Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Dec;7(4):519-522. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.4.519.
High Grade Infective Spondylolisthesis of Cervical Spine Secondary to Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sancheti Institute for Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Pune, India. orthokunal@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2360269
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.4.519
Abstract
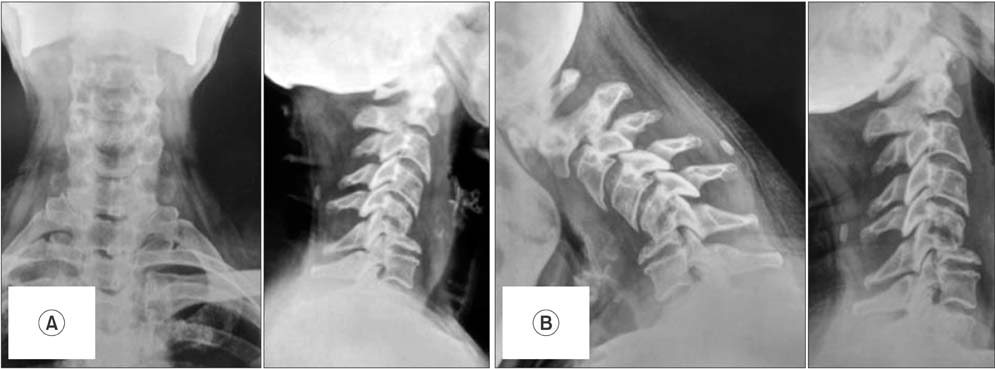
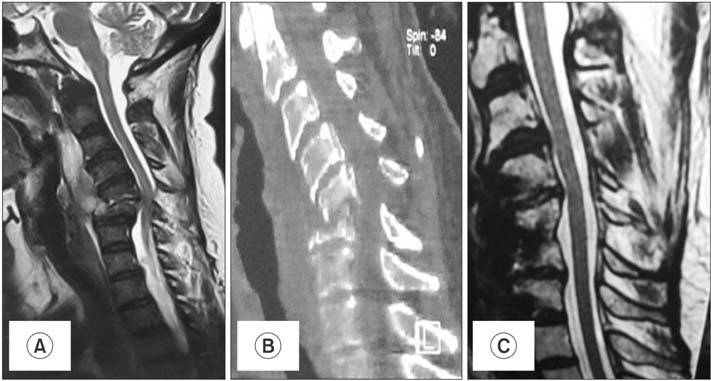
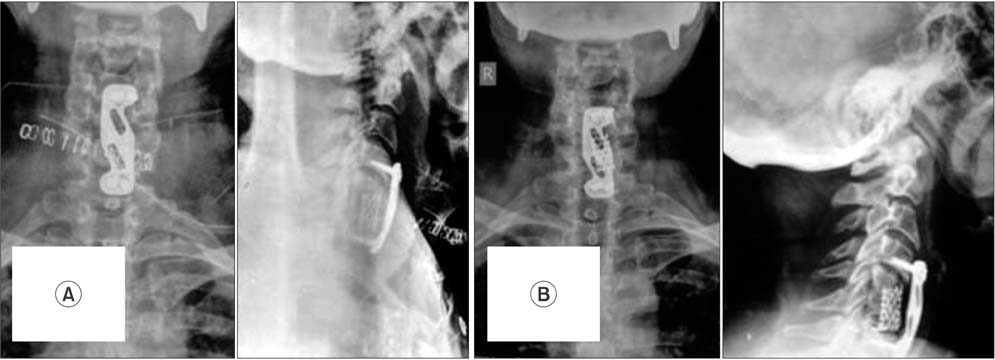
- Spondylolisthesis coexisting with tuberculosis is rarely reported. There is a controversy whether spondylolisthesis coexists or precedes tuberculosis. Few cases of pathological spondylolisthesis secondary to tuberculous spondylodiscitis have been reported in the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. All cases in the literature presented as anterolisthesis, except one which presented as posterolisthesis of lumbar spine. Spondylolisthesis in the cervical spine is mainly degenerative and traumatic. Spondylolisthesis due to tuberculosis is not reported in the lower cervical spine. The exact mechanism of such an occurrence of spondylolisthesis with tuberculosis is sparsely reported in the literature and inadequately understood. We report a rare case of high grade pathological posterolisthesis of the lower cervical spine due to tubercular spondylodiscitis in a 67-year-old woman managed surgically with a three-year follow-up period. This case highlights the varied and complex presentation of tuberculosis of the lower cervical spine and gives insight into its pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hsu LC, Leong JC. Tuberculosis of the lower cervical spine (C2 to C7): a report on 40 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66(1):1–5.
Article2. Woiciechowsky C, Thomale UW, Kroppenstedt SN. Degenerative spondylolisthesis of the cervical spine: symptoms and surgical strategies depending on disease progress. Eur Spine J. 2004; 13(8):680–684.
Article3. Chadha M, Agarwal A, Kumar S. Spinal tuberculosis with concomitant spondylolisthesis: coexisting entities or 'cause andeffect'? Spinal Cord. 2006; 44(6):399–404.
Article4. Newman PH, Stone KH. The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1963; 45(1):39–59.
Article5. Ratliff AH. Tuberculosis at the site of spondylolisthesis. Br J Surg. 1956; 43(181):502–504.
Article6. Tuli SM. Tuberculosis of the skeletal system. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers;1997.7. Kirkman MA, Sridhar K. Posterior listhesis of a lumbar vertebra in spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(1):1–5.
Article8. Ramani PS, Sharma A, Jituri S, Muzumdar DP. Anterior instrumentation for cervical spine tuberculosis: an analysis of surgical experience with 61 cases. Neurol India. 2005; 53(1):83–89.
Article9. Ram C, Swapnil K. Tuberculosis of the lower cervical spine. In : Shetty AP, Jain AK, Kanna RM, Rajasekaran S, editors. Spinal infections and trauma. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers;2011. p. 151–166.10. Yilmaz C, Selek HY, Gurkan I, Erdemli B, Korkusuz Z. Anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81(9):1261–1267.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis of Cervical Spine
- Radiological Characteristics of Low-Grade Lytic Spondylolisthesis: Similarity to Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis
- Concurrent Degenerative Cervical and Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Problems in Reduction of High-Grade Spondylolisthesis
- Asymptomatic Cervical Isthmic Spondylolisthesis and Associated Occult Spinal Bifida: A Case Report