J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Dec;57(12):1874-1881. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.12.1874.
Measurement of Corneal Power and Astigmatism Using Placido-based Videokeratography and Comparison with Other Keratometers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. kcyoon@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2362704
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.12.1874
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In the present study, the repeatability and reproducibility of the corneal power and astigmatism measurements using placido-based video keratography were evaluated and the agreement with other keratometers were compared.
METHODS
This prospective study included 45 patients (45 eyes) scheduled to undergo cataract surgery between November 2015 and January 2016. Three sets of corneal power and astigmatism were measured using placido-based video keratometer (Keratograph® 5M), automatic keratometer (KR-8900®), manual keratometer (B×L manual keratometer®), Placido-scanning-slit keratometer (ORBscan II®), Scheimpflug keratometer (Pentacam®), and low coherence interferometry (Lenstar LS900®). Reliability of each device was analyzed using the coefficient of variation, standard deviation and intraclass correlation coefficient. Repeated measures analysis of variance was used to analyze the interdevice comparison of mean absolute difference. The agreement between the devices was evaluated with 95% limits of agreement (LoA) and Bland-Altman plots.
RESULTS
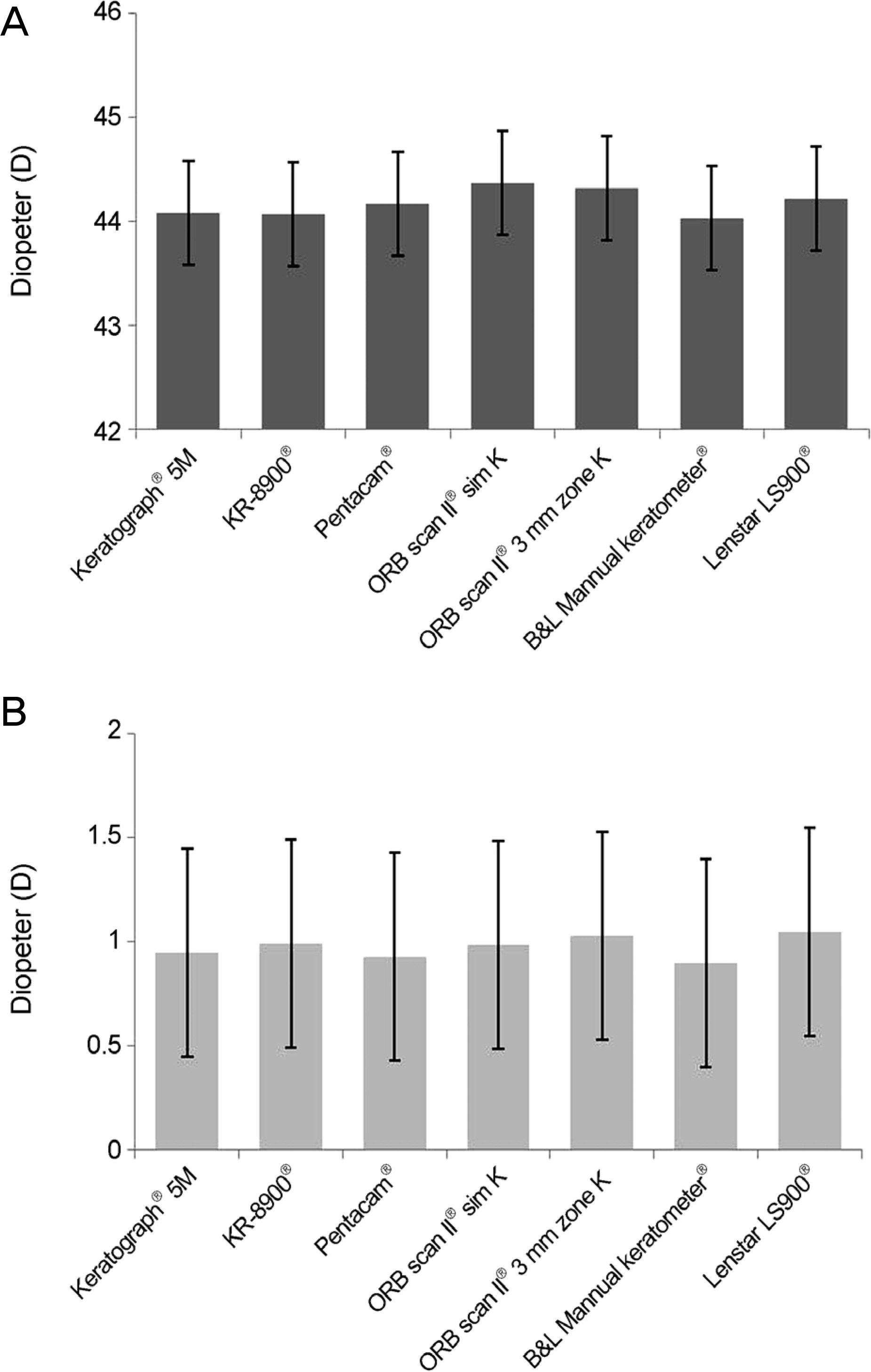
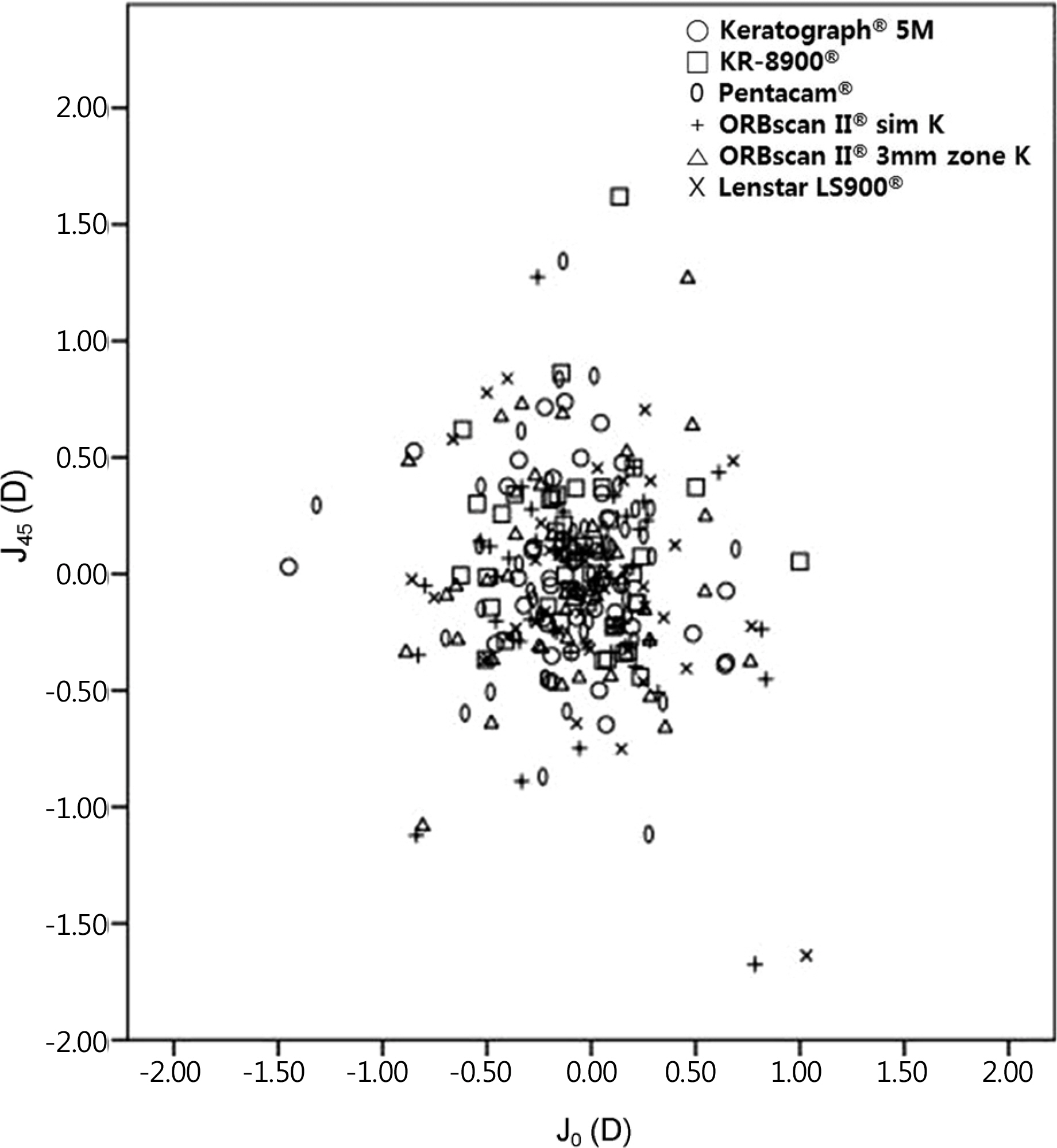
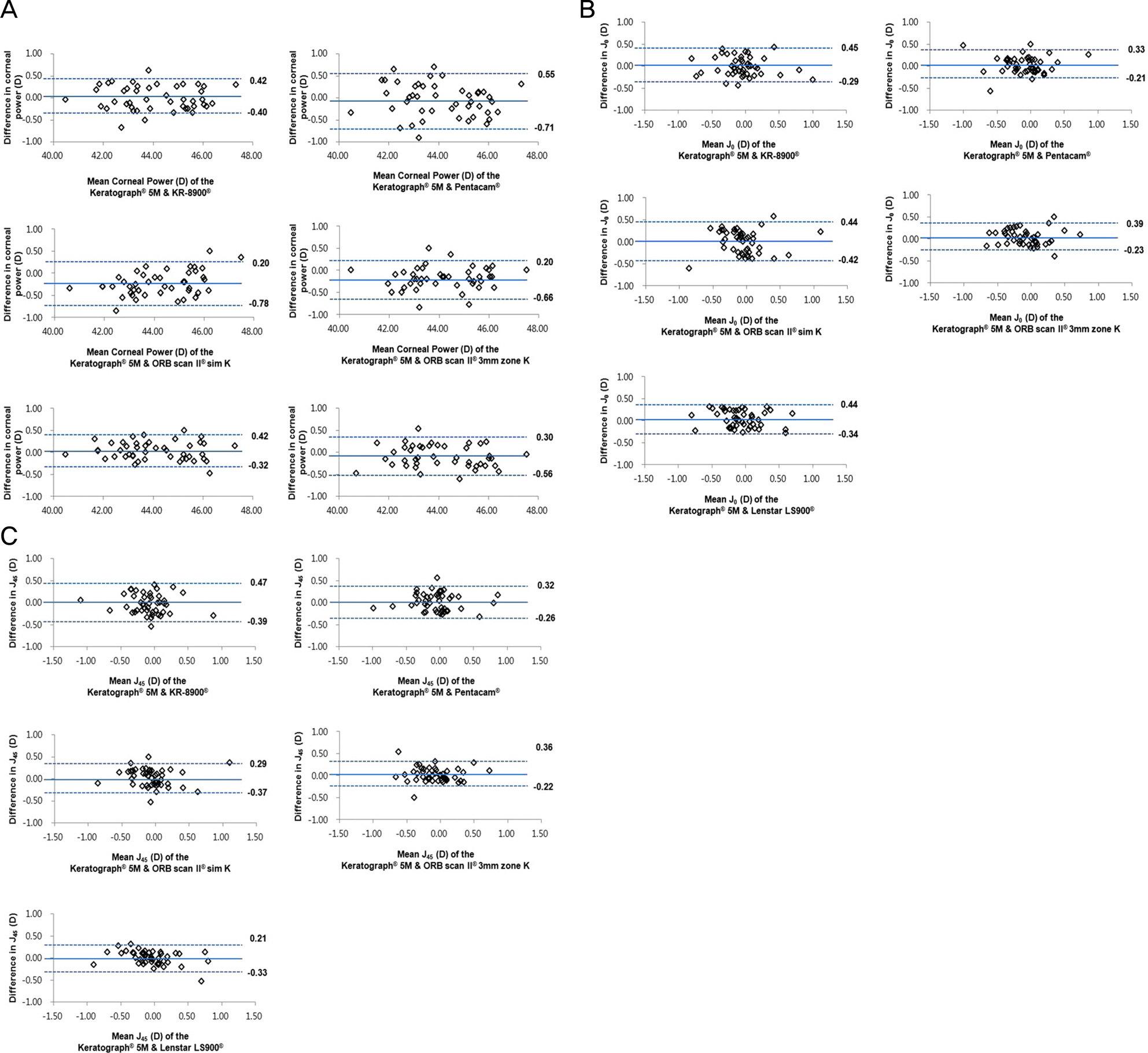
The mean corneal power, astigmatism and power vector analysis (Jâ‚€, Jâ‚„â‚…) were not significantly different among devices (p > 0.05). In the Bland-Altman plot analysis, the 95% LoA of corneal power, Jâ‚€, and J45 when comparing Keratograph® 5M with others ranged from -0.78 to 0.55 D, from -0.42 to 0.45 D, and from -0.39 to 0.47 D, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Keratograph® 5M showed good repeatability and reproducibility of corneal power and astigmatism measurements and was interchangeable with other keratometers.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Qazi MA, Cua IY, Roberts CJ, Pepose JS. Determining corneal power using Orbscan II videokeratography for intraocular lens abdominal after excimer laser surgery for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:21–30.2. Elbaz U, Barkana Y, Gerber Y, et al. Comparison of different abdominals of anterior chamber depth and keratometric measurements. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:48–53.3. Elliott M, Simpson T, Richter D, Fonn D. Repeatability and abdominal of automated refraction: a comparison of the Nikon NRK-8000, the Nidek AR-1000, and subjective refraction. Optom Vis Sci. 1997; 74:434–8.4. Holzer MP, Mamusa M, Auffarth GU. Accuracy of a new partial coherence interferometry analyser for biometric measurements. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93:807–10.
Article5. Choi JH, Roh GH. The reproducibility and accuracy of biometry parameter measurement from IOL Master(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1665–73.6. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. Improved prediction of abdominal lens power using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:861–7.7. Findl O, Drexler W, Menapace R, et al. High precision biometry of pseudophakic eyes using partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998; 24:1087–93.
Article8. Kim S, Chung SK. Comparison of corneal curvatures obtained with different devices. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:618–25.
Article9. Thibos LN, Wheeler W, Horner D. Power vectors: an application of Fourier analysis to the description and statistical analysis of abdominal error. Optom Vis Sci. 1997; 74:367–75.10. Jiang Y, Ye H, Xu J, Lu Y. Noninvasive Keratograph assessment of tear film break-up time and location in patients with age-related cataracts and dry eye syndrome. J Int Med Res. 2014; 42:494–502.
Article11. Best N, Drury L, Wolffsohn JS. Clinical evaluation of the Oculus Keratograph. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2012; 35:171–4.
Article12. Srinivasan S, Menzies K, Sorbara L, Jones L. Infrared imaging of meibomian gland structure using a novel keratograph. Optom Vis Sci. 2012; 89:788–94.
Article13. Wu S, Hong J, Tian L, et al. Assessment of bulbar redness with a newly developed keratograph. Optom Vis Sci. 2015; 92:892–9.
Article14. Wang X, Lu X, Yang J, et al. Evaluation of dry eye and meibomian gland dysfunction in teenagers with myopia through noninvasive keratograph. J Ophthalmol. 2016; 2016:6761206.
Article15. Tian L, Qu JH, Zhang XY, Sun XG. Repeatability and abdominal of noninvasive keratograph 5M measurements in patients with dry eye disease. J Ophthalmol. 2016; 2016:8013621.16. Abdelfattah NS, Dastiridou A, Sadda SR, Lee OL. Noninvasive imaging of tear film dynamics in eyes with ocular surface disease. Cornea. 2015; 34(Suppl 10):S48–52.
Article17. Ngo W, Srinivasan S, Schulze M, Jones L. Repeatability of grading meibomian gland dropout using two infrared systems. Optom Vis Sci. 2014; 91:658–67.
Article18. Mao X, Savini G, Zhuo Z, et al. Repeatability, reproducibility, and agreement of corneal power measurements obtained with a new corneal topographer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:1561–9.
Article19. Ventura BV, Al-Mohtaseb Z, Wang L, et al. Repeatability and abdominal of corneal power and corneal astigmatism obtained from a point-source color light-emitting diode topographer, a Placido-based corneal topographer, and a low-coherence reflectometer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015; 41:2242–50.20. Kawamorita T, Uozato H, Kamiya K, et al. Repeatability, abdominal, and agreement characteristics of rotating Scheimpflug photography and scanning-slit corneal topography for corneal power measurement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:127–33.21. Shin YJ, Kim NH, Kim DH. Comparison of Pentacam with Orbscan. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:637–41.22. Menassa N, Kaufmann C, Goggin M, et al. Comparison and reproducibility of corneal thickness and curvature readings obtained by the Galilei and the Orbscan II analysis systems. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1742–7.
Article23. Laursen JV, Jeppesen P, Olsen T. Precision of 5 different abdominal devices. Int Ophthalmol. 2016; 36:17–20.24. Han JM, Choi HJ, Kim MK, et al. Comparative analysis of corneal abdominal and astigmatism measured with autokeratometer, IOL abdominal, and topography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1427–33.25. Srivannaboon S, Soeharnila , Chirapapaisan C, Chonpimai P. Comparison of corneal astigmatism and axis location in cataract abdominals measured by total corneal power, automated keratometry, and simulated keratometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38:2088–93.26. Tajbakhsh Z, Salouti R, Nowroozzadeh MH, et al. Comparison of abdominal measurements using the Pentacam HR, the Orbscan IIz, and the TMS-4 topographer. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2012; 32:539–46.27. Shirayama M, Wang L, Weikert MP, Koch DD. Comparison of abdominal powers obtained from 4 different devices. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:528–35.e1.28. Dehnavi Z, Khabazkhoob M, Mirzajani A, et al. Comparison of the corneal power measurements with the TMS4-topographer, abdominal HR, IOL master, and Javal keratometer. Middel East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2015; 22:233–7.29. Gonen T, Cosar CB, Sener B, Keskinbora KH. Comparison of abdominal data obtained by automated keratometer, Dicon CT 200, Allegro Topolyzer, and Pentacam. J Refract Surg. 2012; 28:557–61.30. Mejia-Barbosa Y, Malacara-Hernandez D. A review of methods for measuring corneal topography. Optom Vis Sci. 2001; 78:240–53.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Classification of Corneal Topography and Analysis of Astigmatism based on Computer-Assisted Videokeratography
- Corneal Power Estimation Using Orbscan II Videokeratography in Eyes With Previous Corneal Refractive Surgeries
- Keratometry and Computerized Videokeratography in Determining Intraocular Lens Calculation
- Comparison of Anterior, Posterior, and Total Corneal Astigmatism Measured Using a Single Scheimpflug Camera in Healthy and Keratoconus Eyes
- The Corneal Topographic Changes in Sutureless Cataract Surgery