Ann Lab Med.
2015 Nov;35(6):570-577. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.570.
Soluble ST2 Has a Prognostic Role in Patients With Suspected Sepsis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medical-Surgery Sciences and Translational Medicine, School of Medicine and Psychology, 'Sapienza' University, Sant' Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy. salvatore.disomma@uniroma1.it
- 4Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine, School of Medicine and Psychology, 'Sapienza' University, Sant' Andrea Hospital, Rome, Italy.
- KMID: 2363259
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.570
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (sST2) has emerged as a novel biomarker for heart failure, and serum sST2 concentrations could be increased in inflammatory diseases. We explored whether sST2 is related to cardiac dysfunction/failure and has a prognostic role in patients with suspected sepsis.
METHODS
In a total of 397 patients with suspected sepsis, sST2 concentrations were measured by using the Presage ST2 Assay (Critical Diagnostics, USA). sST2 concentrations were analyzed according to procalcitonin (PCT) concentrations, cardiovascular subscores of the sepsis-related organ failure assessment (SOFA) score, and clinical outcomes.
RESULTS
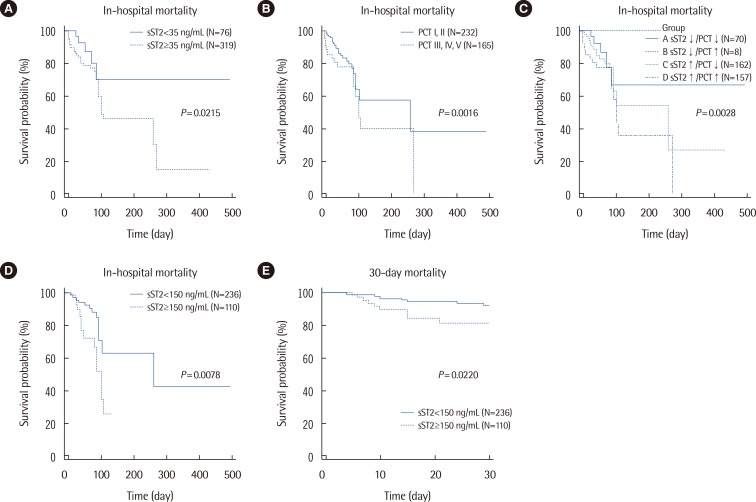
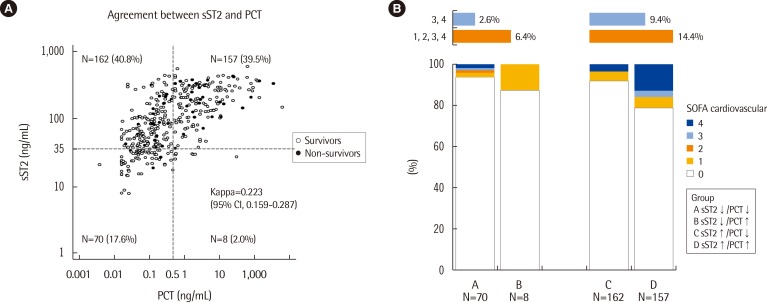
sST2 concentrations were increased significantly according to the five groups of PCT concentrations and cardiovascular subscores of the SOFA score (P<0.000001 and P=0.036, respectively). In-hospital mortality was significantly higher among patients with sST2 concentrations above 35 ng/mL (P=0.0213) and among patients with increased concentrations of both sST2 and PCT (P=0.0028).
CONCLUSIONS
sST2 seems to be related to both cardiac dysfunction/failure and severity in sepsis. Measurement of sST2 and PCT in combination would be useful for risk stratification and prognosis prediction in patients with suspected sepsis.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Biomarkers/blood
Calcitonin/blood
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Female
Hospital Mortality
Humans
Interleukin-1 Receptor-Like 1 Protein/*blood
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Prognosis
Proportional Hazards Models
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Sepsis/*diagnosis/mortality/pathology
Young Adult
Biomarkers
Calcitonin
Interleukin-1 Receptor-Like 1 Protein
Reagent Kits, Diagnostic
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prognostic Value of Soluble ST2 During Hospitalization for ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Olga Barbarash, Olga Gruzdeva, Evgenya Uchasova, Yulia Dyleva, Ekaterina Belik, Olga Akbasheva, Victoria Karetnikova, Aleksandr Shilov
Ann Lab Med. 2016;36(4):313-319. doi: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.4.313.
Reference
-
1. Weinberg EO, Shimpo M, De Keulenaer GW, MacGillivray C, Tominaga S, Solomon SD, et al. Expression and regulation of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor family member, in cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2002; 106:2961–2966. PMID: 12460879.
Article2. Weinberg EO. ST2 protein in heart disease: from discovery to mechanisms and prognostic value. Biomark Med. 2009; 3:495–511. PMID: 20477519.
Article3. Shah RV, Januzzi JL Jr. Soluble ST2 and galectin-3 in heart failure. Clin Lab Med. 2014; 34:87–97. PMID: 24507789.
Article4. Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, et al. American College of Cardiology Foundation. American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62:e147–e239. PMID: 23747642.5. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013; 39:165–228. PMID: 23361625.
Article6. Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, Needham DM, Pronovost PJ, Sevransky JE. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38:1276–1283. PMID: 20308885.
Article7. Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996; 22:707–710. PMID: 8844239.8. Wacker C, Prkno A, Brunkhorst FM, Schlattmann P. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013; 13:426–435. PMID: 23375419.
Article9. Meisner M. Update on procalcitonin measurements. Ann Lab Med. 2014; 34:263–273. PMID: 24982830.
Article10. Mueller T, Dieplinger B. The Presage(®) ST2 Assay: analytical considerations and clinical applications for a high-sensitivity assay for measurement of soluble ST2. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013; 13:13–30. PMID: 23256700.11. Brunner M, Krenn C, Roth G, Moser B, Dworschak M, Jensen-Jarolim E, et al. Increased levels of soluble ST2 protein and IgG1 production in patients with sepsis and trauma. Intensive Care Med. 2004; 30:1468–1473. PMID: 14991091.
Article12. Dieplinger B, Januzzi JL Jr, Steinmair M, Gabriel C, Poelz W, Haltmayer M, et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a novel high-sensitivity assay for measurement of soluble ST2 in human plasma-the Presage ST2 assay. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 409:33–40. PMID: 19699192.13. Alves-Filho JC, Sônego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M, et al. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med. 2010; 16:708–712. PMID: 20473304.
Article14. Hoogerwerf JJ, Tanck MW, van Zoelen MA, Wittebole X, Laterre PF, van der Poll T. Soluble ST2 plasma concentrations predict mortality in severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2010; 36:630–637. PMID: 20151106.
Article15. Felker GM, Fiuzat M, Thompson V, Shaw LK, Neely ML, Adams KF, et al. Soluble ST2 in ambulatory patients with heart failure: Association with functional capacity and long-term outcomes. Circ Heart Fail. 2013; 6:1172–1179. PMID: 24103327.16. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/reviews/k111452.pdf. Accessed in July 22, 2015.17. Kim H, Hur M, Cruz DN, Moon HW, Yun YM. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis. Clin Biochem. 2013; 46:1414–1418. PMID: 23747960.
Article18. Hur M, Kim H, Lee S, Cristofano F, Magrini L, Marino R, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic utilities of multimarkers approach using procalcitonin, B-type natriuretic peptide, and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:224. PMID: 24761764.
Article19. Parenica J, Malaska J, Jarkovsky J, Lipkova J, Dastych M, Helanova K, et al. Soluble ST2 levels in patients with cardiogenic and septic shock are not predictors of mortality. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2012; 17:205–209. PMID: 23592937.20. Tian G, Pan SY, Ma G, Liao W, Su QG, Gu BC, et al. Serum levels of procalcitonin as a biomarker for differentiating between sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome in the neurological intensive care unit. J Clin Neurosci. 2014; 21:1153–1158. PMID: 24508074.
Article21. Lu J, Snider JV, Grenache DG. Establishment of reference intervals for soluble ST2 from a United States population. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:1825–1826. PMID: 20654603.
Article22. Di Somma S, Magrini L, Travaglino F, Lalle I, Fiotti N, Cervellin G, et al. Opinion paper on innovative approach of biomarkers for infectious diseases and sepsis management in the emergency department. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013; 51:1167–1175. PMID: 23392907.
Article23. Schuetz P, Haubitz S, Mueller B. Do sepsis biomarkers in the emergency room allow transition from bundled sepsis care to personalized patient care? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2012; 18:341–349. PMID: 22610364.
Article24. Riedel S, Carroll KC. Laboratory detection of sepsis: biomarkers and molecular approaches. Clin Lab Med. 2013; 33:413–437. PMID: 23931833.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Elevated levels of soluble ST2 but not galectin-3 are associated with increased risk of mortality in hemodialysis patients
- Establishing Reference Intervals for Soluble ST2 Assay in a Korean Population
- Soluble ST2 in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: a New Biomarker that Predicts Recurrence?
- Role of Soluble ST2 as a Marker for Rejection after Heart Transplant
- Role of Soluble ST2 as a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Acute Heart Failure and Renal Insufficiency