Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Jun;8(2):102-110. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.102.
Effects of the Simultaneous Application of Nonlinear Frequency Compression and Dichotic Hearing on the Speech Recognition of Severely Hearing-Impaired Subjects: Simulation Test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. iykim@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2360779
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.2.102
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
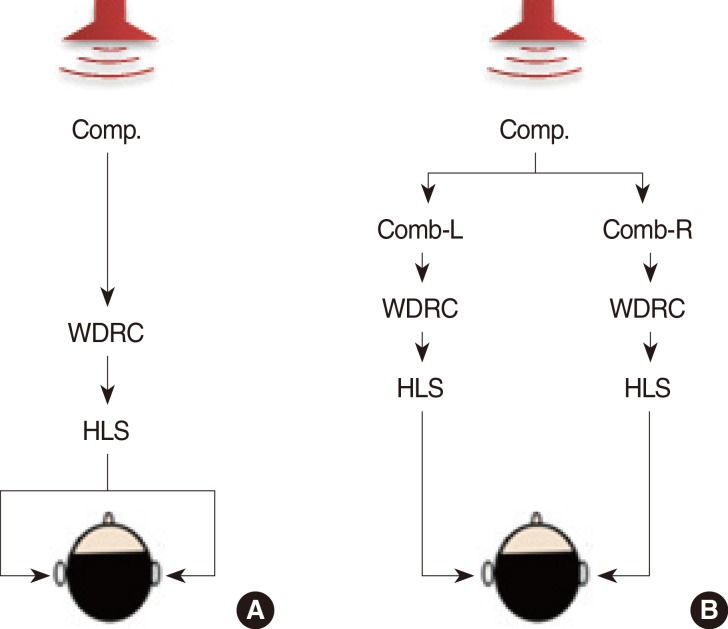
The clinical effects of the simultaneous application of nonlinear frequency compression and dichotic hearing on people with hearing impairments have not been evaluated previously. In this study, the clinical effects of the simultaneous application of these two techniques on the recognition of consonant-vowel-consonant (CVC) words with fricatives were evaluated using normal-hearing subjects and a hearing loss simulator operated in the severe hearing loss setting.
METHODS
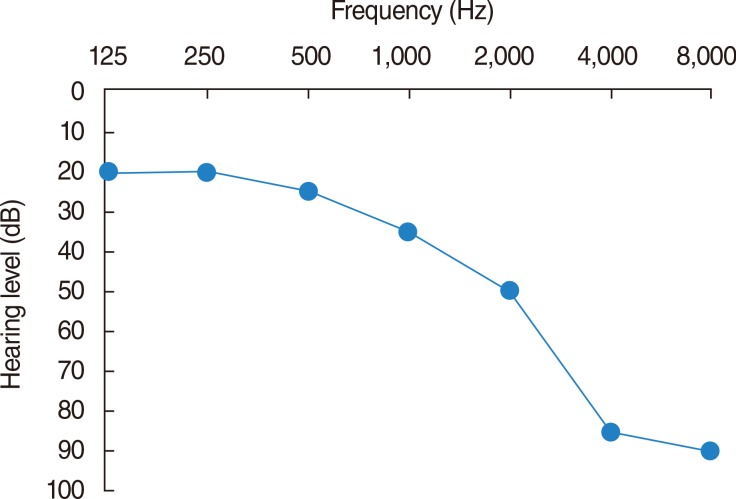
A total of 21 normal-hearing volunteers whose native language was English were recruited for this study, and two different hearing loss simulators, which were configured for severe hearing loss in the high-frequency range, were utilized. The subjects heard 82 English CVC words, and the word recognition score and response time were measured.
RESULTS
The experimental results demonstrated that the simultaneous application of these two techniques showed almost even performance compared to the sole application of nonlinear frequency compression in a severe hearing loss setting.
CONCLUSION
Though it is generally accepted that dichotic hearing can decrease the spectral masking thresholds of an hearing-impaired person, simultaneous application of the nonlinear frequency compression and dichotic hearing techniques did not significantly improve the recognition of words with fricatives compared to the sole application of nonlinear frequency compression in a severe hearing loss setting.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carney AE, Nelson DA. An analysis of psychophysical tuning curves in normal and pathological ears. J Acoust Soc Am. 1983; 1. 73(1):268–278. PMID: 6826895.
Article2. Harvey D. Compression systems in hearing aids. In : Dillon H, editor. Hearing aids. 2nd ed. New York: Thieme;2012. p. 171–172.3. Taylor B. Constructing a hearing aid fitting using the latest clinical evidence [Internet]. Houston (TX): AudiologyOnline;2012. cited 2015 Apr 25. Available from: http://www.audiologyonline.com/articles/constructing-hearing-aid-fitting-using-6584.4. Harvey D. Frequency lowering. In : Dillon H, editor. Hearing aids. 2nd ed. New York: Thieme;2012. p. 239–240.5. Simpson A, Hersbach AA, McDermott HJ. Improvements in speech perception with an experimental nonlinear frequency compression hearing device. Int J Audiol. 2005; 5. 44(5):281–292. PMID: 16028791.
Article6. Kulkarni PN, Pandey PC, Jangamashetti DS. Binaural dichotic presentation to reduce the effects of spectral masking in moderate bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Int J Audiol. 2012; 4. 51(4):334–344. PMID: 22201526.
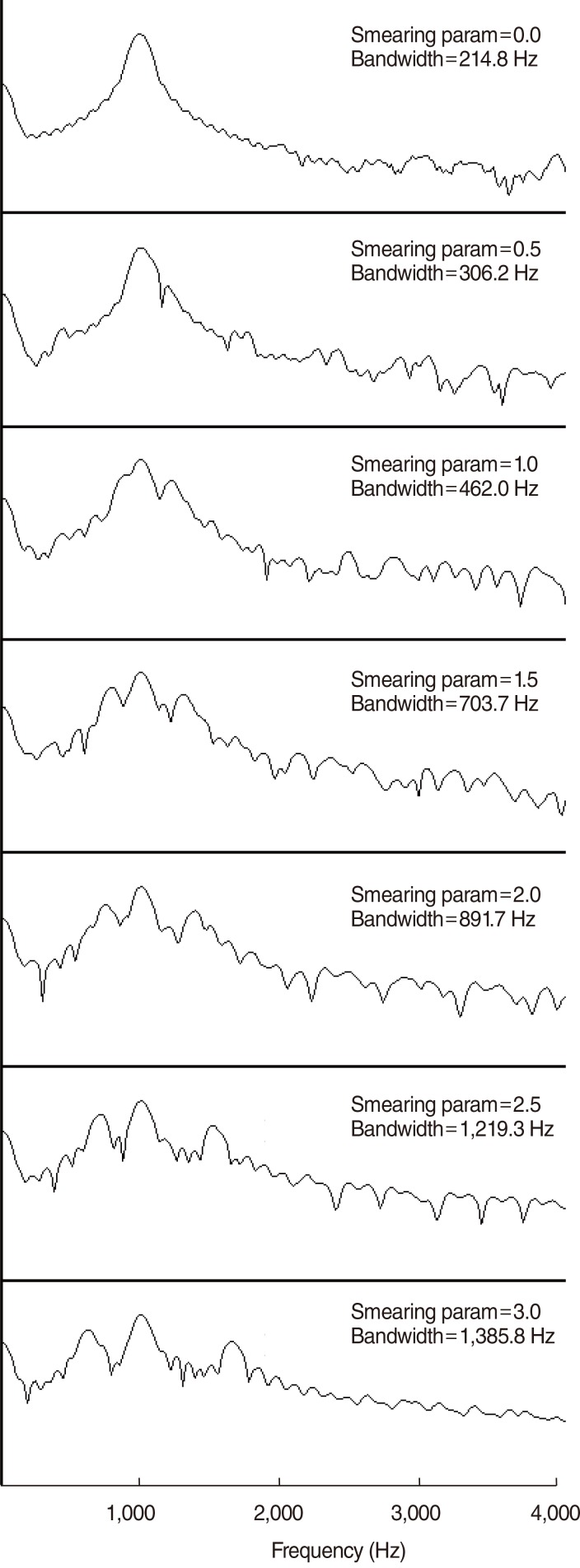
Article7. MATLAB mathematics. R2010b. Natick (MA): The MathWorks Inc;2010.8. Yasu K, Hishitani M, Arai T, Murahara Y. Critical-band based frequency compression for digital hearing aids. Acoust Sci Tech. 2004; 5. 25(1):61–63.
Article9. Cheeran AN, Pandey PC, Jangamashetti DS. Design of comb filters based on auditory filter bandwidths for binaural dichotic presentation for persons with sensorineural hearing impairment. In : 2002 14th Intemational Conference on Digital Signal Processing Proceedings DSP 2002; 2002 Jul 1-3; Santorini, Hellas. Piscataway (NJ): The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers;2002. p. 971–974.10. Staney M. An efficient implementation of the Patterson-Holdsworth auditory filter bank. Cupertino (CA): Apple Computer Inc;1993.11. Desloge JG, Zurek PM, Ghitza O, Wiegand TE, Goldsworthy R, Cheyne H. HeLPS (Hearing Loss and Prosthesis Simulator) [CD-ROM]. Version 1.0. Malden: Senseimetrics;2006.12. Zurek PM, Desloge JG. Hearing loss and prosthesis simulation in audiology. Hear J. 2007; 7. 60(7):32. 33. 36. 38.
Article13. AngelSim (TigerCIS). Cochclear implant and hearing loss simulator [Internet]. Version 1.08.01. Shanghai: TigerSpeech Technology;2012. cited 2015 Apr 25. Available from: http://www.tigerspeech.com/tst_tigercis.html.14. Chatterjee M, Peredo F, Nelson D, Baskent D. Recognition of interrupted sentences under conditions of spectral degradation. J Acoust Soc Am. 2010; 2. 127(2):EL37–EL41. PMID: 20136176.
Article15. Kuk F, Keenan D, Peeters H, Korhonen P, Auriemmo J. 12 Lessons learned about linear frequency transposition. Hear Rev. 2008; 11. 15(12):32–41.16. Glasberg BR, Moore BC. Auditory filter shapes in subjects with unilateral and bilateral cochlear impairments. J Acoust Soc Am. 1986; 4. 79(4):1020–1033. PMID: 3700857.
Article17. Sound express auditory training (SEAT): a new way to learn sound and music [Internet]. Version 5.04.01. Shanghai: TigerSpeech Technology;2012. cited 2015 Apr 25. Available from: http://www.tigerspeech.com/tst_soundex.html.18. House AS, Williams CE, Heker MH, Kryter KD. Articulation-testing methods: consonantal differentiation with a closed-response set. J Acoust Soc Am. 1986; 1. 37:158–166. PMID: 14265103.
Article19. Yellin MW, Roland PS. Special auditory/vestibular testing. In : Roland PS, Marple BF, Meyerhoff WL, editors. Hearing loss. New York: Thieme Medical Publisher Inc;1997. p. 71–106.20. Joe WK. Audiology pure-tone testing [Internet]. New York: Medscape;c2013. cited 2015 Mar 10. Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1822962-overview#a01.21. GraphPad Prism [Internet]. Version 5.01. La Jolla (CA): GraphPad Software Inc;2007. cited 2015 Apr 25. Available from: http://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/.22. Loebach JL, Pisoni DB. Perceptual learning of spectrally degraded speech and environmental sounds. J Acoust Soc Am. 2008; 2. 123(2):1126–1139. PMID: 18247913.
Article23. Kagomiya T, Nakagawa S. Development of a Japanese speaker discrimination test for evaluation of hearing assistance devices. In : Proceedings of the 17th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences (ICPhS XVII); 2011 Aug 17-21; Hong Kong, China. Hong Kong: City University of Hong Kong;2011. p. 998–1001.24. Nejime Y, Moore BC. Evaluation of the effect of speech-rate slowing on speech intelligibility in noise using a simulation of cochlear hearing loss. J Acoust Soc Am. 1998; 1. 103(1):572–576. PMID: 9440342.
Article25. Chaudhari DS, Pandey PC. Dichotic presentation of speech signal using critical filter bank for bilateral sensorineural hearing impairment. In : Proceedings of the 16th International Congresses on Acoustics; 1998 Jun 20-26; Seattle, USA. International Congresses on Acoustics;1998. p. 213–214.26. Murase A, Nakajima F, Sakamoto S, Suzuki V, Kawase T. Effect and sound localization with dichotic-listening digital hearing aids. In : The 18th International Congress on Acoustics ICA 2004; 2004 Apr 4-9; Kyoto, Japan. International Congresses on Acoustics;2004. p. II-1519–II-1522.27. Mani A, Loizou PC, Shoup A, Roland P, Kruger P. Dichotic speech recognition by bilateral cochlear implant users. Int Congr Ser. 2004; 11. 1273(1):466–469.
Article28. Kolte MT, Chaudhari DS. Evaluation of speech processing schemes to improve perception of sensorineural hearing impaired. Curr Sci. 2010; 3. 98(5):613–615.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preferred Compression Threshold and Release Time in Quiet and Noisy Conditions for Elderly Korean Hearing Aid Users
- Study on Effective Improvement of Mobile Phone Sound Quality in a Noise Environment for the Hearing-Impaired
- Auditory Recognition of Digit-in-Noise under Unaided and Aided Conditions in Moderate and Severe Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Speech Intelligibility in Persian Hearing Impaired Children with Cochlear Implants and Hearing Aids
- The Relationship Between Tinnitus Frequency and Speech Discrimination in Patients With Hearing Loss