J Pathol Transl Med.
2016 Jul;50(4):309-311. 10.4132/jptm.2015.12.03.
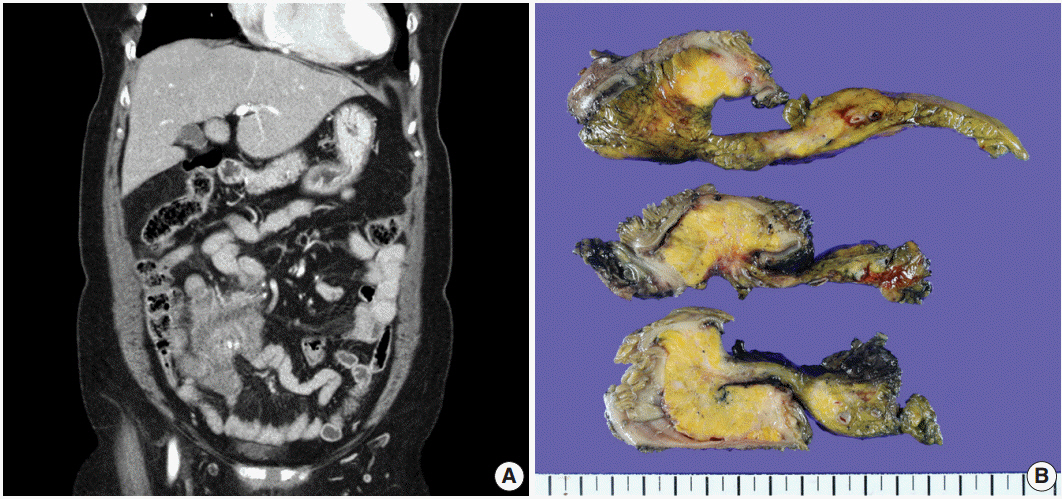
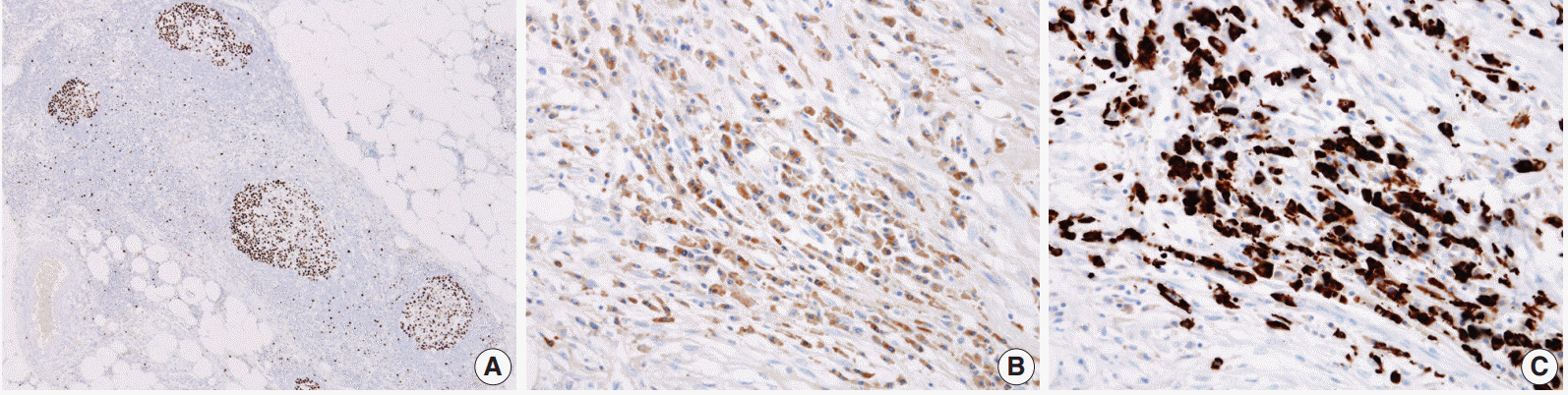
IgG4-Related Sclerosing Mesenteritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Yonsei University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. nicekyumi@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2345555
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.12.03
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Immunoglobulin G4 Unrelated Idiopathic Mesenteric Sclerosis
Tae Hyung Kwon, Kwang Bum Cho, Hyun Jik Lee, Sun Young Kwon, Yoon Suk Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(1):50-55. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.1.50.
Reference
-
1. Sulla JV. Mesenterite e sclerosante. Policlinico Prat. 1924; 31:575–81.2. Emory TS, Monihan JM, Carr NJ, Sobin LH. Sclerosing mesenteritis, mesenteric panniculitis and mesenteric lipodystrophy: a single entity? Am J Surg Pathol. 1997; 21:392–8.
Article3. Kerdsirichairat T, Mesa H, Abraham J, et al. Sclerosing mesenteritis and IgG4-related mesenteritis: case series and a systematic review of natural history and response to treatments. Immunogastroenterology. 2013; 2:119–28.
Article4. Parra-Davila E, McKenney MG, Sleeman D, et al. Mesenteric panniculitis: case report and literature review. Am Surg. 1998; 64:768–71.5. Akram S, Pardi DS, Schaffner JA, Smyrk TC. Sclerosing mesenteritis: clinical features, treatment, and outcome in ninety-two patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:589–96.
Article6. Minato H, Shimizu J, Arano Y, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis: a rare mesenteric disease of unknown etiology. Pathol Int. 2012; 62:281–6.
Article7. Cessna MH, Zhou H, Sanger WG, et al. Expression of ALK1 and p80 in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor and its mesenchymal mimics: a study of 135 cases. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15:931–8.
Article8. Qiu X, Montgomery E, Sun B. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor and low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma: a comparative study of clinicopathologic features and further observations on the immunohistochemical profile of myofibroblasts. Hum Pathol. 2008; 39:846–56.
Article9. Yamamoto H, Yamaguchi H, Aishima S, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor versus IgG4-related sclerosing disease and inflammatory pseudotumor: a comparative clinicopathologic study. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1330–40.