J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Oct;57(10):1535-1541. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.10.1535.
Comparision of Corneal Refractive Power Measured with Opitcal Low-coherence Reflectometry, Autokeratometer, and Topography in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. eddc99@gmail.com
- KMID: 2355407
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.10.1535
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the keratometry obtained from optical low-coherence reflectometry (Lenstar LS900®), autokeratometer (KR-8100®), and topography (Medmont E300®) in children.
METHODS
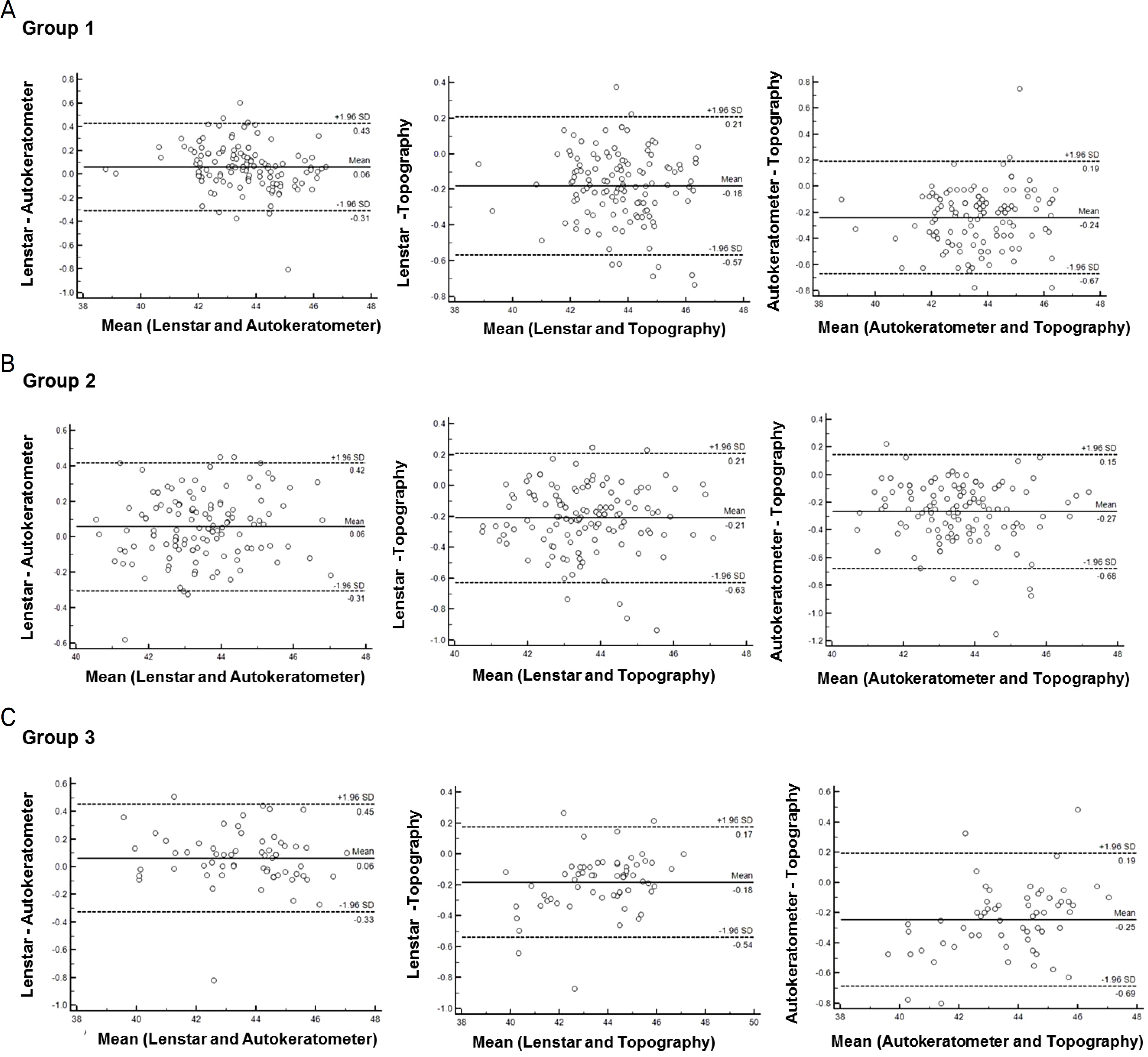
A retrospective study was performed in 316 eyes of 160 subjects. Subjects were divided into 3 groups according to age. Group 1 was younger than 10 years, group 2 was older than 10 years and younger than 18 years, and group 3 was older than 18 years. Subjects were tested using the Lenstar LS900®, KR-8100®, and Medmont E300®. Comparisons were made for steep K, flat K, mean K, and astigmatism among three groups. Agreement among the 3 devices was examined using the Bland-Altman method.
RESULTS
The keratometry measured by Medmont E300® was highest, followed by that of Lenstar LS900® and KR-8100® in all 3 groups. Almost all keratometry was significantly different among the 3 devices except for the flat K measured by LS900® and KR-8100® in all 3 groups and flat K measured by KR-8100® and Medmont E300® in Group 3 (p < 0.05). With regard to mean K, the agreement between Lenstar LS900® and KR-8100® was better than that between the other two pairs in both Groups 1 and 2, while agreement between Lenstar LS900® and Medmont E300® was better in Group 3. The agreement between KR-8100® and Medmont E300® was worse than that between the other two pairs in Groups 1 and 3, while the agreement between Lenstar LS900® and Medmont E300® was worse in Group 2.
CONCLUSIONS
There were significant differences in keratometry among the 3 devices in all 3 groups. In children, Medmont E300® showed relatively less agreement compared with the other two devices. In adults, however, the agreement between 2 devices showed variable results. Consideration of the keratometry measurement from Lenstar LS900®, KR-8100®, and Medmont E300® might be helpful to estimate accurate corneal keratometry in children.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Friedman NE, Mutti DO, Zadnik K. Corneal changes in schoolchildren. Optom Vis Sci. 1996; 73:552–7.
Article2. Lam CS, Edwards M, Millodot M, Goh WS. A 2-year longitudinal study of myopia progression and optical component changes among Hong Kong schoolchildren. Optom Vis Sci. 1999; 76:370–80.3. Huynh SC, Mai TQ, Kifley A, et al. An evaluation of keratometry in 6-year-old children. Cornea. 2006; 25:383–7.
Article4. Park SJ, Lim SH, Lee HY. Comparative analysis of corneal abdominal power measured with AL-Scan(R), autokeratometer, and pentacam(R). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014; 55:984–90.5. Hashemi H, Asgari S, Miraftab M, et al. Agreement study of keratometric values measured by Biograph/LENSTAR, auto-kerato-re-fractometer and Pentacam: decision for IOL calculation. Clin Exp Optom. 2014; 97:450–5.
Article6. Kim S, Chung SK. Comparison of corneal curvatures obtained with different devices. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:618–25.
Article7. Han JM, Choi HJ, Kim MK, et al. Comparative analysis of corneal refraction and astigmatism measured with autokeratometer, IOL Master, and topography. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:1427–33.
Article8. Whang WJ, Byun YS, Joo CK. Comparison of refractive outcomes using five devices for the assessment of preoperative corneal power. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 40:425–32.
Article9. Cruysberg LP, Doors M, Verbakel F, et al. Evaluation of the Lenstar LS 900 non-contact biometer. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010; 94:106–10.
Article10. Rohrer K, Frueh BE, Wälti R, et al. Comparison and evaluation of ocular biometry using a new noncontact optical low-coherence reflectometer. Ophthalmology. 2009; 116:2087–92.
Article11. Cho P, Lam AK, Mountford J, Ng L. The performance of four abdominal corneal topographers on normal human corneas and its impact on orthokeratology lens fitting. Optom Vis Sci. 2002; 79:175–83.12. Read SA, Collins MJ, Iskander DR, Davis BA. Corneal topography with Scheimpflug imaging and videokeratography: comparative study of normal eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1072–81.
Article13. Chui WS, Cho P. A comparative study of the performance of abdominal corneal topographers on children with respect to abdominal practice. Optom Vis Sci. 2005; 82:420–7.14. González-Méijome JM, Jorge J, Queiros A, et al. A comparison of the ARK-700A autokeratometer and Medmont E300 corneal topographer when measuring peripheral corneal curvature. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2004; 24:391–8.15. Wang Q, Savini G, Hoffer KJ, et al. A comprehensive assessment of the precision and agreement of anterior corneal power abdominals obtained using 8 different devices. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e45607.16. Shirayama M, Wang L, Weikert MP, Koch DD. Comparison of abdominal powers obtained from 4 different devices. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009; 148:528–35.e1.17. Liang CL, Hung KS, Park N, et al. Comparison of the handheld Retinomax K-Plus2 and on-table autokeratometers in children with and without cycloplegia. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004; 30:669–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Analysis of Corneal Refractive Power Measured with AL-Scan(R), Autokeratometer, and Pentacam(R)
- The Change of Corneal Refractive Power Measured by Corneal Topography before and after Pterygium Surgery
- Comparative Analysis of Corneal Refraction and Astigmatism Measured with Autokeratometer, IOL Master, and Topography
- The Effect of Strabismus Surgery on Refractive Error Measured with Corneal Topography
- Corneal Topographic Changes after Surgery in Epiblepharon Children