J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Dec;30(12):1723-1732. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.12.1723.
Cost-Utility Analysis of Screening Strategies for Diabetic Retinopathy in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Health Informatics and Management, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. gilwon67@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2359955
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.12.1723
Abstract
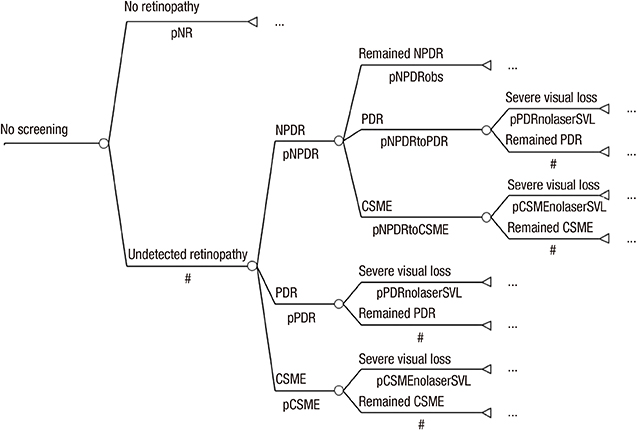
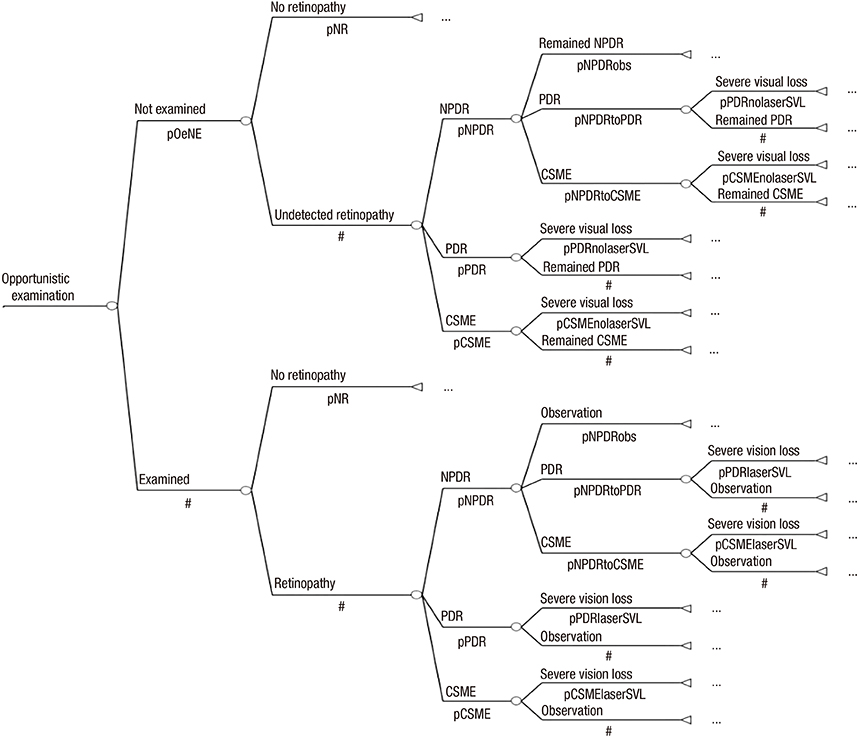
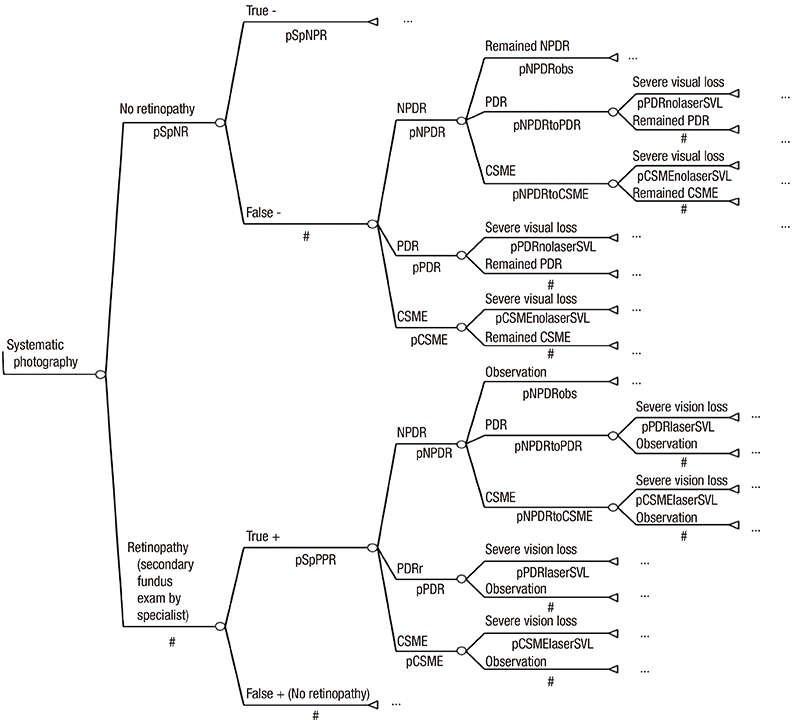
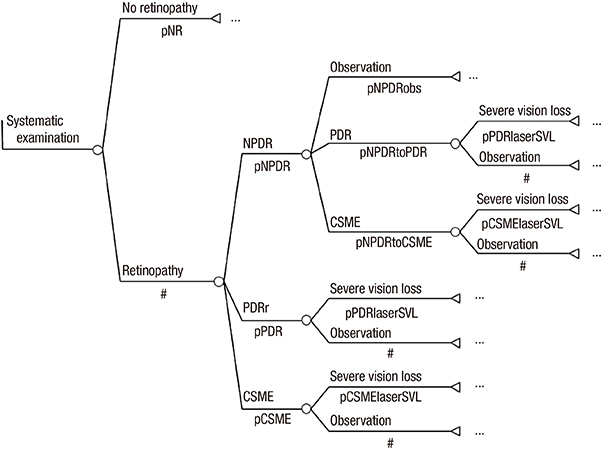
- This study involved a cost-utility analysis of early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy depending on the screening strategy used. The four screening strategies evaluated were no screening, opportunistic examination, systematic fundus photography, and systematic examination by an ophthalmologists. Each strategy was evaluated in 10,000 adults aged 40 yr with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus (hypothetical cohort). The cost of each strategy was estimated in the perspective of both payer and health care system. The utility was estimated using quality-adjusted life years (QALY). Incremental Cost Effectiveness Ratio (ICER) for the different screening strategies was analyzed. After exclusion of the weakly dominating opportunistic strategy, the ICER of systematic photography was 57,716,867 and that of systematic examination by ophthalmologists was 419,989,046 from the perspective of the healthcare system. According to the results, the systematic strategy is preferable to the opportunistic strategy from the perspective of both a payer and a healthcare system. Although systematic examination by ophthalmologists may have higher utility than systematic photography, it is associated with higher cost. The systematic photography is the best strategy in terms of cost-utility. However systematic examination by ophthalmologists can also be a suitable policy alternative, if the incremental cost is socially acceptable.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
*Cost-Benefit Analysis
Diabetic Retinopathy/*diagnosis/economics/*therapy
Diagnostic Techniques, Ophthalmological/economics
Early Diagnosis
Female
Fluorescein Angiography/economics
Health Care Costs
Humans
Male
Markov Chains
Mass Screening/*economics/methods/statistics & numerical data
Middle Aged
Models, Economic
National Health Programs/economics
Quality-Adjusted Life Years
Republic of Korea
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med. 1997; 14:S1–S85.2. Lim HT, Choi KS. Factors associated with screening for diabetic retinopathy in diabetic patients aged > or = 40 years using the KNHANES IV. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:516–521.3. Beckles GL, Zhu J, Moonesinghe R. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Diabetes - United States, 2004 and 2008. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2011; 60:s90–s93.4. Yudkin JS, Boucher BJ, Schopflin KE, Harris BT, Claff HR, Whyte NJ, Taylor B, Mellins DH, Wootliff AB, Safir JG, et al. The quality of diabetic care in a London health district. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1980; 34:277–280.5. Lee DW, Park CY, Song SJ. Study on survey of knowledge and awareness level of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes patients: results from Seoul metro-city diabetes prevention program survey. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1296–1301.6. Jeong H, Kwon H, Han J, Kim Y, Lee A. Cost-effectiveness analysis of type 2 DM screening program of national health insurance corporation. Korean J Health Econ Policy. 2008; 14:29–50.7. Park SK, Park M-K, Suk JH, Kim MK, Kim YK, Kim IJ, Kang YH, Lee KJ, Lee HS, Lee CW. Cause-of-death trends for diabetes mellitus over 10 years. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:65–72.8. Jin JH, Lee SJ, Lee HS, Kim SD. Prognostic factors of visual acuity in diabetes mellitus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:755–762.9. Drummond MF. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford: Oxford University Press;2005.10. Shin KH, Chi MJ. Fundus examination rate in diabetics and the public health factors associated with fundus examination rate. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:1319–1325.11. Kim HK, Oh TS, Lee SM, Lee JB. The initial fundus examination and severity of diabetic retinopathy at a primary eye clinic. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:982–988.12. Maberley D, Walker H, Koushik A, Cruess A. Screening for diabetic retinopathy in James Bay, Ontario: a cost-effectiveness analysis. CMAJ. 2003; 168:160–164.13. Aoki N, Dunn K, Fukui T, Beck JR, Schull WJ, Li HK. Cost-effectiveness analysis of telemedicine to evaluate diabetic retinopathy in a prison population. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1095–1101.14. Younis N, Broadbent DM, Vora JP, Harding SP. Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study. Incidence of sight-threatening retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes in the Liverpool Diabetic Eye Study: a cohort study. Lancet. 2003; 361:195–200.15. Blankenship GW. Fifteen-year argon laser and xenon photocoagulation results of Bascom Palmer Eye Institute's patients participating in the diabetic retinopathy study. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:125–128.16. Facey K, Cummins E, Macpherson K, Morris A, Reay L, Slattery J. Health technology assessment report 1: Organisations of services for diabetic retinopathy screening. Glasgow: Health Technology Board for Scotland;2002.17. Heintz E, Wiréhn AB, Peebo BB, Rosenqvist U, Levin LA. QALY weights for diabetic retinopathy--a comparison of health state valuations with HUI-3, EQ-5D, EQ-VAS, and TTO. Value Health. 2012; 15:475–484.18. Brown MM, Brown GC, Sharma S, Shah G. Utility values and diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999; 128:324–330.19. Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, Ferris FL, Klein R. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes care. 2004; 27:s84–s87.20. Rema M, Premkumar S, Anitha B, Deepa R, Pradeepa R, Mohan V. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in urban India: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) eye study, I. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46:2328–2333.21. Usher D, Dumskyj M, Himaga M, Williamson TH, Nussey S, Boyce J. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy in digital retinal images: a tool for diabetic retinopathy screening. Diabet Med. 2004; 21:84–90.22. James M, Turner DA, Broadbent DM, Vora J, Harding SP. Cost effectiveness analysis of screening for sight threatening diabetic eye disease. BMJ. 2000; 320:1627–1631.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Challenges in Diabetic Retinopathy: Are We Really Doing Better?
- Cost Utility Analysis of National Cancer Screening Program for Gastric Cancer in Korea: A Markov Model Analysis
- The Influences of Arteriosclerosis on the Development and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Factors Associated with Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy in Diabetic Patients Aged > or = 40 Years Using the KNHANES IV
- Cost-Utility Analysis for Colorectal Cancer Screening According to the Initiating Age of National Cancer Screening Program in Korea