Ann Lab Med.
2015 Mar;35(2):275-278. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.275.
First Korean Case of SATB2-Associated 2q32-q33 Microdeletion Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. KAL1119@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2363196
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.275
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Child
Chromosome Disorders/*diagnosis
*Chromosomes, Human, Pair 2
Gene Deletion
Humans
Male
Matrix Attachment Region Binding Proteins/*genetics
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Republic of Korea
Transcription Factors/*genetics
Matrix Attachment Region Binding Proteins
Transcription Factors
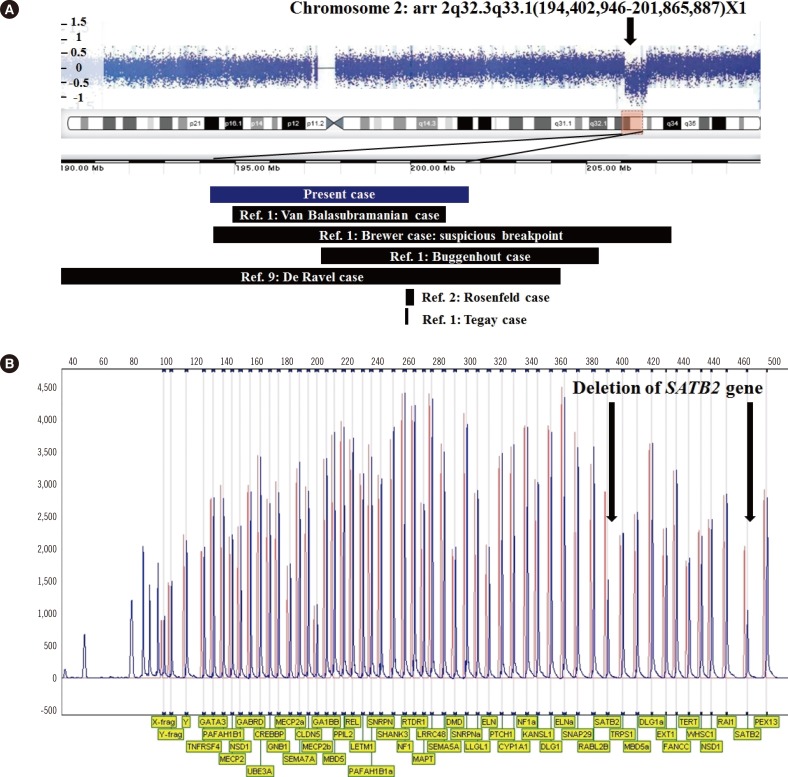
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balasubramanian M, Smith K, Basel-Vanagaite L, Feingold MF, Brock P, Gowans GC, et al. Case series: 2q33.1 microdeletion syndrome--further delineation of the phenotype. J Med Genet. 2011; 48:290–298. PMID: 21343628.
Article2. Rosenfeld JA, Ballif BC, Lucas A, Spence EJ, Powell C, Aylsworth AS, et al. Small deletions of SATB2 cause some of the clinical features of the 2q33.1 microdeletion syndrome. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e6568. PMID: 19668335.
Article3. Döcker D, Schubach M, Menzel M, Munz M, Spaich C, Biskup S, et al. Further delineation of the SATB2 phenotype. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014; 22:1034–1039. PMID: 24301056.
Article4. Zhao X, Qu Z, Tickner J, Xu J, Dai K, Zhang X. The role of SATB2 in skeletogenesis and human disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014; 25:35–44. PMID: 24411565.
Article5. FitzPatrick DR, Carr IM, McLaren L, Leek JP, Wightman P, Williamson K, et al. Identification of SATB2 as the cleft palate gene on 2q32-q33. Hum Mol Genet. 2003; 12:2491–2501. PMID: 12915443.
Article6. Nicholl J, Waters W, Mulley JC, Suwalski S, Brown S, Hull Y, et al. Cognitive deficit and autism spectrum disorders: prospective diagnosis by array CGH. Pathology. 2014; 46:41–45. PMID: 24300712.
Article7. Miller DT, Adam MP, Aradhya S, Biesecker LG, Brothman AR, Carter NP, et al. Consensus statement: chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. Am J Hum Genet. 2010; 86:749–764. PMID: 20466091.
Article8. Urquhart J, Black GC, Clayton-Smith J. 4.5 Mb microdeletion in chromosome band 2q33.1 associated with learning disability and cleft palate. Eur J Med Genet. 2009; 52:454–457. PMID: 19576302.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The first Korean case of 2p15p16.1 microdeletion syndrome, characterized by facial dysmorphism, developmental delay, and congenital hypothyroidism
- Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) in the differential diagnosis of osteogenic and non-osteogenic bone and soft tissue tumors
- The Prevelance of Microdeletion of Y Chromosome in Klinefelter's Syndrome
- Comparing Two Diagnostic Laboratory Tests for Several Microdeletions Causing Mental Retardation Syndromes: Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Amplification vs Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization
- A Case of Miller-Dieker Syndrome