J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2016 Sep;40(3):206-211. 10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.3.206.
Diagnosis and treatment of physiologic halitosis: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Dentistry, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. youn5801@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2354793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.3.206
Abstract
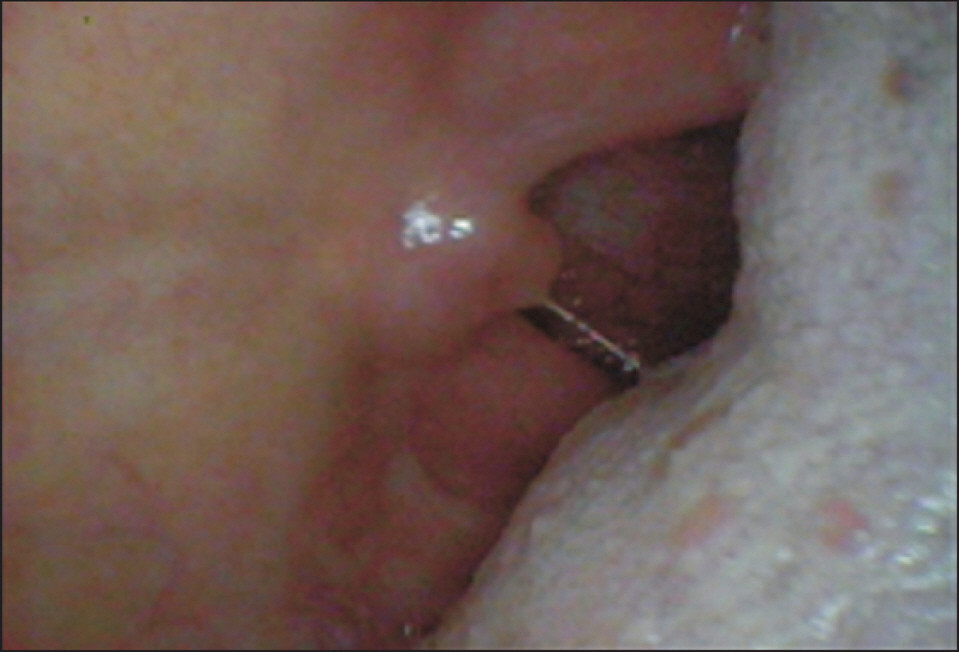
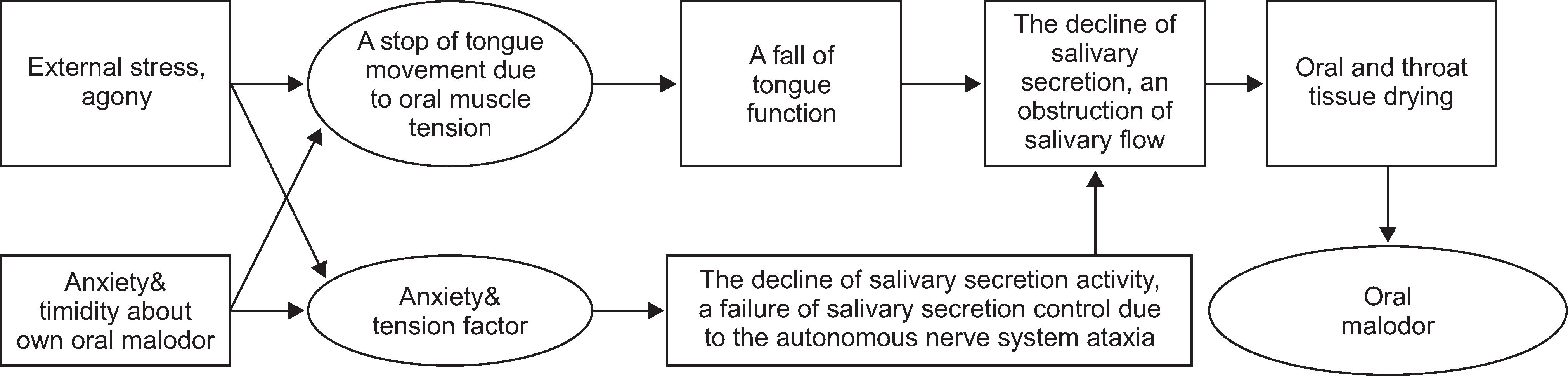
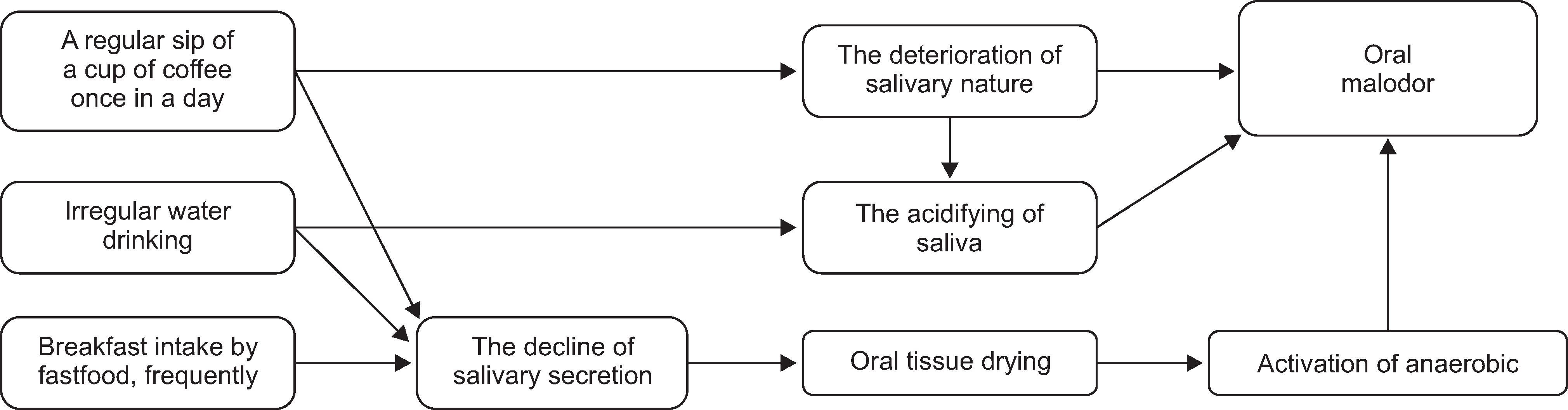
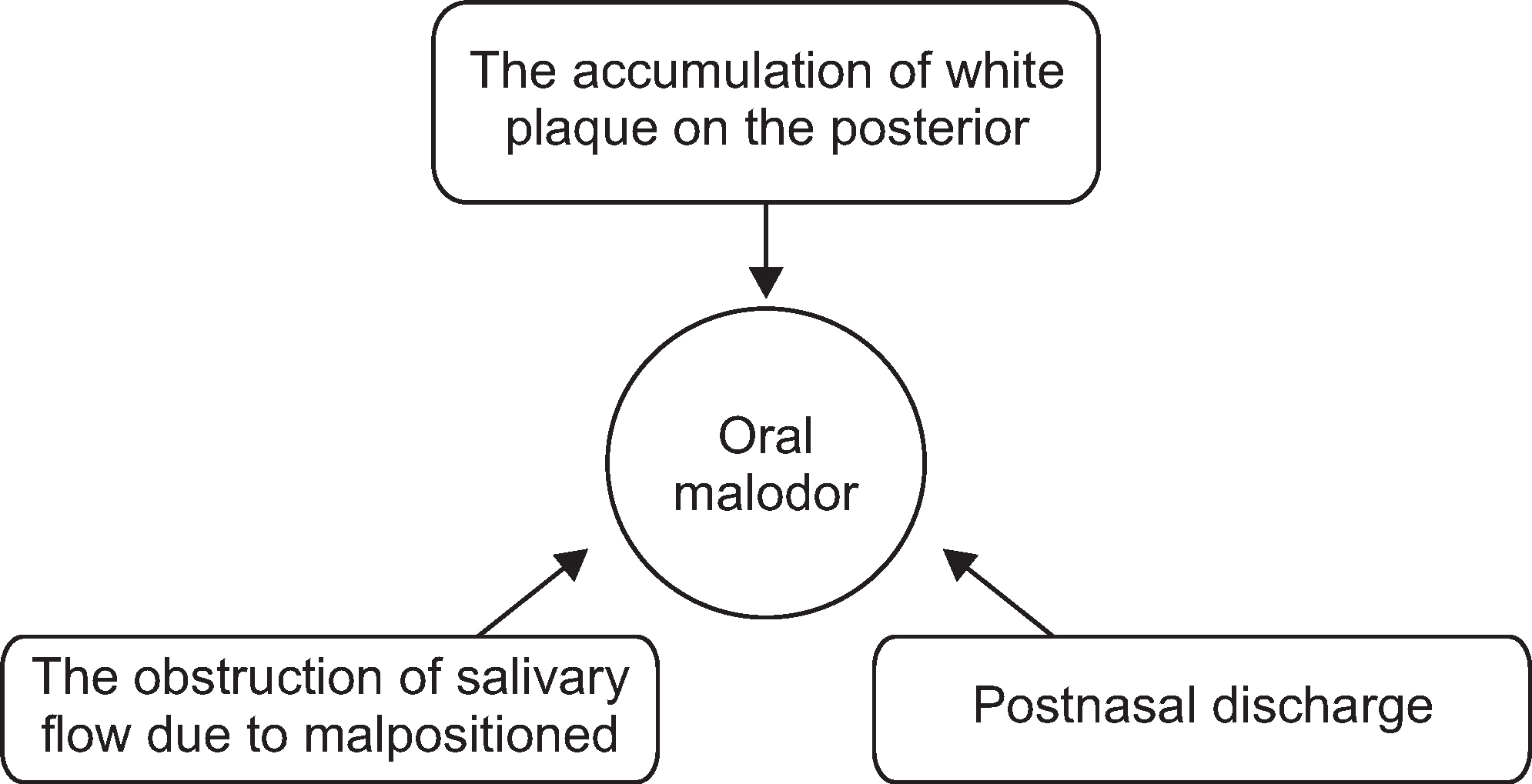
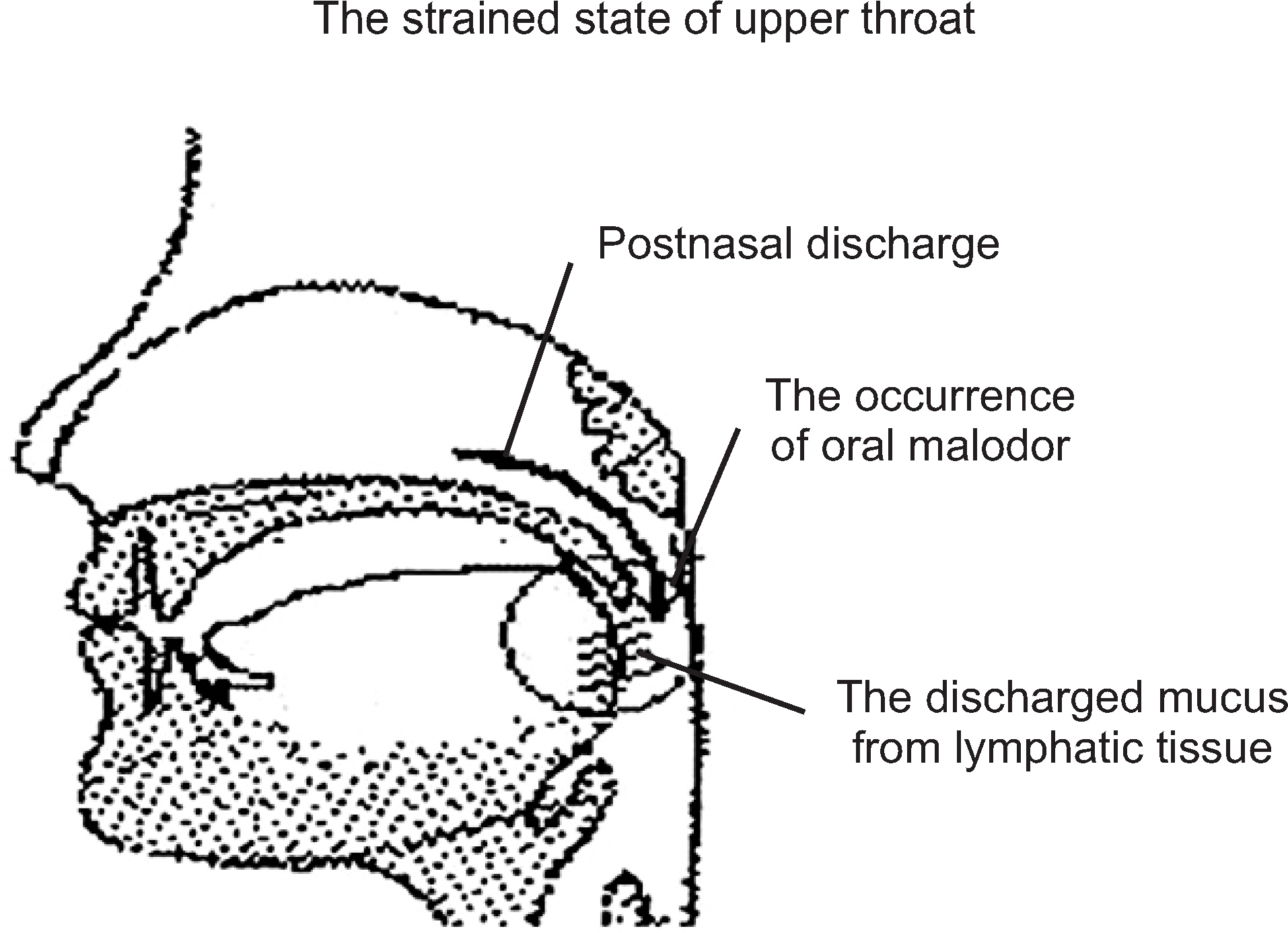
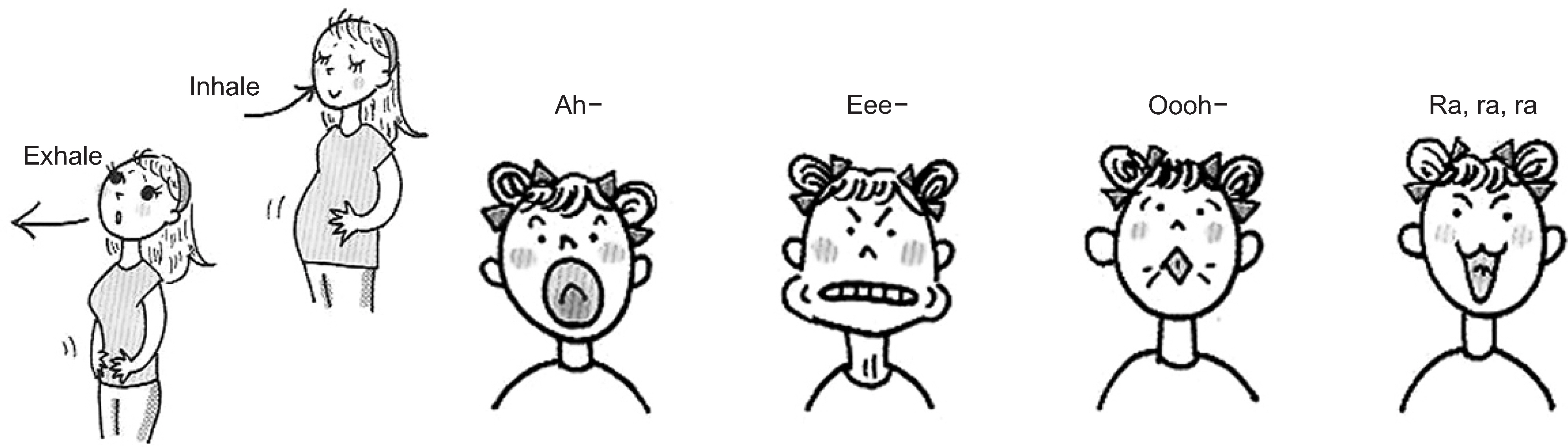
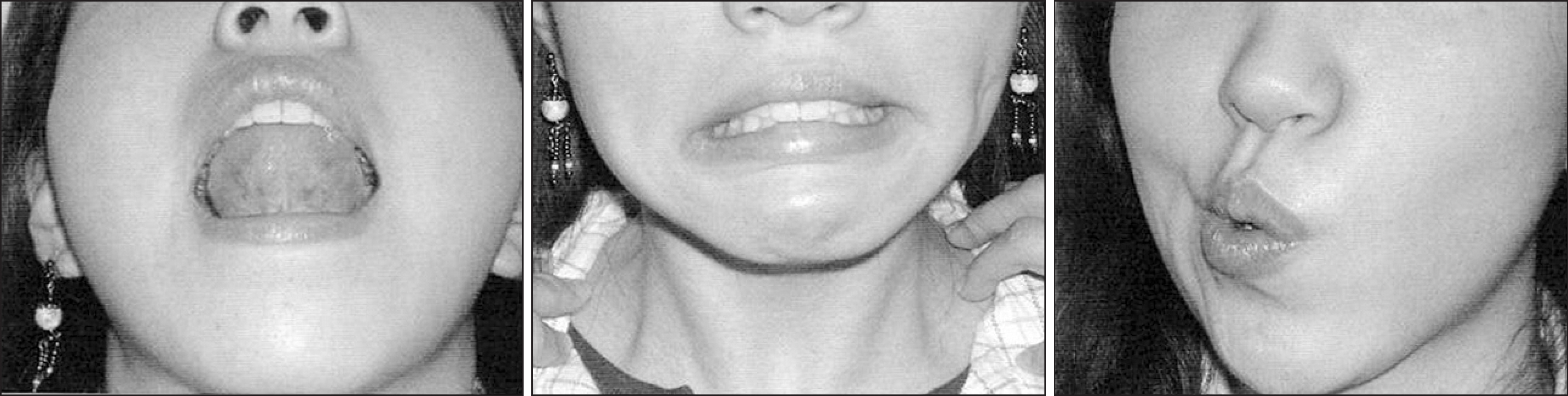
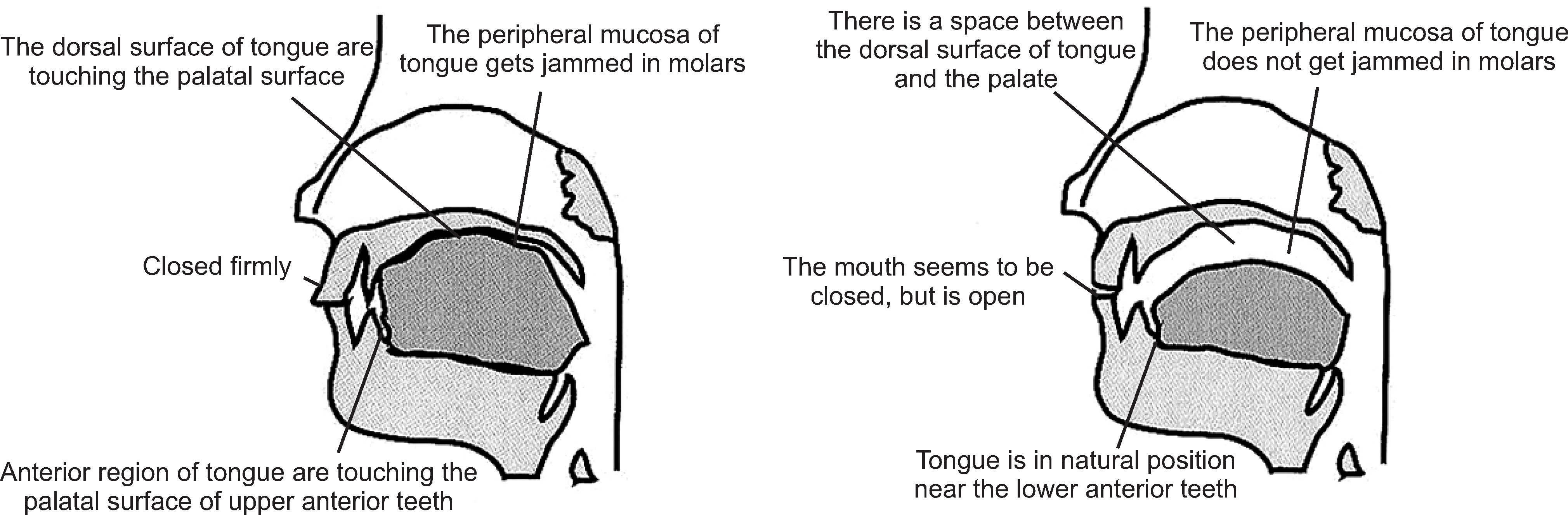
- We selected a patient with physiological bad breath from among the outpatients with bad breath that have visited the halitosis control clinic in KUMC. We identified the factors that were associated with the development of bad breath and assessed the occurrence of discomfort in the mouth; thereafter, we were able to prescribe a treatment method for the patient. We determined the daily routine of the patient through a questionnaire and a diary of dietary life. From these analyses, we deduced the factors associated with her physiologic halitosis. We combined this information with the results of analysis of her oral and exhaled gas measurements, nasal gas measurements by oral malodor measuring devices, and salivary measurements to develop a treatment method that we prescribed to the patient. We conclude that oral health education, including correction of the patient's mismanaged oral-care methods and routines, could act as an alternative treatment method for patients with physiologic halitosis in Korea.
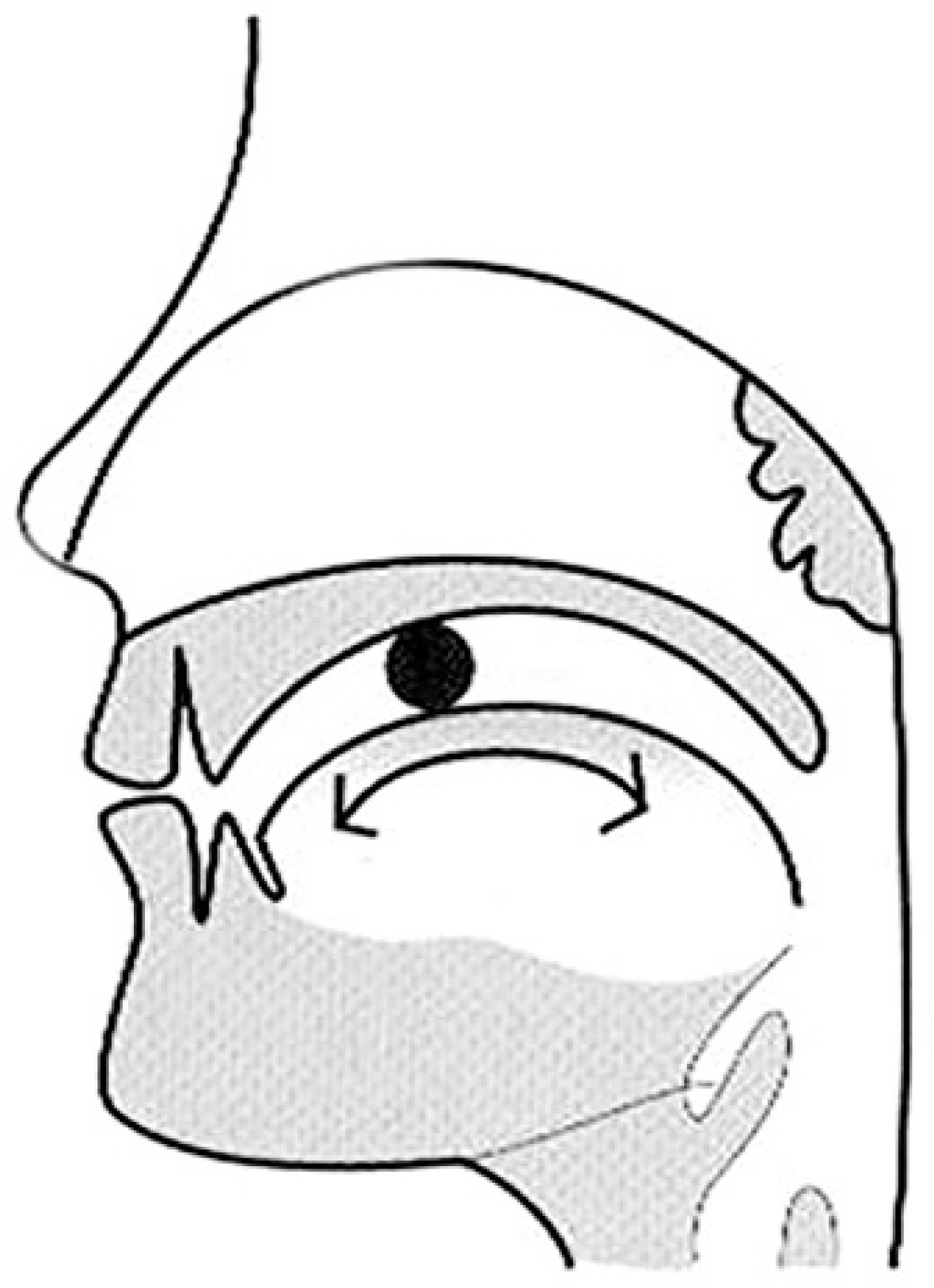
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. The Korean Academy of Halitosis Control. Oral malodor management. 1st edition. Seoul: Komoonsa;2014. p. 3–161.2. Soraya CL, Juliana B, Aline P, Denise PF, Jorge F, Pedro Z. Medication in elderly people: its influence on salivary pattern, signs and symptoms of dry mouth. Gerodontology. 2010; 27:129–33.3. van der Putten GJ, Brand HS, De Visschere LM, Schols JM, de Baat C. Saliva secretion rate and acidity in a group of physically disabled older care home residents. Odontology. 2013; 101:108–115.
Article4. Mahesh DR, Komali G, Jayanthi K, Dinesh D, Saikavitha TV, Preeti D. Evaluation of Salivary Flow Rate, pH and Buffer in Pre, Post & Post Menopausal Women on HRT. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:233–236.5. Rad M, Kakoie S, Niliye Brojeni F. Pourdamghan N. Effect of Longterm Smoking on Whole-mouth Salivary Flow Rate and Oral Health. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2010; 4:110–114.6. Shunichi H. A person with a long life does have much saliva. 1st edition. Tokyo: Forest Shubbansha;2015. p. 70–78.7. Michael E, Colin D, Denis O. Saliva and Oral Health. 4th edition. Bicester: Stephen Hancocks Ltd;2012. p. 57–67.8. Masayuki U, Susumu T, Sachiko T, Yoko K. Saliva viscosity as a potential risk factor for oral malodor. Acta Odontol Scand. 2014; 72:1005–1009.9. Shunichi H. Dental clinical approach of halitosis tratment. 1st edition. Tokyo: Nihon Shika Shinbunsha;2004. p. 25–87.10. Shunichi H. Excellent Breath Bible. 1st edition. Tokyo: Asuka Publishing Inc;2007. p. 16–100.11. Yuki O, Naomi Y, Yoko K, Hirohiko H, Shiro M, Kumiko S. Effectiveness of an oral health educational program on community-dwelling older people with xerostomia. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2015; 15:481–489.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Literature Review on the Causes and Treatments of Halitosis Related to Dental Prosthetics
- Halitosis
- Relationship among Oral Hygiene Management, Halitosis, Interpersonal Relationships and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life in Community-Dwelling Elderly
- Effects of A-solution on Halitosis and Oral Status in Preoperative NPO Patients
- Association Between Halitosis Diagnosed by a Questionnaire and Halimeter and Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease