Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jan;35(1):149-151. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.149.
Simultaneous Occurrence of Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma and Plasma Cell Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363165
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.149
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Humans
Leukemia, Plasma Cell/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Leukocytosis
Lymph Nodes/pathology
Lymphoma, T-Cell/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Male
Paraproteinemias/complications
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell, gamma-delta/genetics/metabolism
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell, gamma-delta
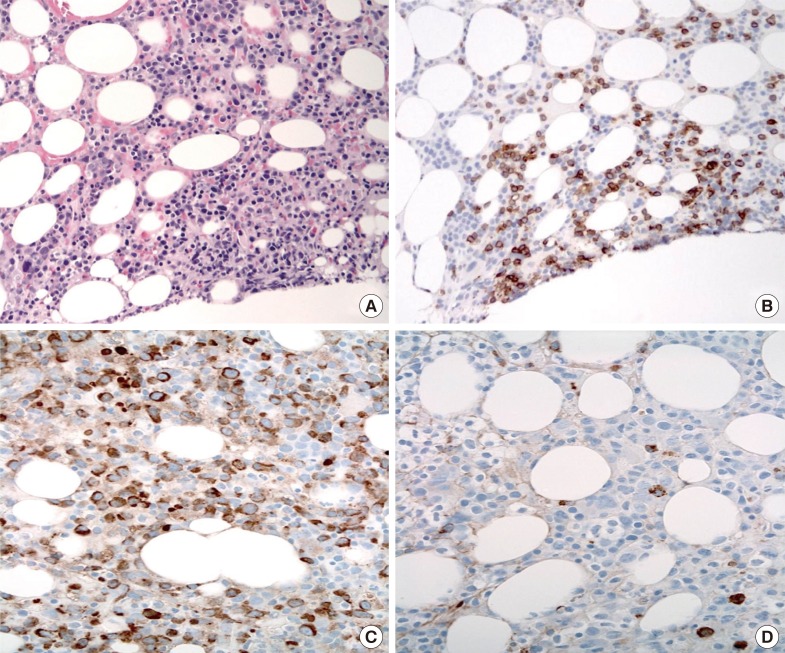
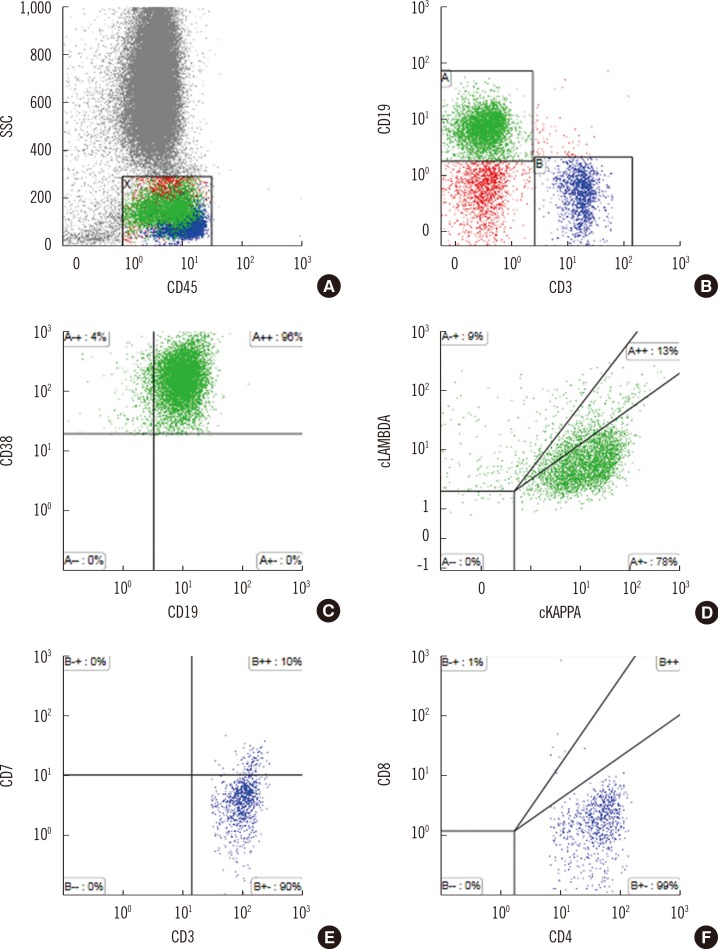
Figure
Reference
-
1. Grogg KL, Morice WG, Macon WR. Spectrum of bone marrow findings in patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2007; 137:416–422. PMID: 17488486.
Article2. Huppmann AR, Roullet MR, Raffeld M, Jaffe ES. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma partially obscured by an Epstein-Barr virus-negative clonal plasma cell proliferation. J ClinOncol. 2013; 31:e28–e30.
Article3. Balagué O, Martínez A, Colomo L, Roselló E, Garcia A, Martónez-Bernal M, et al. Epstein-Barr virus negative clonal plasma cell proliferations and lymphomas in peripheral T-cell lymphomas: a phenomenon with distinctive clinicopathologic features. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:1310–1322. PMID: 17721185.4. Willenbrock K, Bräuninger A, Hansmann ML. Frequent occurrence of B-cell lymphomas in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in early cases. Br J Haematol. 2007; 138:733–739. PMID: 17672882.
Article5. Lin P, Hao S, Handy BC, Bueso-Ramos CE, Medeiros LJ. Lymphoid neoplasms associated with IgM paraprotein: a study of 382 patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005; 123:200–205. PMID: 15842043.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epstein-Barr Virus-positive Diffuse, Large B-cell Lymphoma after Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- Simultaneous presentation of plasma cell myeloma and hairy cell leukemia
- A Case with Plasma Cell Leukemia and Anaplastic Large T cell Lymphoma
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Pure Red Cell Aplasia Associated with Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma