Korean J Pain.
2013 Apr;26(2):186-190. 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.186.
Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency of the Third Occipital Nerve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. demoon@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1978667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.186
Abstract
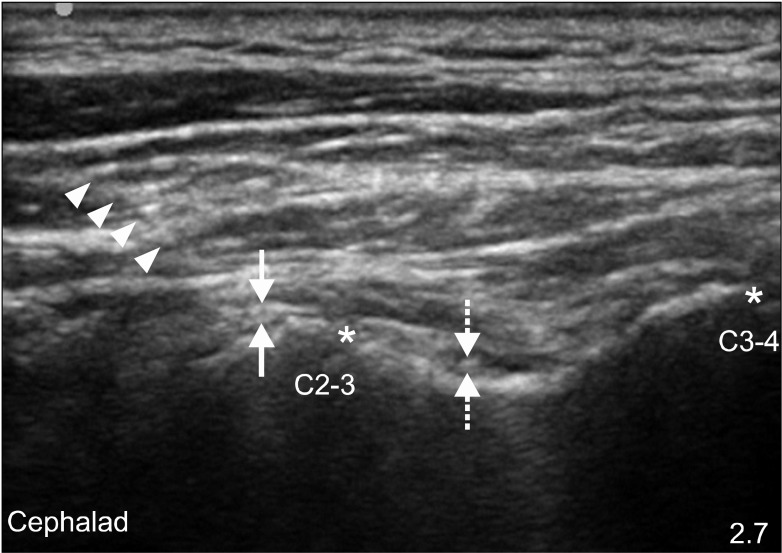
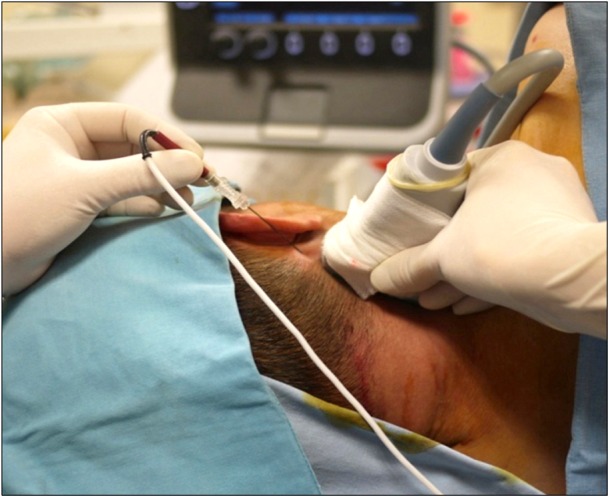
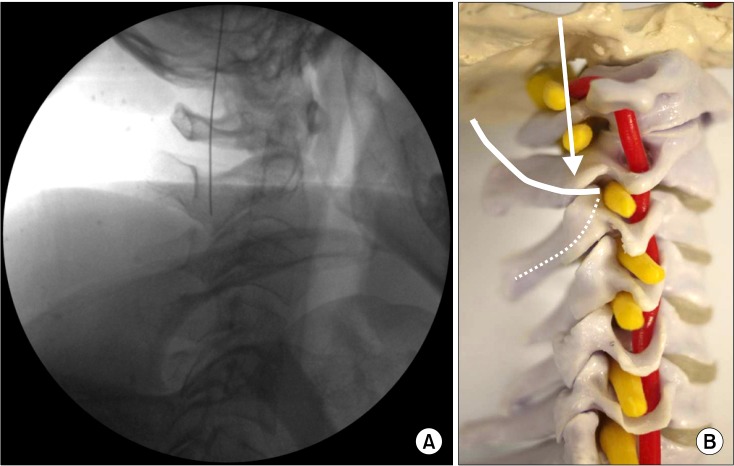
- A C2-3 zygapophygeal joint is a major source of cervicogenic headache. Radiofrequency (RF) neurotomy is preformed widely for zygapophygeal joint pain. Conventional RF denervation technique is generally performed under fluoroscopic control. Recently, ultrasound-guided radiofrequency on zygapophygeal joint has emerged as an alternative method. We report our experiences of two successful ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequencies on 39-year-old and 42-year-old males, who complained occipital headache and posterior neck pain.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dwyer A, Aprill C, Bogduk N. Cervical zygapophyseal joint pain patterns. I: a study in normal volunteers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:453–457. PMID: 2402682.2. Bogduk N, Marsland A. On the concept of third occipital headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986; 49:775–780. PMID: 3018167.
Article3. Lord SM, Barnsley L, Wallis BJ, Bogduk N. Third occipital nerve headache: a prevalence study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994; 57:1187–1190. PMID: 7931379.
Article4. Bogduk N. The clinical anatomy of the cervical dorsal rami. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1982; 7:319–330. PMID: 7135065.
Article5. Sluijter ME, Koetsveld-Baart CC. Interruption of pain pathways in the treatment of the cervical syndrome. Anaesthesia. 1980; 35:302–307. PMID: 7396144.
Article6. Cohen SP, Van Zundert J. Pulsed radiofrequency: rebel without cause. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010; 35:8–10. PMID: 20048652.7. Eichenberger U, Greher M, Kapral S, Marhofer P, Wiest R, Remonda L, et al. Sonographic visualization and ultrasound-guided block of the third occipital nerve: prospective for a new method to diagnose C2-C3 zygapophysial joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2006; 104:303–308. PMID: 16436850.
Article8. Lee SH, Kang CH, Lee SH, Derby R, Yang SN, Lee JE, et al. Ultrasound-guided radiofrequency neurotomy in cervical spine: sonoanatomic study of a new technique in cadavers. Clin Radiol. 2008; 63:1205–1212. PMID: 18929038.
Article9. Barnsley L, Bogduk N. Medial branch blocks are specific for the diagnosis of cervical zygapophyseal joint pain. Reg Anesth. 1993; 18:343–350. PMID: 8117629.10. Bogduk N. International Spinal Injection Society guidelines for the performance of spinal injection procedures. Part 1: Zygapophysial joint blocks. Clin J Pain. 1997; 13:285–302. PMID: 9430809.11. Govind J, King W, Bailey B, Bogduk N. Radiofrequency neurotomy for the treatment of third occipital headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:88–93. PMID: 12486273.
Article12. Siegenthaler A, Schliessbach J, Curatolo M, Eichenberger U. Ultrasound anatomy of the nerves supplying the cervical zygapophyseal joints: an exploratory study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:606–610. PMID: 21937946.
Article13. Cosman ER Jr, Cosman ER Sr. Electric and thermal field effects in tissue around radiofrequency electrodes. Pain Med. 2005; 6:405–424. PMID: 16336478.
Article14. Higuchi Y, Nashold BS Jr, Sluijter M, Cosman E, Pearlstein RD. Exposure of the dorsal root ganglion in rats to pulsed radiofrequency currents activates dorsal horn lamina I and II neurons. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:850–855. PMID: 11904038.
Article15. Van Zundert J, de Louw AJ, Joosten EA, Kessels AG, Honig W, Dederen PJ, et al. Pulsed and continuous radiofrequency current adjacent to the cervical dorsal root ganglion of the rat induces late cellular activity in the dorsal horn. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:125–131. PMID: 15618796.
Article16. Cahana A, Vutskits L, Muller D. Acute differential modulation of synaptic transmission and cell survival during exposure to pulsed and continuous radiofrequency energy. J Pain. 2003; 4:197–202. PMID: 14622704.
Article17. Chaudhari M. Radiofrequency techniques in pain management. Anaesth Intensive Care Med. 2011; 12:63–65.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment for postherpetic neuralgia of supraorbital nerve: A case report
- Ultrasound-guided pudendal nerve pulsed radiofrequency in patients with refractory pudendal neuralgia: Three cases report
- Reduction in mechanical allodynia in complex regional pain syndrome patients with ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment of the superficial peroneal nerve
- Fluoroscopy-guided pudendal nerve block and pulsed radiofrequency treatment : A case report
- Ultrasound-guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Lesioning of the Ulnar Nerve in a Patient with Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: A case report