Korean J Ophthalmol.
2016 Oct;30(5):369-376. 10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.369.
The Efficacy of Intravitreal Aflibercept in Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Wet Age-related Macular Degeneration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kim's Eye Hospital, Myung-Gok Eye Research Institute, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. skhun@kimeye.com
- KMID: 2353830
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.30.5.369
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of intravitreal aflibercept monotherapy in submacular hemorrhage (SMH) secondary to wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
METHODS
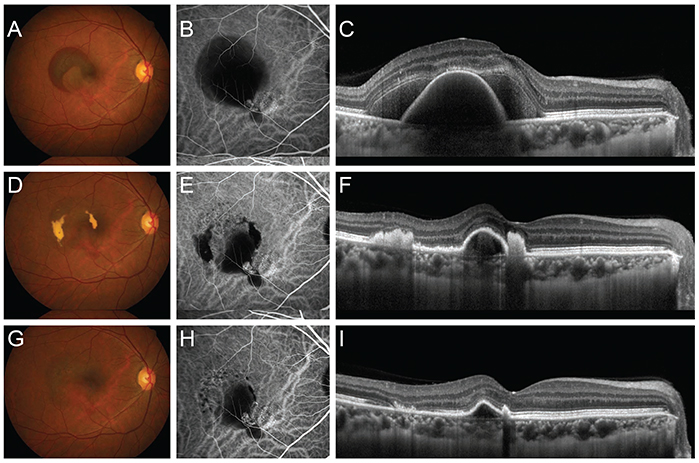
This study included 25 eyes in 25 patients with SMH involving the fovea secondary to wet-AMD. All patients were treated with three consecutive monthly intravitreal aflibercept (2.0 mg/0.05 mL) injections, followed by as-needed reinjection. They were followed for at least 6 months. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), central foveal thickness (CFT), and area of SMH were measured at diagnosis, as well as at 3 and 6 months after treatment initiation.
RESULTS
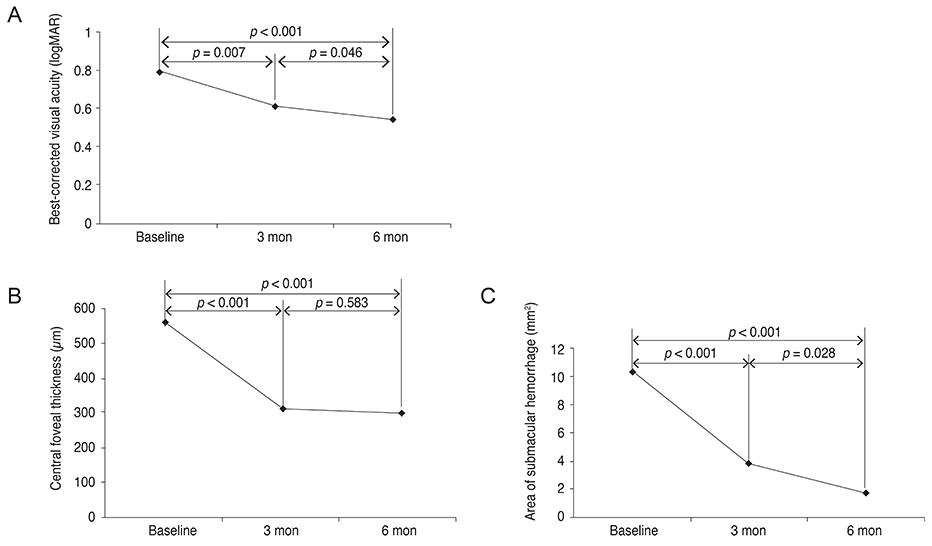
The BCVA significantly improved from 0.79 ± 0.41 logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution (logMAR) at baseline to 0.54 ± 0.41 logMAR at 6 months (p < 0.001). BCVA ≥3 lines and stable vision were observed in 96% of the eyes. The CFT significantly decreased from 560.8 ± 215.3 µm at baseline to 299.8 ± 160.2 µm at 6 months (p < 0.001). The area of SMH significantly decreased from 10.5 ± 7.1 mm² at baseline to 1.8 ± 6.5 mm² at 6 months (p < 0.001). The BCVA, CFT, and area of SMH at baseline, as well as duration of symptoms, all correlated with BCVA at the 6-month follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Intravitreal injection of aflibercept is an effective treatment option for patients with SMH secondary to wet-AMD; however, there may be limited efficacy in eyes with large SMH area and cases in which treatment is delayed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Intravitreal Aflibercept Monotherapy for Treating Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration
Sue Hey Chae, Soh Eun Ahn, Hee Seong Yoon
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(5):437-443. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.5.437.Development of Submacular Hemorrhage in Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration: Influence on Visual Prognosis in a Clinical Setting
Young Suk Chang, Jae Hui Kim, Jong Woo Kim, Chul Gu Kim, Dong Won Lee
Korean J Ophthalmol. 2018;32(5):361-368. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2017.0095.
Reference
-
1. Avery RL, Fekrat S, Hawkins BS, Bressler NM. Natural history of subfoveal subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 1996; 16:183–189.2. Scupola A, Coscas G, Soubrane G, Balestrazzi E. Natural history of macular subretinal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica. 1999; 213:97–102.3. Toth CA, Morse LS, Hjelmeland LM, Landers MB 3rd. Fibrin directs early retinal damage after experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:723–729.4. Bakri SJ, Nickel J, Yoganathan P, Beer PM. Photodynamic therapy for choroidal neovascularization associated with submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2006; 37:278–283.5. Hassan AS, Johnson MW, Schneiderman TE, et al. Management of submacular hemorrhage with intravitreous tissue plasminogen activator injection and pneumatic displacement. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:1900–1906.6. Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, et al. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1419–1431.7. Stifter E, Michels S, Prager F, et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration with large submacular hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:886–892.8. Shienbaum G, Garcia Filho CA, Flynn HW Jr, et al. Management of submacular hemorrhage secondary to neovascular age-related macular degeneration with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 155:1009–1013.9. Altaweel MM, Daniel E, Martin DF, et al. Outcomes of eyes with lesions composed of >50% blood in the comparison of Age-related Macular Degeneration Treatments Trials (CATT). Ophthalmology. 2015; 122:391–398.e5.10. Stewart MW, Grippon S, Kirkpatrick P. Aflibercept. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012; 11:269–270.11. Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V, et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 2012; 119:2537–2548.12. Cho H, Shah CP, Weber M, Heier JS. Aflibercept for exudative AMD with persistent fluid on ranibizumab and/or bevacizumab. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:1032–1035.13. Kim JH, Chang YS, Kim JW, et al. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor for submacular hemorrhage from choroidal neovascularization. Ophthalmology. 2014; 121:926–935.14. Inoue M, Arakawa A, Yamane S, Kadonosono K. Short-term efficacy of intravitreal aflibercept in treatment-naive patients with polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 2014; 34:2178–2184.15. Yamamoto A, Okada AA, Kano M, et al. One-year results of intravitreal aflibercept for polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Ophthalmology. 2015; 122:1866–1872.16. Iacono P, Parodi MB, Introini U, et al. Intravitreal ranibizumab for choroidal neovascularization with large submacular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2014; 34:281–287.17. Cho HJ, Koh KM, Kim HS, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monotherapy in the treatment of submacular hemorrhage secondary to polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013; 156:524–531.e1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intravitreal Aflibercept Monotherapy for Treating Submacular Hemorrhage Secondary to Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration
- Intravitreal Tissue Plasminogen Activator and Gas Injection in Submacular Hemorrhage
- Intravitreal Injection of tPA and Gas for Submacular Hemorrhage Associated with Age-related Macular Degeneration
- The Effect of Intrav it real Injection of tPA and C3F8 Gas in Submacular Hemorrhage
- Full-thickness Macular Hole after Intravitreal Aflibercept Injection in a Patient with Wet Age-related Macular Degeneration