J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Sep;8(3):362-371. 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.362.
Problems in Reduction of High-Grade Spondylolisthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kang-Nam St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kyh@cmc.cuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2209758
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2001.8.3.362
Abstract
- There has been discussion about surgical strategies for treatment of high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis(grade III or IV). Reduction is combined unnecessary by many authors because of the reliability of in situ fusion. However, some investigator have stated a need for reduction is not only restoration of normal spinal alignment and biomechanics; A reduced position is believed to enhance fusion, relieve neurological abnormalities and pain, and improve the cosmetic appearance. Many different techniques have been developed for reduction of spondylolisthesis after Jenkin's initial description in 1936. The techniques include halofemoral traction, cast reduction, instrumentation, L5 corpectomy, and the combined anterior and posterior approach. Recently, newly developed pedicular instrumentation was widely used to reduce high-grade spondylolisthesis and had high fusion rates. But these instrumentations cannot prevent complications such as nerve root lesions due to the traction on the L5 root during reduction. Anyway, there is much controversy about the most effective surgical treatment option for highgrade isthmic spondylolisthesis. As well symptoms may vary depending the age of patient. Surgical decision making and preoperative planning need to address not only the anatomic deformity but also the symptoms complex as manifested by the predominance of either back pain and/or radicular symptoms. However, the patients with high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis are very limited in Korea. Therefore, the best reliable reduction method for high-grade spondylolisthesis remains a challenging procedure, requiring great surgical attention to detail.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Bohlman HH, Cook SS. One-stage decompression and posterolateral and interbody fusion for lumbosacral spondyloptosis through a posterior approach; Report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 64:415–418. 1994.
Article2). Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, Aebi M. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation; A 4-6 followup study. Spine. 12:1655–1661. 1993.3). Bradford DS. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis.Spine. 4:423–429. 1979.4). Bosworth DM, Fielding JW, Demarest L, Bonaquist M. Technique for achievement and maintenance of reduction for severe spondylolisthesis using spinous process traction wiring on external fixation of pelvis. Spine. 10:376–382. 1985.5). Curcin A, Edwards CC. Reduction and fusion of spondyloptosis; Longterm followup. Presented the Scoliosis Research Society, 29th Annual Meeting. Portland, Oregon. 1994.6). Dandy DJ, Shannon MJ. Lumbosacral subluxation.(Group 1 spondylolisthesis). J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 53:578–595. 1971.7). Dewald RL, Faut MM, Taddonio RF, Neuwirth MG. Severe lumbosacral spondylolisthesis in adolescents and children. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 63:619–626. 1981.
Article8). Dick WT, Schnebel B. Severe spondylolisthesis; Reduction and internal fixation. Clin Orthop. 232:70–79. 1988.9). Dubousset J. Treatment of spondylolysis in children and adolescents. Clin Orthop. 337:77–85. 1997.10). Edwards CC. Reduction of spondylolisthesis; Biomechanics and fixation. Orthop Trans. 10:543. 1986.11). Edwards CC. Prospective evaluation of a new method of complete reduction of L5-S1 spondylolisthesis uuing corrective forces alone. Orthop Trans. 14:549. 1990.12). Freeman BL, Donati NL. Spinal arthrodesis for severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents; A longterm followup study. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 71:594–598. 1989.
Article13). Harris IE, Weinstein SL. Longterm followup of patients with grade-III and IV spondylolisthesis; Treatment with and without posterior fusion. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 48:619–641. 1966.
Article14). Hu SS, Bradford DS, Transfeldt EE, Cohen M. Reduction of high-grade spondylolisthesis using Edwards instrumentation. Spine. 21:367–371. 1996.
Article15). Jenkins J. Spondylosisthesis. Br J Surg. 24:80–85. 1936.16). Johnson JR, Kirwan EO. The longterm results of fusion in situ for severe spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 65:43–46. 1983.
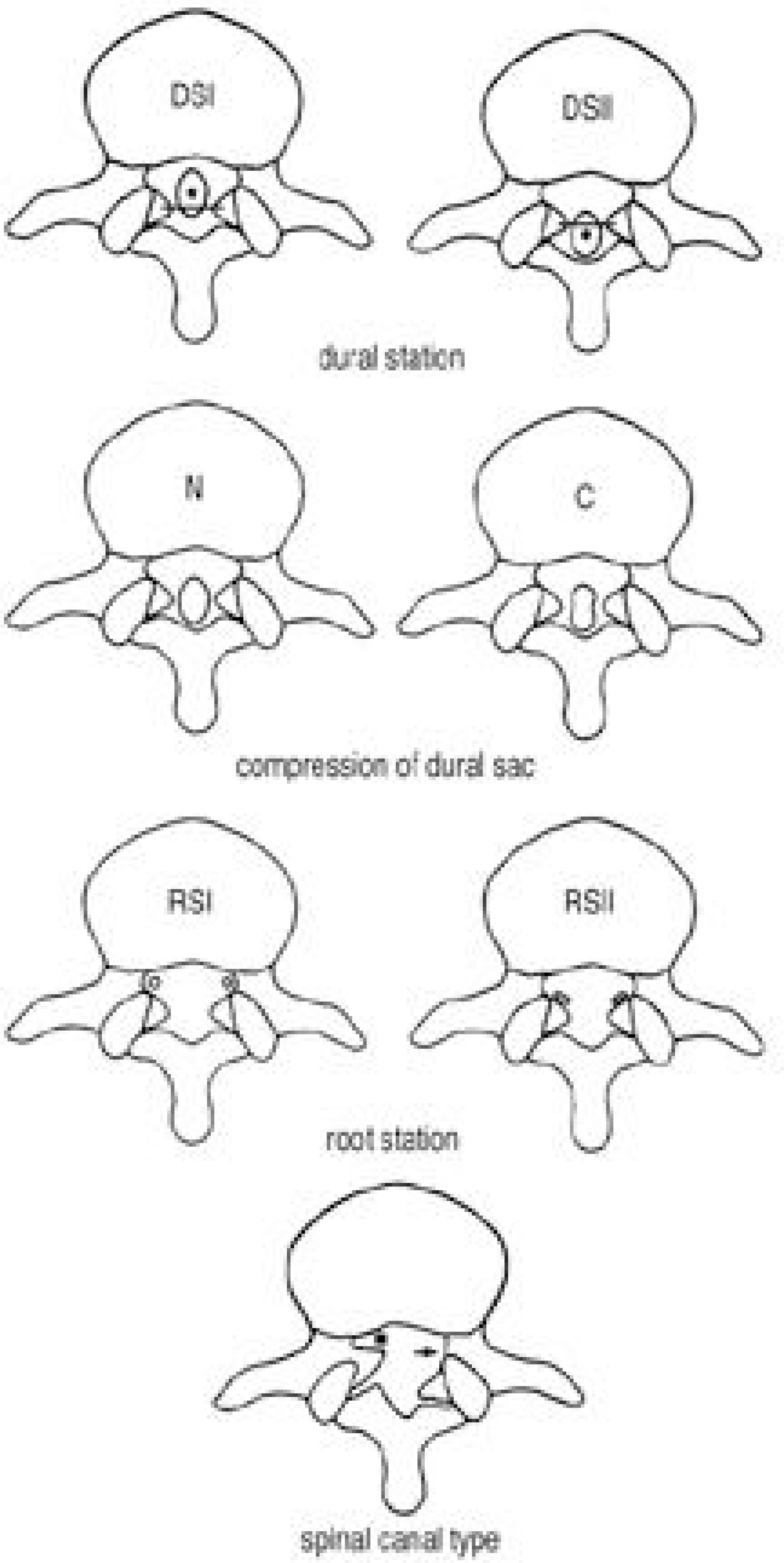
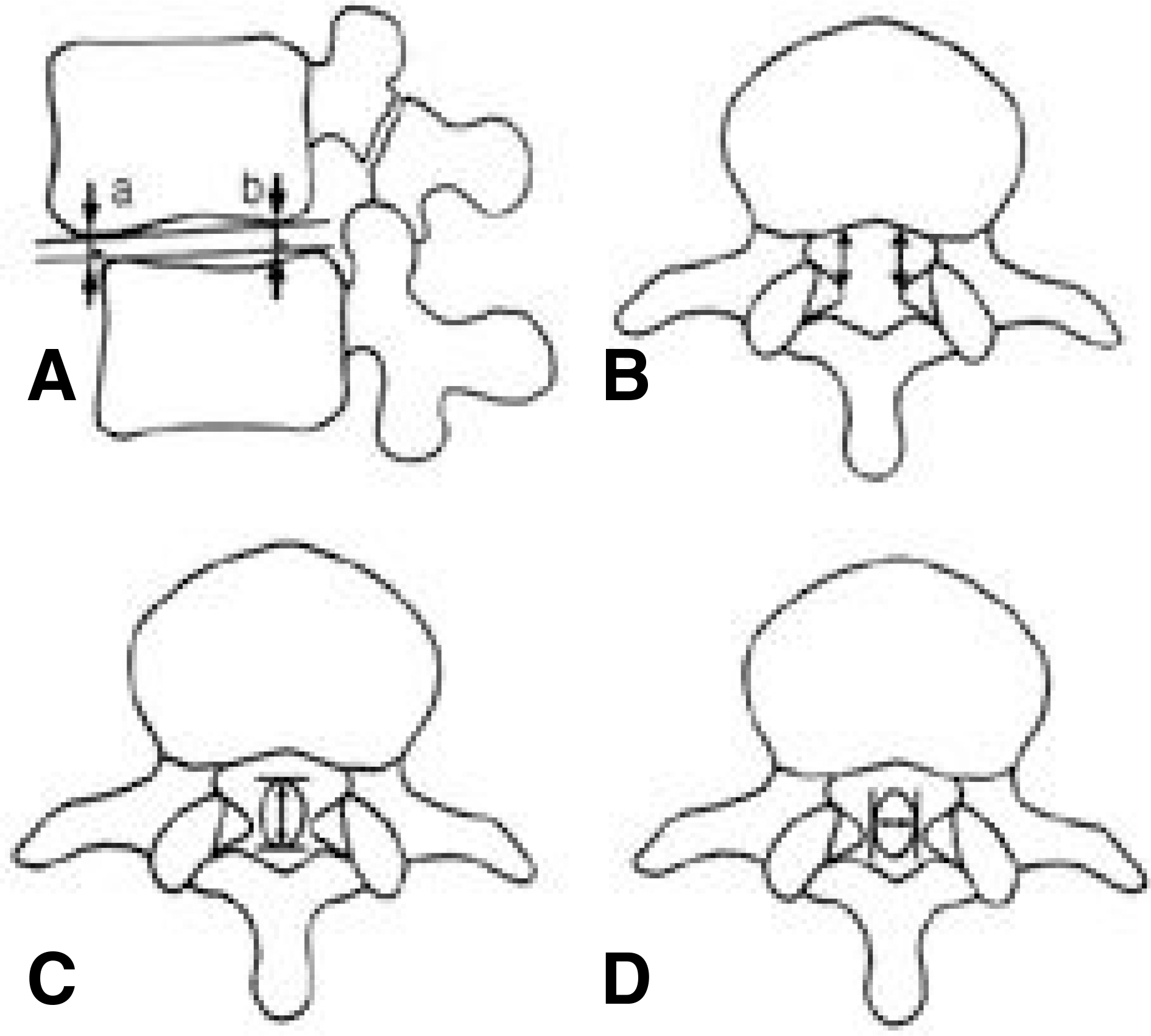
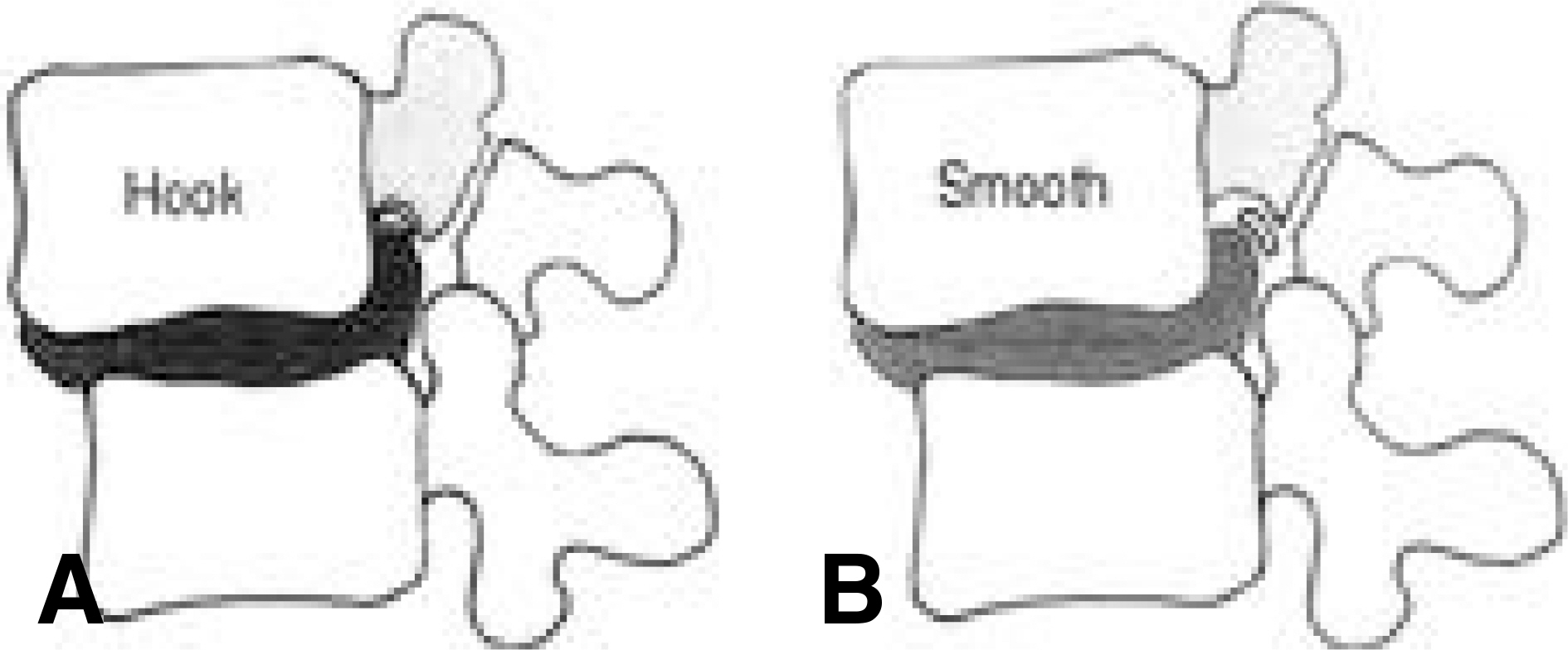
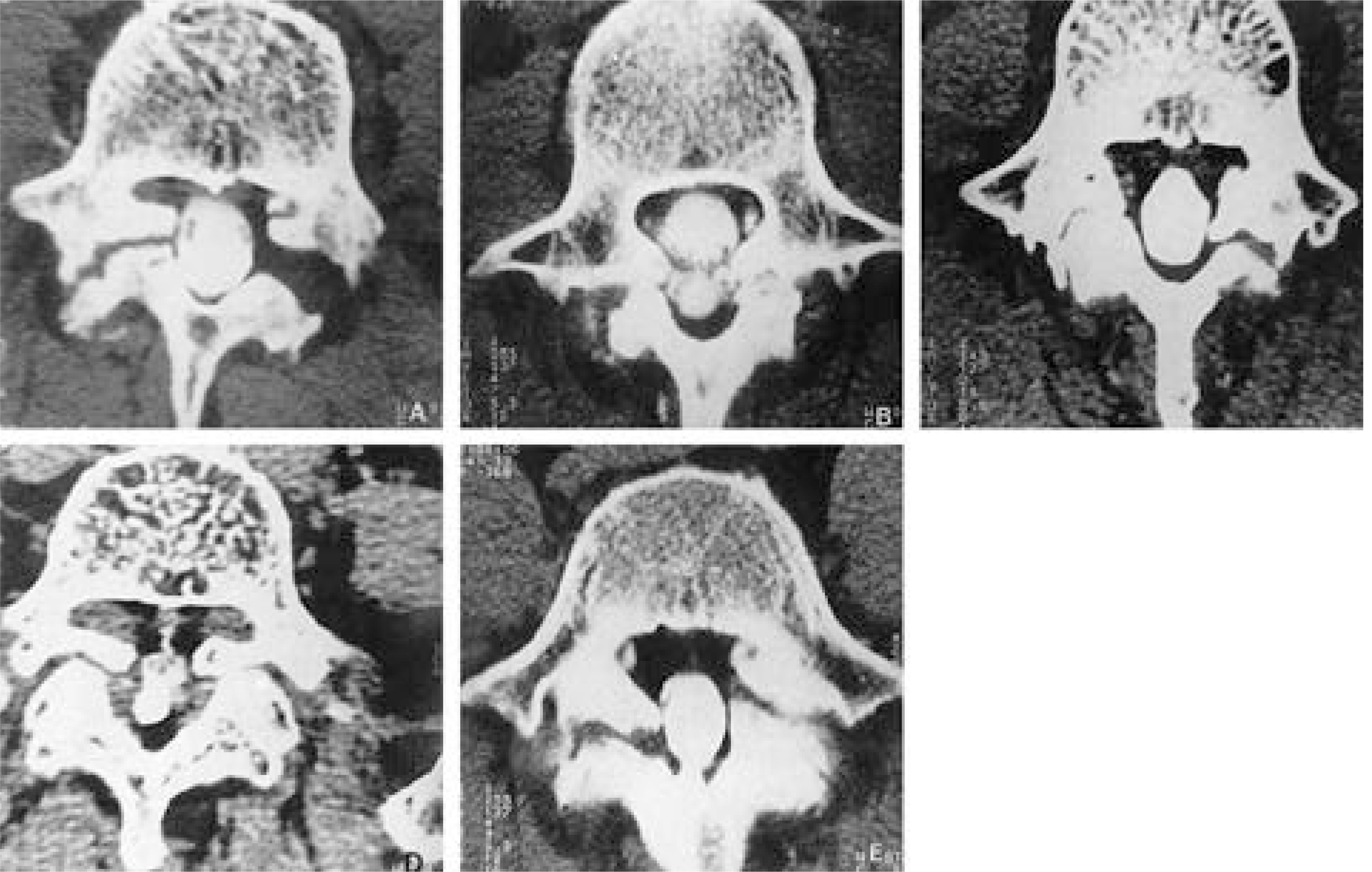
Article17). Kim KW, Ha KY, Kim YS, Kwon SY, Kim HT, Woo YK. Classification of adult isthmic spondylolisthesis; Based on the morphologic changes of spinal canal and neural con -tents by myelography and CT scan. J of Korean Spine Surg. 4:291–299.18). Maurice HD, Morley TR. The surgical reduction of spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop. 203:18–32. 1986.19). Meyerding HW. Spondylolisthesis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 54:371–377. 1932.20). Molinari RW, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Ungacata F, Riew KD. Complications with surgical treatment if pedi -atric high-grade isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis; A comparison of 3 surgical approaches. Spine. 24:1701–1711. 1999.21). Lonstein JE. Spondylolisthesis in children. Cause, Natural history and management. Spine. 24:2640–2648. 1999.22). O'Brien JP, Mehdian H, Jaffray D. Reduction of severe lumbosacral spondylolisthesis. Clin Orhtop. 300:64–69. 1994.23). Petraco DM, Spivak JM, Cappadona JG, Kummer FG, Neuwirth MG. An anatomic evaluation of L5 nerve stretch in spondylolisthesis reduction. Spine. 21:1133–1138. 1996.
Article24). Pizzutillo PD, Hummer CD. Nonoperative treatment for painful adolescent spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 6:311–316. 1986.
Article25). Riley PM, Gillespie R, Koreska J. Severe spondylolisthesis and spondyloptosis; Results of posterolateral fusion in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 68:856. 1986.26). Schoenecker PL, Cole HO, Herring JA, Capelli AM, Bradford DS. Cauda equina syndrome after in situ arthrodesis for severe spondylolisthesis at the lumbosacral junction. J Bone Joint Surg[Am]. 72:369–377. 1990.
Article27). Seitsalo S, Osterman K, Hyvarinen H, Schlenzka D, Poussa M. Severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. A longterm review of fusion in situ. J Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 72:259–265. 1990.
Article28). Shufflebarger HL. High grade isthmic spondylolisthesis; Monosegmental surgical treatment. Scoliosis Research Society;Annual Meeting, New York, NY. 1998.29). Steffee A, Sitkowski D. Reduction and stabilization of grade IV spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 227:82–89. 1988.
Article30). Wiltse LL, Jackson DW. Treatment of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in children. Clin Orthop. 117:23–29. 1976.
Article31). Wiltse LL, Rothman LG. Spondylolisthesis; Classification, diagnosis and natural history. Semin Spine Surg. 1:78–94. 1989.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Reduction in Surgical Treatment of Low Grade Spondylolisthesis
- The Change of Segmental Sagittal angle in Low - grade spondylolisthesis after Pedicular Screw Fixation with or without PLIF - PLIF + PLF versus PLF groups -
- Redisplacement after Operative Reduction of Spondylolisthesis: Comparison between Pedicle screw system and Luque ring system
- Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Posterior Interbody Fusion for High-Grade Spondylolisthesis
- Radiological Characteristics of Low-Grade Lytic Spondylolisthesis: Similarity to Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis