J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2016 Jun;23(2):93-99. 10.4184/jkss.2016.23.2.93.
Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes of Posterior Interbody Fusion for High-Grade Spondylolisthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. bonjourksk@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2328002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2016.23.2.93
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the clinical and radiological outcomes of posterior interbody fusion using pedicle screw fixation after posterior decompression for high-grade spondylolisthesis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: The surgical treatment of high-grade spondylolisthesis has been controversial. However, few reports on the results of reduction and posterior interbody fusion after posterior decompression have been published.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
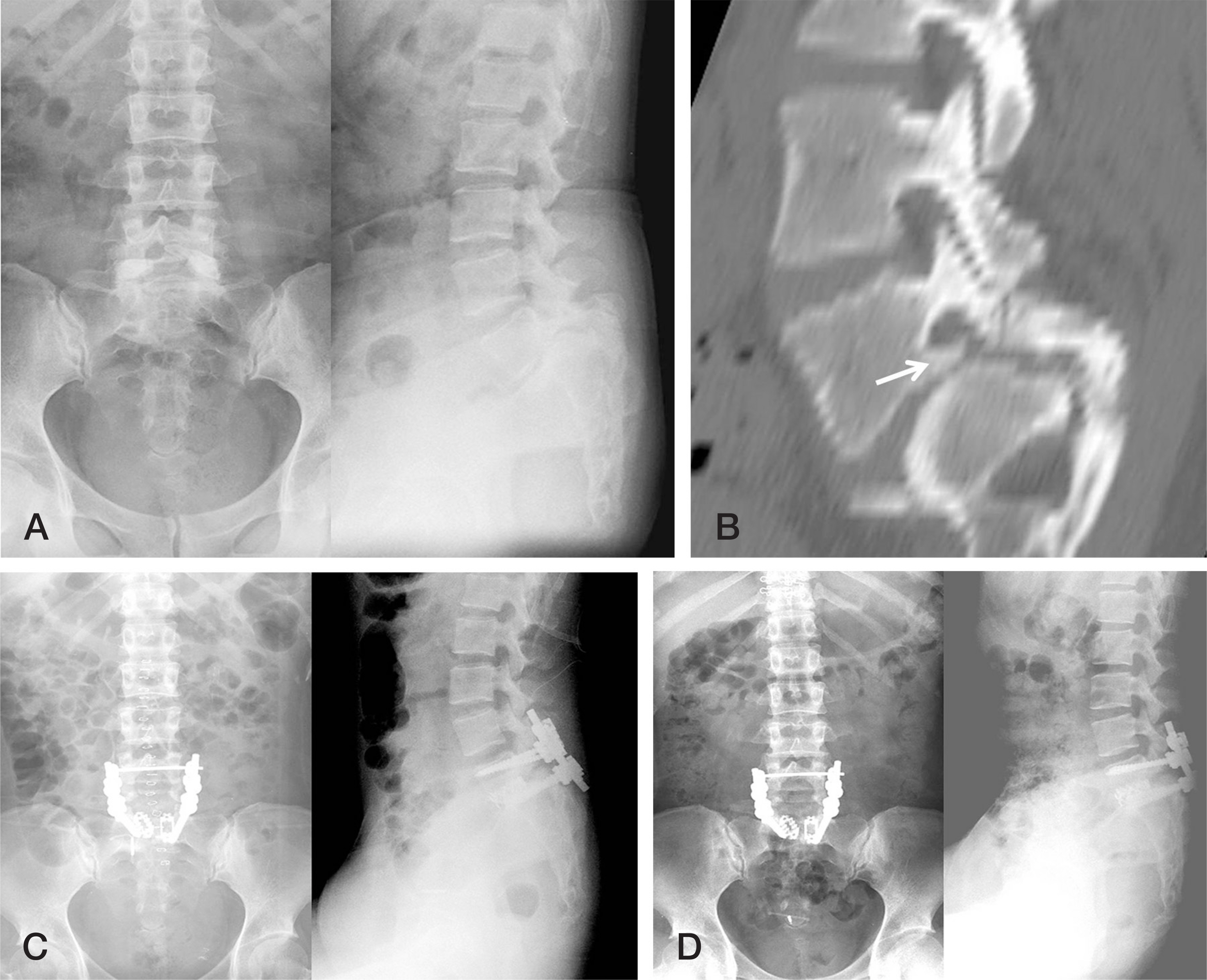
Thirteen patients with L5-S1 high-grade spondylolisthesis (Meyerding grade III, IV) who underwent reduction and posterior interbody fusion were analyzed with at least 2 years of follow-up. The mean age of the patients (male 2, female 11) was 51 years. Classified by the type of spondylolisthesis, 10 cases were isthmic, 2 cases dysplastic, and 1 case degenerative. A visual analogue scale (VAS), the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) score, bone union, anterior slippage, and slip angle were used in comparing clinical and radiographic outcomes.
RESULTS
All cases showed improvement of preoperative symptoms. The VAS and ODI score improved from a mean of 8.9 points and 36.2 points preoperatively to 2.1 points and 10.2 points, respectively, at last follow-up. The degree of anterior slippage measured by Taillard's method was improved from a mean of 57.7% before surgery to mean of 14.6% at last follow-up. The slip angle also changed from a mean of 2.4° kyphosis before surgery to a mean of 7.6°C lordosis at last follow-up. There were two complications: infection and new radiating pain.
CONCLUSIONS
Reduction and posterior interbody fusion using pedicle screw fixation after posterior decompression was a useful surgical method for high-grade spondylolisthesis that corrected lumbosacral kyphosis, filled the structural space of the anterior column, and acheived fusion of interbody movement.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jeong SH, Kim HS, Kim SW. Mini-open PLIF for Moderate to High Grade Spondylolisthesis: Technique to Achieve Spontaneous Reduction. Korean J Spine. 2015; 12:251–5.
Article2. Murray MR, Skovrlj B, Qureshi SA. Surgical Treatment of Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. Clin Spine Surg. 2016; 29:1–5.
Article3. Garet M, Reiman MP, Mathers J, et al. Nonoperative treatment in lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Sports Health. 2013; 5:225–32.4. Huang KF, Chen TY. Clinical results of a single central interbody fusion cage and transpedicle screws fixation for recurrent herniated lumbar disc and low-grade spondylo-listhesis. Chang Gung Med J. 2003; 26:170–7.5. Sonntag VK. Treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis: still controversial. World Neurosurg. 2010; 73:469–70.
Article6. Okuyama K, Kido T, Unoki E, et al. PLIF with a titanium cage and excised facet joint bone for degenerative spon-dylolisthesis in augmentation with a pedicle screw. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007; 20:53–9.7. Ye YP, Chen D, Xu H. The comparison of instrumented and non-instrumented fusion in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23:1918–26.
Article8. Omidi-Kashani F, Hasankhani EG, Rahimi MD, et al. Comparison of functional outcomes following surgical decompression and posterolateral instrumented fusion in single level low grade lumbar degenerative versus isthmic spondy-lolisthesis. Clin Orthop Surg. 2014; 6:185–9.
Article9. Wang SJ, Han YC, Liu XM, et al. Fusion techniques for adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014; 134:777–84.
Article10. Harris EB, Sayadipour A, Massey P, et al. Mini-open versus open decompression and fusion for lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis with stenosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011; 40:E257–61.11. Lamberg T, Remes V, Helenius I, et al. Uninstrumented in situ fusion for high-grade childhood and adolescent isthmic spondylolisthesis: long-term outcome. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007; 89:512–8.12. Remes V, Lamberg T, Tervahartiala P, et al. Long-term outcome after posterolateral, anterior and circumferential fusion for high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents: magnetic resonance imaging findings after average of 17-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:2491–9.13. Burkus JK, Foley K, Haid RW, et al. Surgical Interbody Research Group–radiographic assessment of interbody fusion devices: fusion criteria for anterior lumbar interbody surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2001; 10:E11.
Article14. Eismont FJ, Norton RP, Hirsch BP. Surgical management of lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22:203–13.
Article15. Yong-Ping Ye, Hao Xu, Dan Chen. Comparison between posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion with transpedicular screw fixation for isthmic spon-dylolithesis: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133:1649–55.16. Shim JH, Kim WS, Kim JH, et al. Comparison of instrumented posterolateral fusion versus percutaneous pedicle screw fixation combined with anterior lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients with L5-S1 isthmic spondylolisthesis and foraminal stenosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 15:311–9.
Article17. Hu SS, Bradford DS, Transfeldt EE, et al. Reduction of high-grade spondylolisthesis using Edwards instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:367–71.
Article18. Boos N, Marchesi D, Zuber K, et al. Treatment of severe spondylolisthesis by reduction and pedicular fixation. A 4–6-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:1655–61.19. Molinari RW, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Complications in the surgical treatment of pediatric high-grade, isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis. A comparison of three surgical approaches. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1701–11.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Change of Segmental Sagittal angle in Low - grade spondylolisthesis after Pedicular Screw Fixation with or without PLIF - PLIF + PLF versus PLF groups -
- Anterior Interbody Fusion for the Spondylolisthesis
- Posterior Fixation and Interbody for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
- Comparison between Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation and Posterolateral Fusion with Pedicle Screw Fixation in Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis in Adults
- A Comparison of Posterolateral and Posterior Interbody Fusion in the Surgical Treatment of Lumbar Spondylolisthesis