Korean Circ J.
2016 Nov;46(6):851-861. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.6.851.
Comparison of Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure in Children, Adolescents and adults: Differences, Challenges and Short-, Mid- and Long-Term Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Istanbul Medipol University, Medicine Faculty, Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Istanbul, Turkey. turkaysaritas@yahoo.com
- 2Dr. Siyami Ersek Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Center and Research Hospital, Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2355463
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.6.851
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
This study aims to compare the characteristics, effectiveness and results of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect between children, adolescents, and adults.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
In this study, 683 patients who underwent atrial septal defect closure in the last 10 years were divided into three groups: children (age <12), adolescents (age 12 to 16), and adults (age >16) as group 1, group 2 and group 3, respectively.
RESULTS
The average defect size and incidence of complex atrial septal defect were higher in group 3 (p=0.0001 and 0.03 respectively). While the average size of the devic was higher in adults (22.6±6.4 mm vs. 18.5±4.9 mm; p=0.0001), the ratio of the device size/total septum was higher in both children and adolescents (Group 1 and 2). In the child and adolescent groups and patients with only complex atrial septal defect, the use of techniques, other than standard deployment, was similar in all three groups (p=0.86 and 0.41, respectively). The ratio of the residual shunt was similar in all three groups. Major complications were seen in 5 cases (4 cases with migration, and 1 case with dislocation) in group 3 and 1 case (migration) in group 1.
CONCLUSION
Depending on the complexity of the defect and age of the patient, transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect might have certain difficulties and complications. Patients must be evaluated in detail to avoid major complications and possible problems during the procedure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
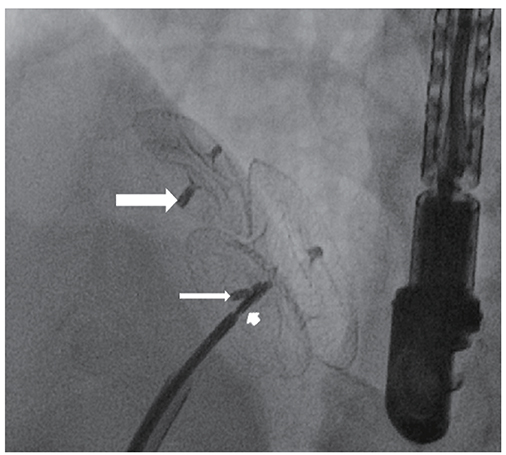
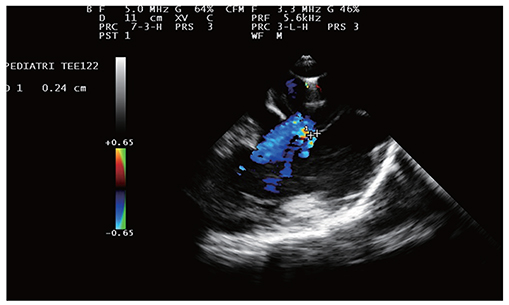
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Association between the Use of Diuretics and Size Reduction in Pediatric Atrial Septal Defect
Jue Seong Lee, Gi Beom Kim, Won Jung Lee, Seok Hyun Song, Hyo Soon An, Sang Yun Lee, Mi Kyoung Song, Hye Won Kwon, Eun Jung Bae
Korean Circ J. 2021;51(12):1017-1029. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2021.0076.
Reference
-
1. Kim NK, Park SJ, Choi JY. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect: does age matter? Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:633–638.2. Park SJ, Kim NK, Kim JO, Yoo BW, Choi JY, Sul JH. Morphologic Characteristics and RelatingFactors to the Need of Technical Modification in Transcatheter Closure of Large Atrial Septal Defect (>/=25 mm). Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:191–196.3. Bishnoi RN, Everett AD, Ringel RE, et al. Device closure of secundum atrial septal defects in infants weighing less than 8 kg. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014; 35:1124–1131.4. Lairakdomrong K, Srimahachota S, Lertsapcharoen P, Chaipromprasit J, Boonyaratavej S, Kaewsukkho P. Clinical results of large secundum atrial septal defect closure in adult using percutaneous transcatheter Cocoon atrial septal occluder. J Med Assoc Thai. 2013; 96:1127–1134.5. Cardenas L, Panzer J, Boshoff D, Malekzadeh-Milani S, Ovaert C. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial defect in small children. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007; 69:447–452.6. Dalvi B, Pinto R, Gupta A. Device closure of large atrial septal defects requiring devices > or =20 mm in small children weighing <20 kg. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008; 71:679–686.7. Zhang H, Chen Q, Chen LW, Cao H, Zhang GC, Chen DZ. Intraoperative device closure of atrial septal defects in the older population. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 6:123.8. Gabriels C, De Meester P, Pasquet A, et al. A different view on predictors of pulmonary hypertension in secundum atrial septal defect. Int J Cardiol. 2014; 176:833–840.9. Lakhdhar R, Drissa M, Drissa H. Natural history of atrial septal defect in the sixth decade : study of 5 cases. Tunis Med. 2013; 91:243–247.10. Beitzke A, Zobel G, Nagel B, Koestenberger M. Transcatheter closure of an atrial septal defect in a newborn with aortic stenosis. Acta Paediatr. 2009; 98:582–583.11. Du ZD, Hijazi ZM, Kleinman CS, Silverman NH, Larntz K. Amplatzer Investigators. Comparison between transcatheter and surgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect in children and adults: results of a multicenter nonrandomized trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002; 39:1836–1844.12. Knirsch W, Dodge-Khatami A, Valsangiacomo-Buechel E, Weiss M, Berger F. Challenges encountered during closure of atrial septal defects. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005; 26:147–153.13. Cooke JC, Gelman JS, Harper RW. Chiari network entanglement and herniation into the left atrium by an atrial septal defect occluder device. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1999; 12:601–603.14. Masseli J, Bertog S, Stanczak L, et al. Transcatheter closure of multiple interatrial communications. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013; 81:825–836.15. Turkay S, Abdullah E, Celal A, et al. Multiple transcatheter interventions in the same session in congenital cardiopathies. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2010; 1:181–190.16. Erdem A, Sarıtas T, Zeybek C, et al. Transthoracic echocardiographic guidance during transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in children and adults. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013; 29:53–61.17. Geva T, Martins JD, Wald RM. Atrial septal defects. Lancet. 2014; 383:1921–1932.18. El-Said H, Hegde S, Foerster S, et al. Device therapy for atrial septal defects in a multicenter cohort: acute outcomes and adverse events. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015; 85:227–233.19. Diab KA, Cao QL, Bacha EA, Hijazi ZM. Device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder: safety and outcome in infants. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007; 134:960–966.20. Mahadevan VS, Gomperts N, Haberer K, et al. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with multiple devices in adults: procedural and clinical outcomes. Int J Cardiol. 2009; 133:359–363.21. Butera G, Romagnoli E, Saliba Z, et al. Percutaneous closure of multiple defects of the atrial septum: procedural results and long-term follow-up. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2010; 76:121–128.22. Awad SM, Garay FF, Cao QL, Hijazi ZM. Multiple Amplatzer septal occluder devices for multiple atrial communications: immediate and long-term follow-up results. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007; 70:265–273.23. Kawamura A, Nishiyama N, Kawakami T, Fukuda K. Retrieval of embolized Amplatzer septal occluder using ablation catheter and triple-loop snare. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2014; 29:350–353.24. Mashman WE, King SB, Jacobs WC, Ballard WL. Two cases of late embolization of Amplatzer septal occluder devices to the pulmonary artery following closure of secundum atrial septal defects. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2005; 65:588–592.25. Goel PK, Kapoor A, Batra A, Khanna R. Transcatheter retrieval of embolized AMPLATZER Septal Occluder. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012; 39:653–656.26. Dhaliwal RS, Singh H, Swami N, Srivastava V. Removal of displaced and impacted ASD device after 4 years. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 57:233–235.27. Szkutnik M, Lenarczyk A, Kusa J, Białkowski J. Symptomatic tachy- and bradyarrhythmias after transcatheter closure of interatrial communications with Amplatzer devices. Cardiol J. 2008; 15:510–516.28. Nehgme RA, Huddleston AR, Cheatham JP. Progression to late complete atrioventricular block following amplatzer device closure of atrial septal defect in a child. Pediatr Cardiol. 2009; 30:367–370.29. Rohit MK, Puri K, Vadivelu R. Reversible complete atrioventricular block after percutaneous ASD device closure in a child <15 kg. Indian Heart J. 2014; 66:366–369.30. Amoozgar H, Ahmadipoor M, Amirghofran AA. Complete heart block following transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect due to growth of inflammatory tissue. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014; 35:1301–1303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Procedural, Early and Long-Term Outcomes after Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defects Closure: Comparison between Large and Very Large Atrial Septal Defect Groups
- Emergent Surgical Intervention for Embolization of Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device
- Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defect: Does Age Matter?
- Comprehensive understanding of atrial septal defects by imaging studies for successful transcatheter closure
- Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder