Korean J Pain.
2016 Oct;29(4):266-269. 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.266.
Reduction in mechanical allodynia in complex regional pain syndrome patients with ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment of the superficial peroneal nerve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. anpjuno@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2354220
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2016.29.4.266
Abstract
- The superficial peroneal nerve is vulnerable to damage from ankle sprain injuries and fractures as well as surgery to this region. And it is also one of the most commonly involved nerves in complex regional pain syndrome type II in the foot and ankle region. We report two cases of ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment of superficial peroneal nerve for reduction of allodynia in CRPS patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
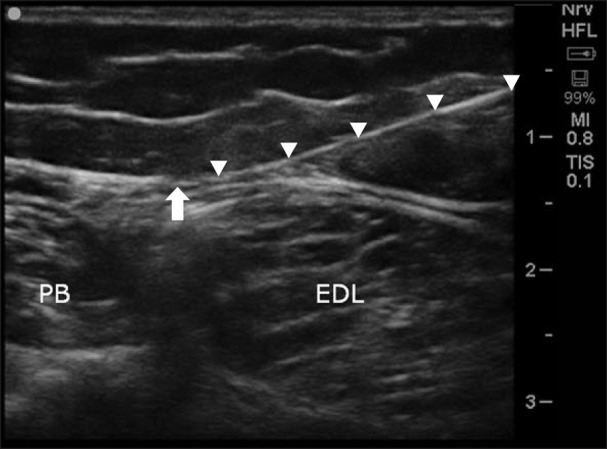
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Multicenter survey of symptoms, work life, economic status, and quality of life of complex regional pain syndrome patients
Jaemoon Lee, Yun Hee Lim, Sung Jun Hong, Jae Hun Jeong, Hey Ran Choi, Sun Kyung Park, Jung Eun Kim, Eun Hi Park, Jae Hun Kim
Korean J Pain. 2021;34(3):288-303. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2021.34.3.288.
Reference
-
1. Trevino SG, Panchbhavi VK, Castro-Aragon O, Rowell M, Jo J. The "kick-off" position: a new sign for early diagnosis of complex regional pain syndrome in the leg. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:92–95. PMID: 17257546.
Article2. Zengerink M, van Dijk CN. Complications in ankle arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20:1420–1431. PMID: 22669362.
Article3. Byrd D, Mackey S. Pulsed radiofrequency for chronic pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2008; 12:37–41. PMID: 18417022.
Article4. Finch PM, Knudsen L, Drummond PD. Reduction of allodynia in patients with complex regional pain syndrome: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial of topical ketamine. Pain. 2009; 146:18–25. PMID: 19703730.
Article5. Ozsoylar O, Akçali D, Cizmeci P, Babacan A, Cahana A, Bolay H. Percutaneous pulsed radiofrequency reduces mechanical allodynia in a neuropathic pain model. Anesth Analg. 2008; 107:1406–1411. PMID: 18806060.
Article7. Gierthmühlen J, Binder A, Baron R. Mechanism-based treatment in complex regional pain syndromes. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014; 10:518–528. PMID: 25134708.
Article8. Jensen TS, Finnerup NB. Allodynia and hyperalgesia in neuropathic pain: clinical manifestations and mechanisms. Lancet Neurol. 2014; 13:924–935. PMID: 25142459.
Article9. Coutaux A, Adam F, Willer JC, Le Bars D. Hyperalgesia and allodynia: peripheral mechanisms. Joint Bone Spine. 2005; 72:359–371. PMID: 16214069.
Article10. Safarpour D, Salardini A, Richardson D, Jabbari B. Botulinum toxin A for treatment of allodynia of complex regional pain syndrome: a pilot study. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1411–1414. PMID: 20609130.
Article11. Ushida T, Tani T, Kanbara T, Zinchuk VS, Kawasaki M, Yamamoto H. Analgesic effects of ketamine ointment in patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2002; 27:524–528. PMID: 12373705.
Article12. Karmarkar A, Lieberman I. Management of complex regional pain syndrome type II using lidoderm 5% patches. Br J Anaesth. 2007; 98:261–262. PMID: 17251215.
Article13. Gofeld M, Restrepo-Garces CE, Theodore BR, Faclier G. Pulsed radiofrequency of suprascapular nerve for chronic shoulder pain: a randomized double-blind active placebo-controlled study. Pain Pract. 2013; 13:96–103. PMID: 22554345.
Article14. Akbas M, Luleci N, Dere K, Luleci E, Ozdemir U, Toman H. Efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency treatment on the saphenous nerve in patients with chronic knee pain. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2011; 24:77–82. PMID: 21558611.
Article15. Lim SM, Park HL, Moon HY, Kang KH, Kang H, Baek CH, et al. Ultrasound-guided infraorbital nerve pulsed radiofrequency treatment for intractable postherpetic neuralgia -a case report -. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:84–88. PMID: 23342215.
Article16. Restrepo-Garces CE, Marinov A, McHardy P, Faclier G, Avila A. Pulsed radiofrequency under ultrasound guidance for persistent stump-neuroma pain. Pain Pract. 2011; 11:98–102. PMID: 20642489.
Article17. Fowler IM, Tucker AA, Mendez RJ. Treatment of meralgia paresthetica with ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency ablation of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Pain Pract. 2012; 12:394–398. PMID: 22151457.
Article18. Todorov L. Pulsed radiofrequency of the sural nerve for the treatment of chronic ankle pain. Pain Physician. 2011; 14:301–304. PMID: 21587334.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment for postherpetic neuralgia of supraorbital nerve: A case report
- Ultrasound-guided pudendal nerve pulsed radiofrequency in patients with refractory pudendal neuralgia: Three cases report
- Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of the Ulnar Nerve in a Patient with Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: A case report
- Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency of the Third Occipital Nerve
- Fluoroscopy-guided pudendal nerve block and pulsed radiofrequency treatment : A case report