants in the National Lung Screening Trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:1165–1169.17. Hall EJ. Radiation biology for pediatric radiologists. Pediatr Radiol. 2009; 39:Suppl 1. S57–64.18. International Commission on Radiological Protection. Pregnancy and medical radiation. Ann ICRP. 2000; 30:iii–viii.19. McCollough CH, Schueler BA, Atwell TD, Braun NN, Regner DM, Brown DL, LeRoy AJ. Radiation exposure and pregnancy: when should we be concerned? Radiographics. 2007; 27:909–917.20. ACR Committee on Drugs and Contrast Media. Administration of contrast media to women who are breast-feeding. ACR manual on contrast media. Version 10.1. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology;2015. p. 99.21. ImPACT (Imaging Performance and Assessment of CT scanners). CT patient dosimetry Excel spreadsheet (version 0.99v, 17 June 2004). accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.impactscan.org/.22. Stamm G, Nagel HD. CT-expo--a novel program for dose evaluation in CT. Rofo. 2002; 174:1570–1576.23. Jung SE. Research for national medical radiation exposure reduction infrastructure. Seoul: National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation;2012.24. American College of Radiology. Dose index registry. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/National-Radiology-Data-Registry/Dose-Index-Registry.25. Qureshi ZP, Sartor O, Bennett CL. Radiation overexposure following brain perfusion CT scans in California, Florida, and Alabama (2008–2009). Community Oncol. 2011; 8:89–91.26. Hogan M. NIH leads effort to lower radiation doses in CT scans. Community Oncol. 2011; 8:143–144.27. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety Investigation of CT brain perfusion scans. 2010. 11. 09. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/Safety/AlertsandNotices/ucm185898.htm.28. California. Regulating CT radiation dose practices in California into law. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.leginfo.ca.gov/pub/09-10/bill/sen/sb_1201-1250/sb_1237_bill_20100929_chaptered.html.29. California. AB-510 radiation control: health facilities and clinics: records. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201120120AB510.30. Connecticut General Assembly (US). An act concerning radiation safety in health care. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available at http://www.cga.ct.gov/2013/TOB/H/2013HB-06423-R00-HB.htm.31. Texas Administrative Code. Radiation control. accessed on 10 October 2015. Available from http://texreg.sos.state.tx.us/public/readtac$ext.TacPage?sl=T&app=9&p_dir=N&p_rloc=165023&p_tloc=14545&p_ploc=1&pg=2&p_tac=&ti=25&pt=1&ch=289&rl=226.32. Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E, Berdon W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:289–296.33. Bolus NE. NCRP report 160 and what it means for medical imaging and nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med Technol. 2013; 41:255–260.34. Tanimura M, Matsui I, Abe J, Ikeda H, Kobayashi N, Ohira M, Yokoyama M, Kaneko M. Increased risk of hepatoblastoma among immature children with a lower birth weight. Cancer Res. 1998; 58:3032–3035.35. Doody MM, Lonstein JE, Stovall M, Hacker DG, Luckyanov N, Land CE. Breast cancer mortality after diagnostic radiography: findings from the U.S. Scoliosis Cohort Study. Spine. 2000; 25:2052–2063.36. Nelson TR. Practical strategies to reduce pediatric CT radiation dose. J Am Coll Radiol. 2014; 11:292–299.37. Calabrese EJ, O’Connor MK. Estimating risk of low radiation doses - a critical review of the BEIR VII report and its use of the linear no-threshold (LNT) hypothesis. Radiat Res. 2014; 182:463–474.38. Donnelly LF. Reducing radiation dose associated with pediatric CT by decreasing unnecessary examinations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:655–657.39. Strauss KJ, Goske MJ, Kaste SC, Bulas D, Frush DP, Butler P, Morrison G, Callahan MJ, Applegate KE. Image gently: ten steps you can take to optimize image quality and lower CT dose for pediatric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:868–873.