J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Aug;42(4):231-235. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.231.
Benign cementoblastoma of the anterior mandible: an unusual case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Ondokuz Mayis University, Samsun, Turkey. armagan.caliskan@omu.edu.tr
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Ondokuz Mayis University, Samsun, Turkey.
- 3Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ondokuz Mayis University, Samsun, Turkey.
- KMID: 2350077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.231
Abstract
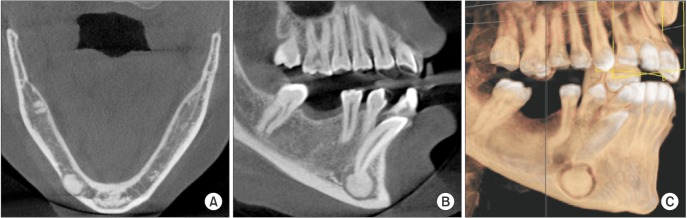
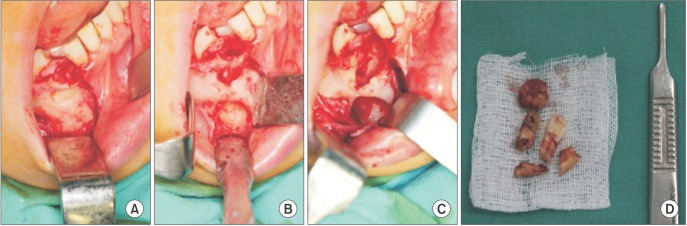
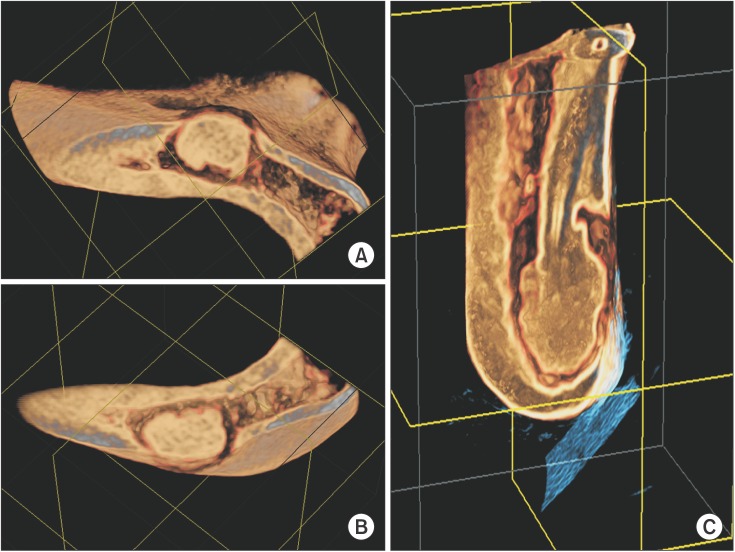
- A benign cementoblastoma, which is another name for a true cementoma, is a rare neoplasm that develops from odontogenic ectomesenchyme. It is characterized by a mineralized mass attached to the apex of the root produced by neoplastic cementoblasts. More than 75% of cases arise in the mandible, with 90% of them manifesting in the molar and premolar regions. This neoplasm occurs most commonly in children and young adults, with males being affected slightly more than females. Radiographically, the tumor is observed as a well-defined radiopaque mass that is fused to a tooth root and is surrounded by a radiolucent rim. The treatment of benign cementoblastoma consists of removal of the lesion and extraction of the affected tooth. This report presents an unusual case of benign cementoblastoma in a 31-year-old female, presenting as a densely mineralized mass seen at the apex of the impacted right mandibular canine tooth on radiographs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Oral and maxillofacial pathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;2002.2. Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D. World Health Organization classification of tumors pathology & genetics head and neck tumors. Lyon: IARC Press;2005.3. Noffke CE, Raubenheimer EJ, MacDonald D. Fibro-osseous disease: harmonizing terminology with biology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012; 114:388–392. PMID: 22862981.
Article4. Brannon RB, Fowler CB, Carpenter WM, Corio RL. Cementoblastoma: an innocuous neoplasm? A clinicopathologic study of 44 cases and review of the literature with special emphasis on recurrence. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002; 93:311–320. PMID: 11925541.
Article5. Pynn BR, Sands TD, Bradley G. Benign cementoblastoma: a case report. J Can Dent Assoc. 2001; 67:260–262. PMID: 11398388.6. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2009.7. Monti LM, Souza AM, Soubhia AM, Jorge WA, Anichinno M, Da Fonseca GL. Cementoblastoma: a case report in deciduous tooth. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 17:145–149. PMID: 22855308.
Article8. Ohki K, Kumamoto H, Nitta Y, Nagasaka H, Kawamura H, Ooya K. Benign cementoblastoma involving multiple maxillary teeth: report of a case with a review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2004; 97:53–58. PMID: 14716256.
Article9. Karaçal N, Agdoğan Ö, Livaoğlu M, Uraloğlu M, Özel B. Giant cementoblastoma of the impacted mandibular incisor. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:e26–e27. PMID: 22134313.
Article10. Papageorge MB, Cataldo E, Nghiem FT. Cementoblastoma involving multiple deciduous teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987; 63:602–605. PMID: 3473380.
Article11. Hirai E, Yamamoto K, Kounoe T, Kondo Y, Yonemasu H, Kurokawa H. Benign cementoblastoma of the anterior maxilla. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:671–674. PMID: 20171487.
Article12. Costa FW, Pereira KM, Magalhães Dias M, da Costa Miguel MC, de Paula Miranda MA, Studart Soares EC. Maxillary cementoblastoma in a child. J Craniofac Surg. 2011; 22:1910–1913. PMID: 21959464.
Article13. Slimani F, Elbouihi M, Oukerroum A, Lazreqh H, Mahtar M, Karkouri M, et al. Maxillary cementoblastoma. A case report. Rev Med Brux. 2009; 30:185–188. PMID: 19642490.14. Keyes G, Hilderbrand K. Successful surgical endodontics for benign cementoblastoma. J Endod. 1987; 13:566–569. PMID: 3482232.
Article15. Brocheriou C, Guilbert F, Matar A, Champion P, Couly G. Benign cementoblastoma of jaws: report of 6 cases and review of the literature (author's transl). Arch Anat Cytol Pathol. 1979; 27:29–34. PMID: 453932.16. Souza AS, Cardoso JA, Silva VP, Oliveira MC, Azoubel E, Farias JG. Cementoblastoma affecting the maxilla of a pediatric patient: a case report. Rev Port Estomatol Med Dent Cir Maxillofac. 2013; 54:43–47.
Article17. Eversole LR, Sabes WR, Dauchess VG. Benign cementoblastoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973; 36:824–830. PMID: 4524834.
Article18. Slootweg PJ. Cementoblastoma and osteoblastoma: a comparison of histologic features. J Oral Pathol Med. 1992; 21:385–389. PMID: 1432731.
Article19. Lee JM, Song WW, Lee JY, Hwang DS, Kim YD, Shin SH, et al. Clinical study of benign and malignant fibrous-osseous lesions of the jaws. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 38:29–37.
Article