J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2016 Jul;54(3):226-233. 10.4047/jkap.2016.54.3.226.
Comparison of micro CT and cross-section technique for evaluation of marginal and internal fit of lithium disilicate crowns
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, Graduate School, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Republic of Korea. hwcho@wku.ac.kr
- 2Dental Laboratory, Wonkwang University Dental Hospital, Iksan, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2344860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2016.54.3.226
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the adaptation of lithium disilicate crowns fabricated by CAD-CAM (computer aided design-computer aided manufacturing) and heat-press technique to compare two different measurement methods in assessing fit of the ceramic crowns: micro CT and cross-section technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
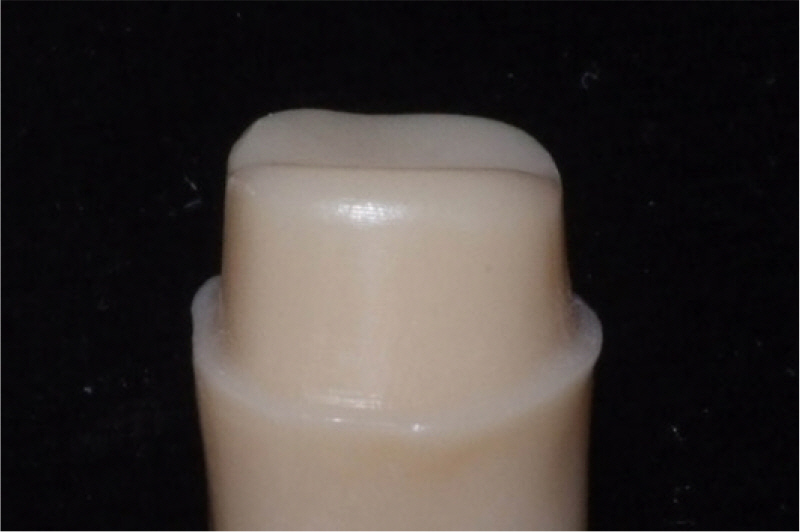
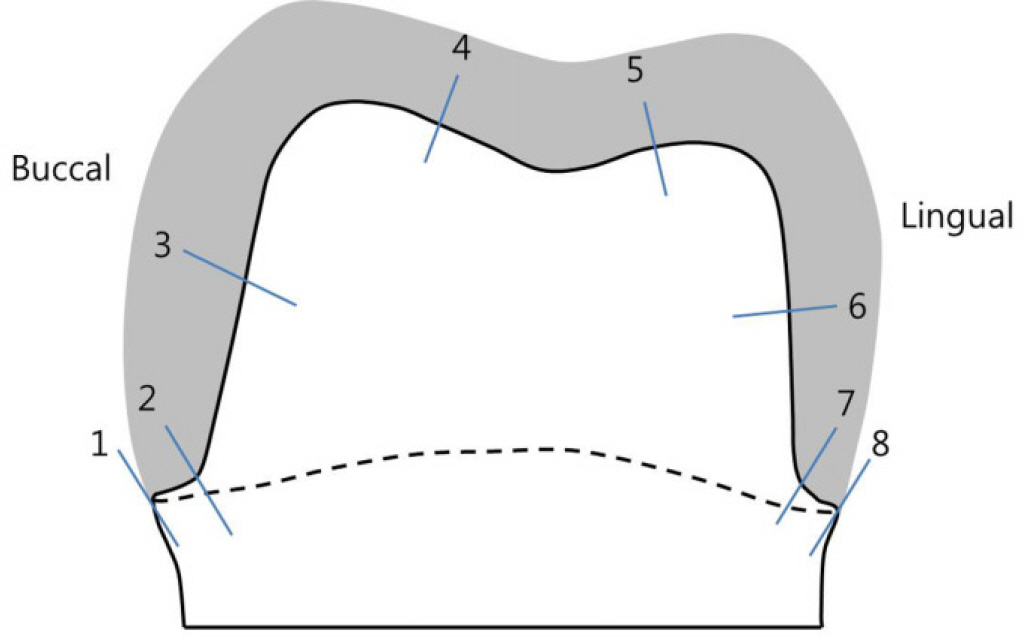
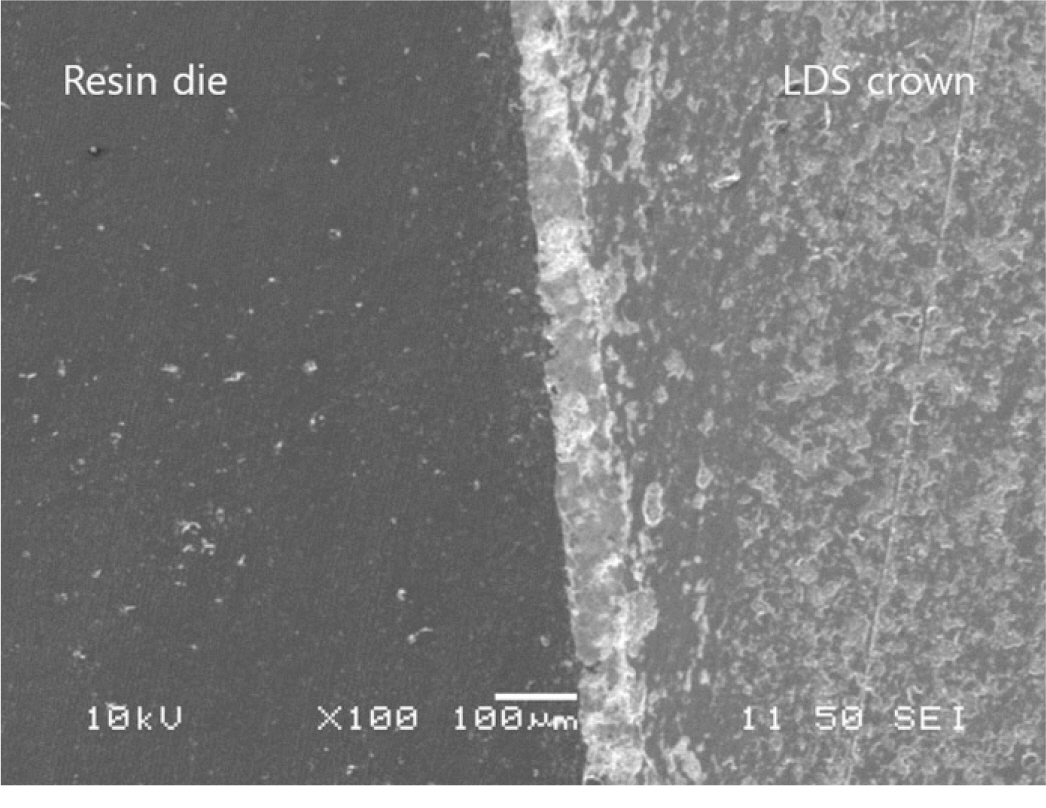
A prepared typodont mandibular molar for ceramic crown was duplicated and ten dies were produced by milling the PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate) resin. Ten vinyl polysiloxane impressions were made and stone casts were produced. Five dies were used for IPS e.max Press crowns with heat-press technique. The other five dies were used for IPS e.max CAD crowns with CAD-CAM technique. Ten lithium disilicate crowns were cemented on the resin dies using zinc phosphate cement with finger pressure. The marginal and internal fits in central buccolingual plane were evaluated using a micro CT. Then the specimens were embedded and cross-sectioned and the marginal and internal fits were measured using scanning electronic microscope. The two measurement methods and two manufacturing methods were compared using Mann-Whitney U test (SPSS 22.0).
RESULTS
The marginal and internal fit values using micro CT and cross-section technique were similar, showing no significant differences. There were no significant differences in adaptation between lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM and heat-press technique.
CONCLUSION
Both micro CT and cross-section technique were acceptable methods in the evaluation of marginal and internal fit of lithium disilicate crown. There was no difference in adaptation between lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM and heat-press technique except occlusal fit.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Marginal and internal fit of all ceramic crown using the replica technique and the triple-scan protocol
Mi-Sun Shin, Jang-Hoon Lee
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2017;55(4):372-380. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2017.55.4.372.
Reference
-
1.Heffernan MJ., Aquilino SA., Diaz-Arnold AM., Haselton DR., Stanford CM., Vargas MA. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part I: core materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 88:4–9.
Article2.Heffernan MJ., Aquilino SA., Diaz-Arnold AM., Haselton DR., Stanford CM., Vargas MA. Relative translucency of six all-ceramic systems. Part II: core and veneer materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 88:10–5.
Article3.Conrad HJ., Seong WJ., Pesun IJ. Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007. 98:389–404.
Article4.Seghi RR., Daher T., Caputo A. Relative flexural strength of dental restorative ceramics. Dent Mater. 1990. 6:181–4.
Article5.Sulaiman F., Chai J., Jameson LM., Wozniak WT. A comparison of the marginal fit of In-Ceram, IPS Empress, and Procera crowns. Int J Prosthodont. 1997. 10:478–84.6.Miyazaki T., Hotta Y., Kunii J., Kuriyama S., Tamaki Y. A review of dental CAD/CAM: current status and future perspectives from 20 years of experience. Dent Mater J. 2009. 28:44–56.
Article7.Reich S., Wichmann M., Nkenke E., Proeschel P. Clinical fit of all-ceramic three-unit fixed partial dentures, generated with three different CAD/CAM systems. Eur J Oral Sci. 2005. 113:174–9.
Article8.Contrepois M., Soenen A., Bartala M., Laviole O. Marginal adaptation of ceramic crowns: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2013. 110:447–54.
Article9.Moon BH., Yang JH., Lee SH., Chung HY. A study on the marginal fit of all-ceramic crown using CCD camera. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1998. 36:273–92.10.Groten M., Girthofer S., Pröbster L. Marginal fit consistency of copy-milled all-ceramic crowns during fabrication by light and scanning electron microscopic analysis in vitro. J Oral Rehabil. 1997. 24:871–81.
Article11.Rahmé HY., Tehini GE., Adib SM., Ardo AS., Rifai KT. In vitro evaluation of the "replica technique" in the measurement of the fit of Procera crowns. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008. 9:25–32.12.Wolfart S., Wegner SM., Al-Halabi A., Kern M. Clinical evaluation of marginal fit of a new experimental all-ceramic system before and after cementation. Int J Prosthodont. 2003. 16:587–92.13.Pelekanos S., Koumanou M., Koutayas SO., Zinelis S., Eliades G. Micro-CT evaluation of the marginal fit of different In-Ceram alumina copings. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2009. 4:278–92.14.Neves FD., Prado CJ., Prudente MS., Carneiro TA., Zancopé K., Davi LR., Mendonça G., Cooper LF., Soares CJ. Micro-computed tomography evaluation of marginal fit of lithium disilicate crowns fabricated by using chairside CAD/CAM systems or the heat-pressing technique. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. 112:1134–40.15.Gardner FM. Margins of complete crowns-literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1982. 48:396–400.
Article16.Council on Dental Materials and Devices. Revised American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association Specification No. 8 for zinc phosphate cement. J Am Dent Assoc. 1978. 96:121–3.17.McLean JW., von Fraunhofer JA. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J. 1971. 131:107–11.
Article18.Gulker I. Margins. N Y State Dent J. 1985. 51:213–5. 217.19.Moldovan O., Rudolph H., Quaas S., Bornemann G., Luthardt RG. Internal and external fit of CAM-made zirconia bridge frameworks-a pilot study. Dtsch Zahnärztl Z. 2006. 61:38–42.20.Kydd WL., Nicholls JI., Harrington G., Freeman M. Marginal leakage of cast gold crowns luted with zinc phosphate cement: an in vivo study. J Prosthet Dent. 1996. 75:9–13.
Article21.White SN., Kipnis V. Effect of adhesive luting agents on the marginal seating of cast restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 1993. 69:28–31.
Article22.Davis DR. Comparison of fit of two types of all-ceramic crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 59:12–6.
Article23.Abbate MF., Tjan AH., Fox WM. Comparison of the marginal fit of various ceramic crown systems. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 61:527–31.
Article24.Pimenta MA., Frasca LC., Lopes R., Rivaldo E. Evaluation of marginal and internal fit of ceramic and metallic crown copings using x-ray microtomography (micro-CT) technology. J Prosthet Dent. 2015. 114:223–8.
Article25.Keshvad A., Hooshmand T., Asefzadeh F., Khalilinejad F., Alihemmati M., Van Noort R. Marginal gap, internal fit, and fracture load of leucite-reinforced ceramic inlays fabricated by CEREC inLab and hot-pressed techniques. J Prosthodont. 2011. 20:535–40.
Article26.Mörmann WH., Schug J. Grinding precision and accuracy of fit of CEREC 2 CAD-CIM inlays. J Am Dent Assoc. 1997. 128:47–53.27.Mously HA., Finkelman M., Zandparsa R., Hirayama H. Marginal and internal adaptation of ceramic crown restorations fabricated with CAD/CAM technology and the heat-press technique. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. 112:249–56.
Article28.Raigrodski AJ. Contemporary materials and technologies for all-ceramic fixed partial dentures: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 92:557–62.
Article29.Rungruanganunt P., Kelly JR., Adams DJ. Two imaging techniques for 3D quantification of pre-cementation space for CAD/CAM crowns. J Dent. 2010. 38:995–1000.
Article30.Krasanaki ME., Pelekanos S., Andreiotelli M., Koutayas SO., Eliades G. X-ray microtomographic evaluation of the influence of two preparation types on marginal fit of CAD/CAM alumina copings: a pilot study. Int J Prosthodont. 2012. 25:170–2.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of marginal fit of 2 CAD-CAM anatomic contour zirconia crown systems and lithium disilicate glass-ceramic crown
- Effect of machining precision of single ceramic restorations on the marginal and internal fit
- Marginal and internal fit of all ceramic crown using the replica technique and the triple-scan protocol
- How adjustment could affect internal and marginal adaptation of CAD/CAM crowns made with different materials
- Ceramic molar crown reproducibility by digital workflow manufacturing: An in vitro study