Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2016 Dec;9(4):382-384. 10.21053/ceo.2015.00724.
Esophageal Stent Insertion for Postesophagectomy Anastomosis Site Leakage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. chkang@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2360772
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2015.00724
Abstract
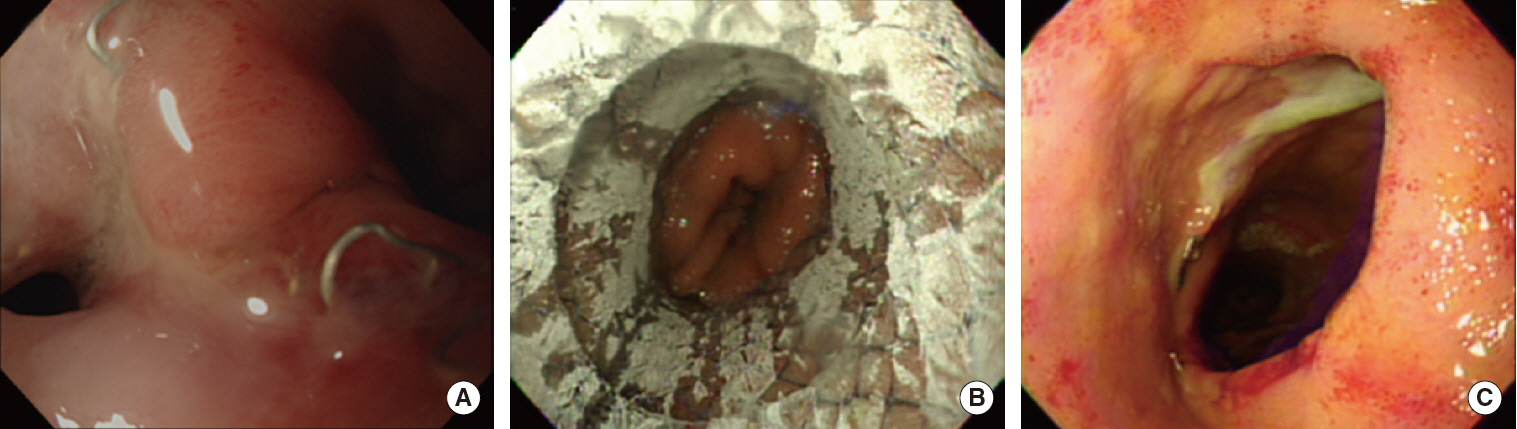
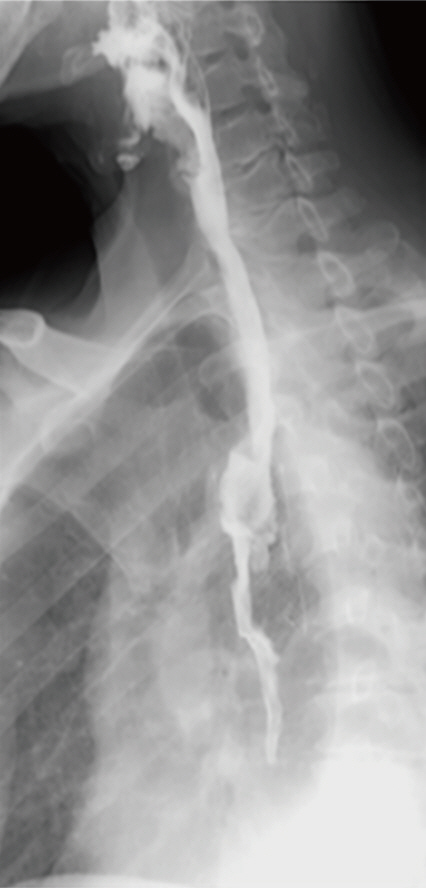
- In Ivor Lewis operation, anastomosis site leakage is a critical complication. Interventional approach utilizing covered metal stent has been introduced for the management of this complication. This patient was diagnosed as esophageal cancer and underwent robot-assisted Ivor Lewis operation. Due to symptoms suggesting anastomosis site leakage, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery exploration was performed without identification of gross leakage site. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy, anastomosis site leakage was detected and esophageal stent was placed. Four weeks later, the stent was removed, and the patient could intake all his diet orally without discomfort. Esophageal stent insertion can be an option to manage postesophagectomy leakage problem.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Externally Monitored Versus Conventional Buried Flaps in Laryngopharyngeal Reconstruction
Myung Jin Ban, Gina Na, Sungchul Ko, Joohyun Kim, Nam Hun Heo, Eun Chang Choi, Jae Hong Park, Won Shik Kim
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;14(4):407-413. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2020.00234.
Reference
-
1. Freeman RK, Ascioti AJ. Esophageal stent placement for the treatment of perforation, fistula, or anastomotic leak. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; Summer. 23(2):154–8.
Article2. Freeman RK, Vyverberg A, Ascioti AJ. Esophageal stent placement for the treatment of acute intrathoracic anastomotic leak after esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011; Jul. 92(1):204–8.
Article3. Segalin A, Bonavina L, Lazzerini M, De Ruberto F, Faranda C, Peracchia A. Endoscopic management of inveterate esophageal perforations and leaks. Surg Endosc. 1996; Sep. 10(9):928–32.
Article4. Al-issa MA, Petersen TI, Taha AY, Shehatha JS. The role of esophageal stent placement in the management of postesophagectomy anastomotic leak. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2014; Jan-Feb. 20(1):39–42.
Article5. Langer FB, Wenzl E, Prager G, Salat A, Miholic J, Mang T, et al. Management of postoperative esophageal leaks with the Polyflex self-expanding covered plastic stent. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005; Feb. 79(2):398–403.
Article6. D’Cunha J, Rueth NM, Groth SS, Maddaus MA, Andrade RS. Esophageal stents for anastomotic leaks and perforations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; Jul. 142(1):39–46. e1.
Article7. Nguyen NT, Rudersdorf PD, Smith BR, Reavis K, Nguyen XM, Stamos MJ. Management of gastrointestinal leaks after minimally invasive esophagectomy: conventional treatments vs. endoscopic stenting. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; Nov. 15(11):1952–60.
Article8. Blackmon SH, Santora R, Schwarz P, Barroso A, Dunkin BJ. Utility of removable esophageal covered self-expanding metal stents for leak and fistula management. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010; Mar. 89(3):931–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Esophageal Perforation Cured by Conservative Management after Stent Insertion
- A Case of Endoscopic Stenting for Anastomotic Leakage after Total Gastrectomy
- Fluoroscopically Guided Three-Tube Insertion for the Treatment of Postoperative Gastroesophageal Anastomotic Leakage
- Guidelines of Esophageal Stent Insertion for Benign and Malignant Diseases
- Long Percutaneous Stent Insertion in Pancreatic Duct and Monitoring of Pancreaticojejunostomy Site Leakage in Periampullary Cancer Patients