J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Feb;31(2):301-309. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.301.
Falls in Korean Polio Survivors: Incidence, Consequences, and Risk Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. drlim1@snu.ac.kr
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Red Cross College of Nursing, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Ewha Womans University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Rehabilitation Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2360057
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.2.301
Abstract
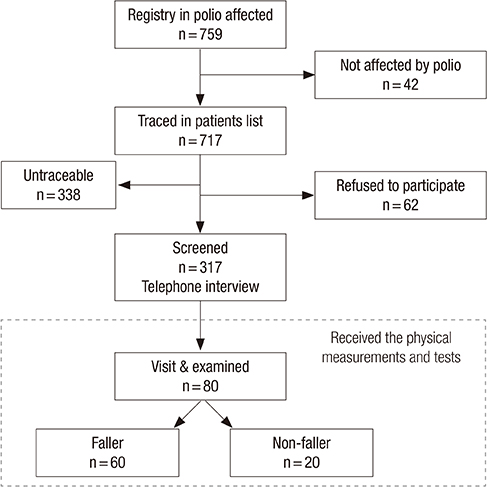
- Falls and fall-related injuries are important issue among polio survivors. The purpose of this study was to determine the incidence of, and consequences and factors associated with falls among Korean polio survivors. A total of 317 polio survivors participated in this study. All participants completed a questionnaire including fall history, symptoms related to post-polio syndrome and other information through a telephone interview. Among them, 80 participants visited our clinic for additional physical measurements and tests. Of the 317 respondents, 68.5% reported at least one fall in the past year. Of the fallers, 42.5% experienced at least one fall during one month. Most falls occurred during ambulation (76.6%), outside (75.2%) and by slipping down (29.7%). Of fallers, 45% reported any injuries caused by falls, and 23.3% reported fractures specifically. Female sex, old age, low bone mineral density, the presence of symptoms related to post-polio syndrome (PPS), poor balance confidence, short physical performance battery and weak muscle strength of knee extensor were not significantly associated with falls. Only leg-length discrepancy using spine-malleolar distance (SMD) was a significant factor associated with falls among Korean polio survivors. Our findings suggest that malalignment between the paralytic and non-paralytic limb length should be addressed in polio survivors for preventing falls.
MeSH Terms
-
Accidental Falls/*statistics & numerical data
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Asian Continental Ancestry Group
Female
Fractures, Bone/etiology
Humans
Incidence
Interviews as Topic
Logistic Models
Male
Middle Aged
Postpoliomyelitis Syndrome/*pathology
Postural Balance
Republic of Korea
Risk Factors
Surveys and Questionnaires
Telephone
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heinze C, Halfens RJ, Dassen T. Falls in German in-patients and residents over 65 years of age. J Clin Nurs. 2007; 16:495–501.2. Nelson RC, Amin MA. Falls in the elderly. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1990; 8:309–324.3. Rubenstein LZ. Falls in older people: epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention. Age Ageing. 2006; 35:Suppl 2. ii37–41.4. Aizen E, Shugaev I, Lenger R. Risk factors and characteristics of falls during inpatient rehabilitation of elderly patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2007; 44:1–12.5. Saskatoon Falls Prevention Consortium (CA). Falls risk screening: multifactor questionnaire. Saskatoon: Saskatoon Falls Prevention Consortium;2005.6. Choi EJ, Kim SA, Kim NR, Rhee JA, Yun YW, Shin MH. Risk factors for falls in older Korean adults: the 2011 Community Health Survey. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1482–1487.7. World Health Organization. WHO statistical information system. accessed on 24 August 2015. Available at http://www.who.int.8. Ministry of Health & Welfare. The Korean disabled condition investigation. accessed on 24 August 2015. Available at http://download.mw.go.kr/front_new/modules/download.jsp?BOARD_ID=1003&CONT_SEQ=270741&FILE_SEQ=94258.9. Lexell J. Postpoliomyelitis syndrome. In : Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD, editors. Essentials of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders;2014. p. 775–781.10. Bang H, Suh JH, Lee SY, Kim K, Yang EJ, Jung SH, Jang SN, Han SJ, Kim WH, Oh MG, et al. Post-polio syndrome and risk factors in Korean polio survivors: a baseline survey by telephone interview. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014; 38:637–647.11. Ivanyi B, Nollet F, Redekop WK, de Haan R, Wohlgemuht M, van Wijngaarden JK, de Visser M. Late onset polio sequelae: disabilities and handicaps in a population-based cohort of the 1956 poliomyelitis outbreak in the Netherlands. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 80:687–690.12. Brogårdh C, Lexell J. Falls, fear of falling, self-reported impairments, and walking limitations in persons with late effects of polio. PM R. 2014; 6:900–907.13. Bickerstaffe A, Beelen A, Nollet F. Circumstances and consequences of falls in polio survivors. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42:908–915.14. Mohammad AF, Khan KA, Galvin L, Hardiman O, O’Connell PG. High incidence of osteoporosis and fractures in an aging post-polio population. Eur Neurol. 2009; 62:369–374.15. Winberg C, Brogardh C, Flansbjer UB, Carlsson G, Rimmer J, Lexell J. Physical activity and the association with self-reported impairments, walking limitations, fear of falling and incidence of falls in persons with late effects of polio. J Aging Phys Act. 2015; 23:425–432.16. Ragonese P, Fierro B, Salemi G, Randisi G, Buffa D, D’Amelio M, Aloisio A, Savettieri G. Prevalence and risk factors of post-polio syndrome in a cohort of polio survivors. J Neurol Sci. 2005; 236:31–35.17. Jang SN, Cho SI, Oh SW, Lee ES, Baik HW. Time since falling and fear of falling among community-dwelling elderly. Int Psychogeriatr. 2007; 19:1072–1083.18. Gilhus NE, Barnes MP, Brainin M. European handbook of neurological management. 2nd ed. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell;2011.19. Powell LE, Myers AM. The Activities-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995; 50A:M28–34.20. Myers AM, Fletcher PC, Myers AH, Sherk W. Discriminative and evaluative properties of the activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1998; 53:M287–94.21. Silver JK, Aiello DD. Polio survivors: falls and subsequent injuries. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:567–570.22. Hill KD, Stinson AT. A pilot study of falls, fear of falling, activity levels and fall prevention actions in older people with polio. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2004; 16:126–131.23. Lim JY, Park WB, Oh MK, Kang EK, Paik NJ. Falls in a proportional region population in Korean elderly: incidence, consequences, and risk factors. J Korean Geriatr Soc. 2010; 14:8–17.24. Chang KH, Lai CH, Chen SC, Tang IN, Hsiao WT, Liou TH, Lee CM. Femoral neck bone mineral density in ambulatory men with poliomyelitis. Osteoporos Int. 2011; 22:195–200.25. Emara KM, Khames A. Functional outcome after lengthening with and without deformity correction in polio patients. Int Orthop. 2008; 32:403–407.26. Blake RL, Ferguson H. Limb length discrepancies. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1992; 82:33–38.27. Gurney B. Leg length discrepancy. Gait Posture. 2002; 15:195–206.28. Hennessey WJ. Lower limb orthotic devices. In : Braddom RL, Chan L, Harrast MA, editors. Physical medicine & rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier;2011. p. 337.29. Esquenazi A. Lower extremity orthotics, shoes, and gait aids. In : Frontera WR, DeLisa JA, editors. Delisa's physical medicine and rehabilitation. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health;2010. p. 2069–2070.30. Lajoie Y, Gallagher SP. Predicting falls within the elderly community: comparison of postural sway, reaction time, the Berg balance scale and the Activities-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) scale for comparing fallers and non-fallers. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2004; 38:11–26.31. Lord SR, Allen GM, Williams P, Gandevia SC. Risk of falling: predictors based on reduced strength in persons previously affected by polio. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 83:757–763.32. Gillespie LD, Robertson MC, Gillespie WJ, Sherrington C, Gates S, Clemson LM, Lamb SE. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 9:CD007146.33. Weerdesteyn V, de Niet M, van Duijnhoven HJ, Geurts AC. Falls in individuals with stroke. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2008; 45:1195–1213.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Falls in a Proportional Region Population in Korean Elderly: Incidence, Consequences, and Risk Factors
- Post-Polio Syndrome and Risk Factors in Korean Polio Survivors: A Baseline Survey by Telephone Interview
- Obesity and Pulmonary Function in Polio Survivors
- Incidence of Osteoporosis and Falls and Predictors of Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Women
- Swallowing Difficulties in Polio Survivors