Ann Lab Med.
2015 May;35(3):336-340. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.336.
Mutation Analysis of the TGFBI Gene in Consecutive Korean Patients With Corneal Dystrophies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. changski@skku.edu
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tychung@skku.edu
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, Catholic University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.336
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Mutations in the transforming growth factor beta-induced gene (TGFBI) are major causes of genetic corneal dystrophies (CDs), which can be grouped into TGFBI CDs. Although a few studies have reported the clinical and genetic features of Korean patients with TGFBI CD, no data are available regarding the frequency and spectrum of TGFBI mutations in a consecutive series of Korean patients with clinically diagnosed CDs.
METHODS
Patients with any type of CD, who underwent both ophthalmologic examination and TGFBI gene analysis by Sanger sequencing at a tertiary care hospital in Seoul, Korea from 2006 to 2013, were enrolled in this study.
RESULTS
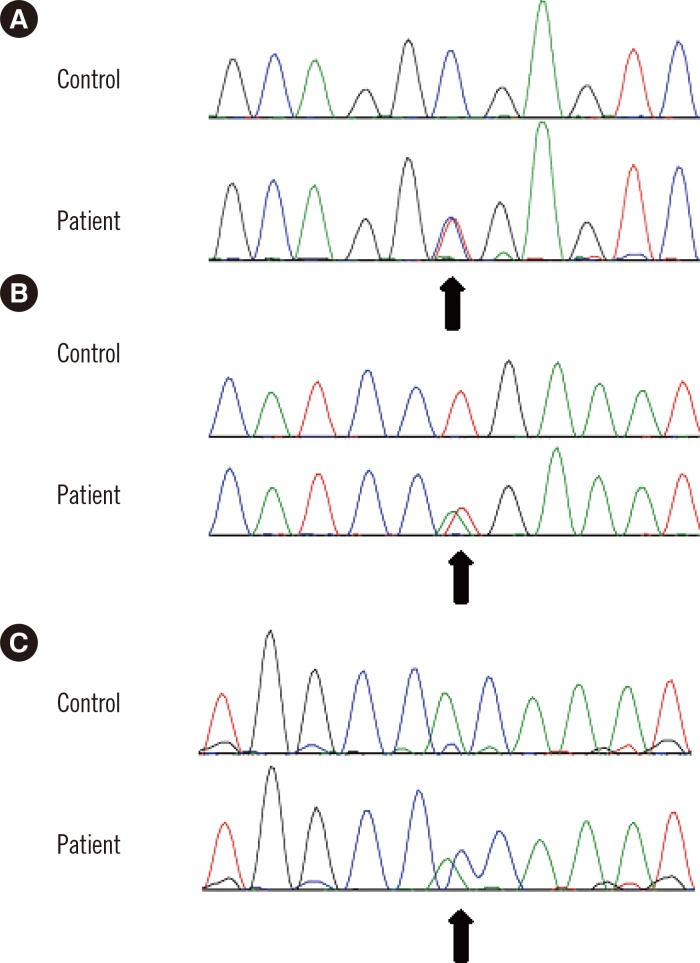
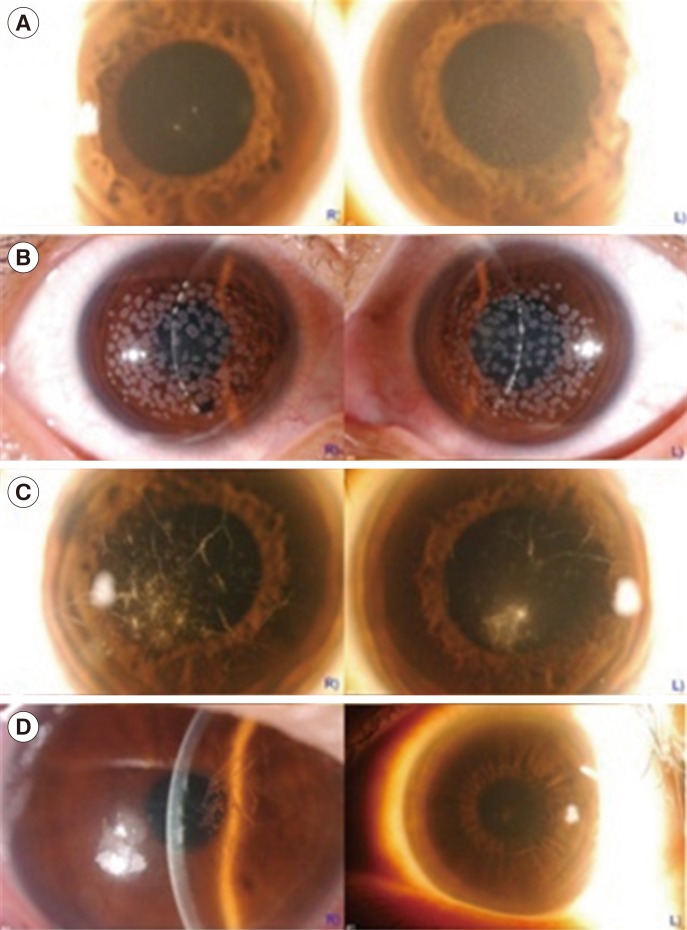
Among a total of 89 patients, 77 (86.5%) were diagnosed as having clinical TGFBI CD. Seventy-three out of 74 patients (98.6%) with granular CD type 2 (GCD2), had the p.R124H mutation. Of particular note, one patient with rapidly progressive CD had the p.R124H mutation as well as a novel nonsense variant with unknown clinical significance (p.A179*). In three patients with lattice CD type 1 (LCD1), one known mutation (p.R124C) and two novel variants (p.L569Q and p.T621P) in the TGFBI gene were identified.
CONCLUSIONS
This study provides epidemiological insight into CDs in a Korean population and reaffirms that GCD2 is the most common TGFBI CD phenotype and that p.R124H is the only mutation identified in patients with GCD2. In addition, we broaden the spectrum of TGFBI mutations by identifying two novel missense variants in patients with LCD1.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Corneal Dystrophies, Hereditary/diagnosis/*genetics
DNA Mutational Analysis
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Phenotype
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide
Republic of Korea
Retrospective Studies
Transforming Growth Factor beta1/*genetics
Young Adult
Transforming Growth Factor beta1
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang T, Yan N, Yu W, Liu Y, Liu G, Wu X, et al. Molecular genetics of Chinese families with TGFBI corneal dystrophies. Mol Vis. 2011; 17:380–387. PMID: 21311742.3. Weiss JS, Moller HU, Lisch W, Kinoshita S, Aldave AJ, Belin MW, et al. The IC3D classification of the corneal dystrophies. Cornea. 2008; 27:S1–S83. PMID: 19337156.4. Zhu Y, Shentu X, Wang W. The TGFBI R555W mutation induces a new granular corneal dystrophy type I phenotype. Mol Vis. 2011; 17:225–230. PMID: 21264234.5. Abazi Z, Magarasevic L, Grubisa I, Risovic D. Individual phenotypic variances in a family with Avellino corneal dystrophy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2013; 13:30. PMID: 23837658.
Article6. Aldave AJ, Sonmez B. Elucidating the molecular genetic basis of the corneal dystrophies: are we there yet? Arch Ophthalmol. 2007; 125:177–186. PMID: 17296893.7. Nowinska AK, Wylegala E, Janiszewska DA, Dobrowolski D, Aragona P, Roszkowska AM, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation of TGFBI corneal dystrophies in Polish patients. Mol Vis. 2011; 17:2333–2342. PMID: 21921985.8. Yoshida S, Yoshida A, Nakao S, Emori A, Nakamura T, Fujisawa K, et al. Lattice corneal dystrophy type I without typical lattice lines: role of mutational analysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:586–588. PMID: 15013897.
Article9. Kim HS, Yoon SK, Cho BJ, Kim EK, Joo CK. BIGH3 gene mutations and rapid detection in Korean patients with corneal dystrophy. Cornea. 2001; 20:844–849. PMID: 11685063.
Article10. Jun RM, Tchah H, Kim TI, Stulting RD, Jung SE, Seo KY, et al. Avellino corneal dystrophy after LASIK. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:463–468. PMID: 15019320.
Article11. Lee JH, Cristol SM, Kim WC, Chung ES, Tchah H, Kim MS, et al. Prevalence of granular corneal dystrophy type 2 (Avellino corneal dystrophy) in the Korean population. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2010; 17:160–165. PMID: 20455845.
Article12. Cho KJ, Mok JW, Na KS, Rho CR, Byun YS, Hwang HS, et al. TGFBI gene mutations in a Korean population with corneal dystrophy. Mol Vis. 2012; 18:2012–2021. PMID: 22876129.13. Han KE, Kim TI, Chung WS, Choi SI, Kim BY, Kim EK. Clinical findings and treatments of granular corneal dystrophy type 2 (avellino corneal dystrophy): a review of the literature. Eye Contact Lens. 2010; 36:296–299. PMID: 20724852.
Article14. Holland EJ, Daya SM, Stone EM, Folberg R, Dobler AA, Cameron JD, et al. Avellino corneal dystrophy. Clinical manifestations and natural history. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:1564–1568. PMID: 1454323.15. Yam GH, Wang K, Jhanji V, Choy KW, Baum L, Pang CP. In vitro amyloid aggregate forming ability of TGFBI mutants that cause corneal dystrophies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012; 53:5890–5898. PMID: 22850414.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Korean Patient with Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type IV with Leu527Arg Mutation in the TGFBI Gene
- A Case of Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Type 1 Initially Showing Phenotypic Characteristics of Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2 in One Eye and Dot and Map Lesions in the Contralateral Eye
- A Comparative Study of the Diagnostic Performance of the GENEDIA Avellino Corneal Dystrophy Mutation Detection Kit and Screening Master Mix and a Direct Sequencing Method to Detect Mutations in the TGFB1 Gene
- Long-Term Outcomes of Penetrating Keratoplasty in Treating Macular Corneal Dystrophy, TGFBI Dystrophy, and Fuchs' Dystrophy
- N102S Mutation of UBIAD1 Gene in a Family with Schnyder Crystalline Corneal Dystrophy