J Korean Med Sci.
2016 Jan;31(1):55-60. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.1.55.
Erythropoiesis-stimulating Agents and Anemia in Patients with Non-dialytic Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. uptoyousm@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2359992
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.1.55
Abstract
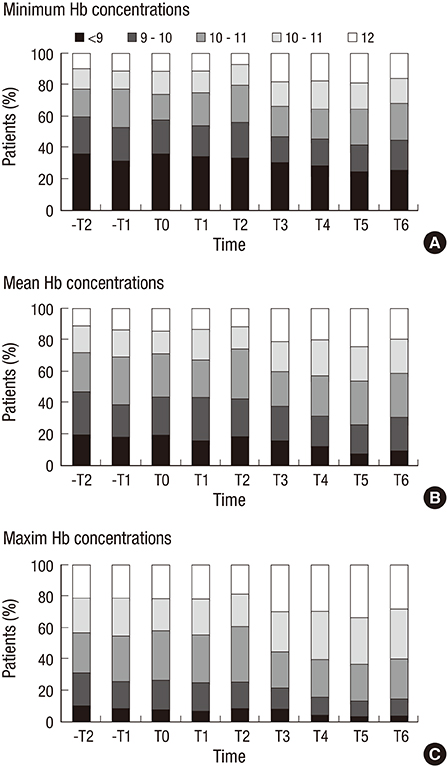
- Anemia is common in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD). Though erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) have been strongly endorsed in guidelines, it is of particular financial interest. Recently, the reimbursement of ESAs in non-dialytic patients was started by the Korean National Health Insurance System. Thus, we investigated the impact of the reimbursement of ESAs on the anemia care in non-dialytic CKD patients. Medical records of patients with advanced CKD (estimated GFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) were reviewed. Use of ESAs, blood transfusion, and hemoglobin concentrations were analyzed from one year prior to reimbursement to three years following. We used multivariable modified Poisson regression to estimate the utilization prevalence ratio (PRs). A total of 1,791 medical records were analyzed. The proportion of patients receiving ESAs increased from 14.8% before reimbursement to a peak 33.6% in 1 yr after reimbursement; thereafter, ESA use decreased to 22.4% in 3 yr after reimbursement (compared with baseline; PR, 2.19 [95% CI, 1.40-3.42]). In patients with Hb <10 g/dL, the proportion of receiving ESAs increased from 32.1% before reimbursement to 66.7% in 3 yr after reimbursement (compared with baseline; PR, 2.04 [95% CI, 1.25-3.32]). Mean hemoglobin concentrations were 10.06±1.54 g/dL before reimbursement and increased to 10.78±1.51 g/dL in 3 yr after the reimbursement change (P=0.001). However, the requirement of blood transfusion was not changed over time. With the reimbursement of ESAs, the advanced CKD patients were more likely to be treated with ESAs, and the hemoglobin concentrations increased.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Anemia/complications/*drug therapy/epidemiology
Blood Transfusion
Female
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Hematinics/*therapeutic use
Hematocrit
Hemoglobins/analysis
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
National Health Programs
Poisson Distribution
Prevalence
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic/complications/*drug therapy/epidemiology
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Retrospective Studies
Young Adult
Hematinics
Hemoglobins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eschbach JW, Adamson JW. Anemia of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Kidney Int. 1985; 28:1–5.2. Lim CS. Medical therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Korean Med Assoc. 2012; 55:381–389.3. Oak CY, Kim NH. Anemia and nutrition in end stage renal disease patient. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:592–599.4. Hsu CY, McCulloch CE, Curhan GC. Epidemiology of anemia associated with chronic renal insufficiency among adults in the United States: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:504–510.5. Eschbach JW, Abdulhadi MH, Browne JK, Delano BG, Downing MR, Egrie JC, Evans RW, Friedman EA, Graber SE, Haley NR, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in anemic patients with end-stage renal disease. Results of a phase III multicenter clinical trial. Ann Intern Med. 1989; 111:992–1000.6. NKF-DOQI clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of anemia of chronic renal failure. National Kidney Foundation-Dialysis Outcomes Quality Initiative. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997; 30:Suppl 3. S192–S240.7. Horl WH, Macdougall IC, Rossert J, Rutkowski B, Wauters JP, Valderrabano F. Predialysis survey on anemia management: Patient referral. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 41:49–61.8. Valderrabano F, Horl WH, Macdougall IC, Rossert J, Rutkowski B, Wauters JP. PRE-dialysis survey on anaemia management. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003; 18:89–100.9. Pisoni RL, Bragg-Gresham JL, Young EW, Akizawa T, Asano Y, Locatelli F, Bommer J, Cruz JM, Kerr PG, Mendelssohn DC, et al. Anemia management and outcomes from 12 countries in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Am J Kidney Dis. 2004; 44:94–111.10. Drueke TB, Locatelli F, Clyne N, Eckardt KU, Macdougall IC, Tsakiris D, Burger HU, Scherhag A. Normalization of hemoglobin level in patients with chronic kidney disease and anemia. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2071–2084.11. Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, Barnhart H, Sapp S, Wolfson M, Reddan D. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2085–2098.12. Pfeffer MA, Burdmann EA, Chen CY, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Eckardt KU, Feyzi JM, Ivanovich P, Kewalramani R, Levey AS, et al. A trial of darbepoetin alfa in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2019–2032.13. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline and Clinical Practice Recommendations for anemia in chronic kidney disease: 2007 update of hemoglobin target. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 50:471–530.14. Jung MY, Hwang SY, Hong YA, Oh SY, Seo JH, Lee YM, Park SW, Kim JS, Wang JK, Kim JY, et al. Optimal hemoglobin level for anemia treatment in a cohort of hemodialysis patients. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2015; 34:20–27.15. Scott SD. Dose conversion from recombinant human erythropoietin to darbepoetin alfa: recommendations from clinical studies. Pharmacotherapy. 2002; 22:160S–165S.16. ESRD Registry Committee. Korean Society of Nephrology. Current Renal Replacement Therapy in Korea - Insan Memorial Dialysis Registry, 2013. In : Proceedings of the 34th Annual Spring Meeting of the Korean Society of Nephrology; 2014. 1:p. 134–154.17. Ibrahim HN, Ishani A, Foley RN, Guo H, Liu J, Collins AJ. Temporal trends in red blood transfusion among US dialysis patients, 1992-2005. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008; 52:1115–1121.18. Ibrahim HN, Ishani A, Guo H, Gilbertson DT. Blood transfusion use in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients aged 65 years and older. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009; 24:3138–3143.19. Winkelmayer WC, Mitani AA, Goldstein BA, Brookhart MA, Chertow GM. Trends in anemia care in older patients approaching end-stage renal disease in the United States (1995-2010). JAMA Intern Med. 2014; 174:699–707.20. Gill KS, Muntner P, Lafayette RA, Petersen J, Fink JC, Gilbertson DT, Bradbury BD. Red blood cell transfusion use in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013; 28:1504–1515.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New Oral Agent for Treatment of Anemia in Patient with Chronic Kidney Disease: Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor
- The Prevalence and Management of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: Result from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD)
- Treatment of renal anemia: Erythropoiesis stimulating agents and beyond
- Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of darbepoetin alfa once every 4 weeks versus continuous erythropoietin receptor activator once every 4 weeks for anemia correction in patients with chronic kidney disease not on dialysis
- Anemia and nutrition in end stage renal disease patient