J Korean Acad Nurs.
2015 Apr;45(2):159-168. 10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.159.
A Methodological Quality Assessment of South Korean Nursing Research using Structural Equation Modeling in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, College of Health Sciences, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, College of Medicine, Soonchunhyang University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3College of Nursing, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea. parkjh07@cu.ac.kr
- 4The Research Institute of Nursing Science, Catholic University of Daegu, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2359854
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.2.159
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methodological quality of nursing studies using structural equation modeling in Korea.
METHODS
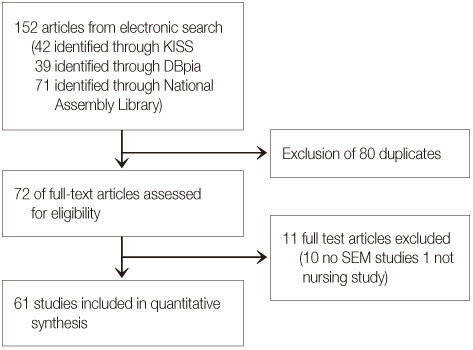
Databases of KISS, DBPIA, and National Assembly Library up to March 2014 were searched using the MeSH terms 'nursing', 'structure', 'model'. A total of 152 studies were screened. After removal of duplicates and non-relevant titles, 61 papers were read in full.
RESULTS
Of the sixty-one articles retrieved, 14 studies were published between 1992 and 2000, 27, between 2001 and 2010, and 20, between 2011 and March 2014. The methodological quality of the review examined varied considerably.
CONCLUSION
The findings of this study suggest that more rigorous research is necessary to address theoretical identification, two indicator rule, distribution of sample, treatment of missing values, mediator effect, discriminant validity, convergent validity, post hoc model modification, equivalent models issues, and alternative models issues should be undergone. Further research with robust consistent methodological study designs from model identification to model respecification is needed to improve the validity of the research.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Martens MP. The use of structural equation modeling in counseling psychology research. Couns Psychol. 2005; 33(3):269–298. DOI: 10.1177/0011000004272260.2. Mueller RO. Structural equation modeling: Back to basics. Struct Equ Modeling. 1997; 4(4):353–369. DOI: 10.1080/10705519709540081.3. Kim J, Hong S, Choo B. Applications of structural equation modeling in management studies: A critical review. Korean Manage Rev. 2007; 36(4):897–923.4. Lee GS, Yom YH. Structural equation modeling on life-world integration in people with severe burns. Asian Nurs Res. 2013; 7(3):112–119. DOI: 10.1016/j.anr.2013.06.003.5. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 3rd ed. New York, NY: Guilford Press;2011.6. Lim NY, Kang HS, Lee SE, Suh YO, Kwon YE. The trend of Korean nursing research with the LISREL. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2001; 31(2):221–231.7. Weston R. A brief guide to structural equation modeling. Couns Psychol. 2006; 34(5):719–751. DOI: 10.1177/0011000006286345.8. Baumgartner H, Homburg C. Applications of structural equation modeling in marketing and consumer research: A review. Int J Res Mark. 1996; 13(2):139–161. DOI: 10.1016/0167-8116(95)00038-0.9. Boomsma A. Reporting analyses of covariance structures. Struct Equ Modeling. 2009; 7(3):461–483. DOI: 10.1207/S15328007SEM0703_6.10. Breckler SJ. Applications of covariance structure modeling in psychology: Cause for concern? Psychol Bull. 1990; 107(2):260–273.11. Hoyle RH, Panter AT. Writing about structural equation models. In : Hoyle RH, editor. Structural equation modeling: Concepts, issues, and applications. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage;1995. p. 158–176.12. MacCallum RC, Austin JT. Applications of structural equation modeling in psychological research . Annu Rev Psychol. 2000; 51:201–226. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.psych.51.1.201.13. McDonald RP, Ho MH. Principles and practice in reporting structural equation analyses. Psychol Methods. 2002; 7(1):64–82.14. Raykov T, Tomer A, Nesselroade JR. Reporting structural equation modeling results in psychology and aging: Some proposed guidelines. Psychol Aging. 1991; 6(4):499–503.15. Steiger JH. Driving fast in reverse: The relationship between software development, theory, and education in structural equation modeling. J Am Stat Assoc. 2001; 96(453):331–338.16. Cho HD. A study on issues of using structure equation modeling in education study [master's thesis]. Seoul: Korea University;2011.17. Bentler PM, Chou CP. Practical issues in structural modeling. In : Long JS, editor. Common problems/proper solutions: Avoiding error in survey research. Newbury Park, CA: Sage;1988. p. 161–192.18. Moon SB. Basic concepts and applications of structural equation modeling with AMOS 17.0. Seoul: Hakjisa;2009.19. Yu JP. The misunderstanding and prejudice of structural equation models. Seoul: Hannare Publishing Co.;2014.20. Holbert RL, Stephenson MT. Structural equation modeling in the communication sciences, 1995-2000. Hum Commun Res. 2002; 28(4):531–551. DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-2958.2002.tb00822.x.21. Shook CL, Ketchen DJ Jr, Hult GTM, Kacmar KM. An assessment of the use of structural equation modeling in strategic management research. Strategic Manage J. 2004; 25(4):397–404. DOI: 10.1002/smj.385.22. Polit DF, Beck CT, Owen SV. Is the CVI an acceptable indicator of content validity? Appraisal and recommendations. Res Nurs Health. 2007; 30(4):459–467. DOI: 10.1002/nur.20199.23. Kim KMJ, Cha YN, Jang HS, Han HS, Chung JS, Yoon J, et al. NANDA nursing diagnosis, goals and interventions. Seoul: Hyunmoon;2013.24. Chen F, Bollen KA, Paxton P, Curran PJ, Kirby JB. Improper solutions in structural equation models: Causes, consequences and strategies. Sociol Methods Res. 2001; 29(4):468–508. DOI: 10.1177/0049124101029004003.25. Jöeskog KG, Söbom D. LISREL 7: A guide to the program and applications. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: SPSS Inc.;1989.26. Mitchell RJ. Path analysis: Pollination. In : Scheiner SM, Gurevitch J, editors. Design and analysis of ecological experiments. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Chapman and Hall;1993. p. 211–231.27. Arbuckle JL. Full information estimation in the presence of incomplete data. In : Marcoulides GA, Schumacker RE, editors. Advanced structural equation modeling: Issues and techniques. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1996.28. Enders CK, Bandalos DL. The relative performance of full information maximum likelihood estimation for missing data in structural equation models. Struct Equ Modeling. 2001; 8(3):430–457. DOI: 10.1207/S15328007SEM0803_5.29. Schreiber JB. Core reporting practices in structural equation modeling. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2008; 4(2):83–97. DOI: 10.1016/j.sapharm.2007.04.003.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Structural Equation Modeling on Life-world Integration in People with Severe Burns
- A Structural Equation Model on Happiness among Adolescents in South Korea
- Structural Equation Modeling Based on PRECEDE Model for the Quality of Life in the Elderly with Dementia in Rural Area
- Recent Research Trends in Meta-analysis
- Model Setting and Interpretation of Results in Research Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Checklist with Guiding Questions for Reporting