Korean J Gastroenterol.
2016 Jul;68(1):29-35. 10.4166/kjg.2016.68.1.29.
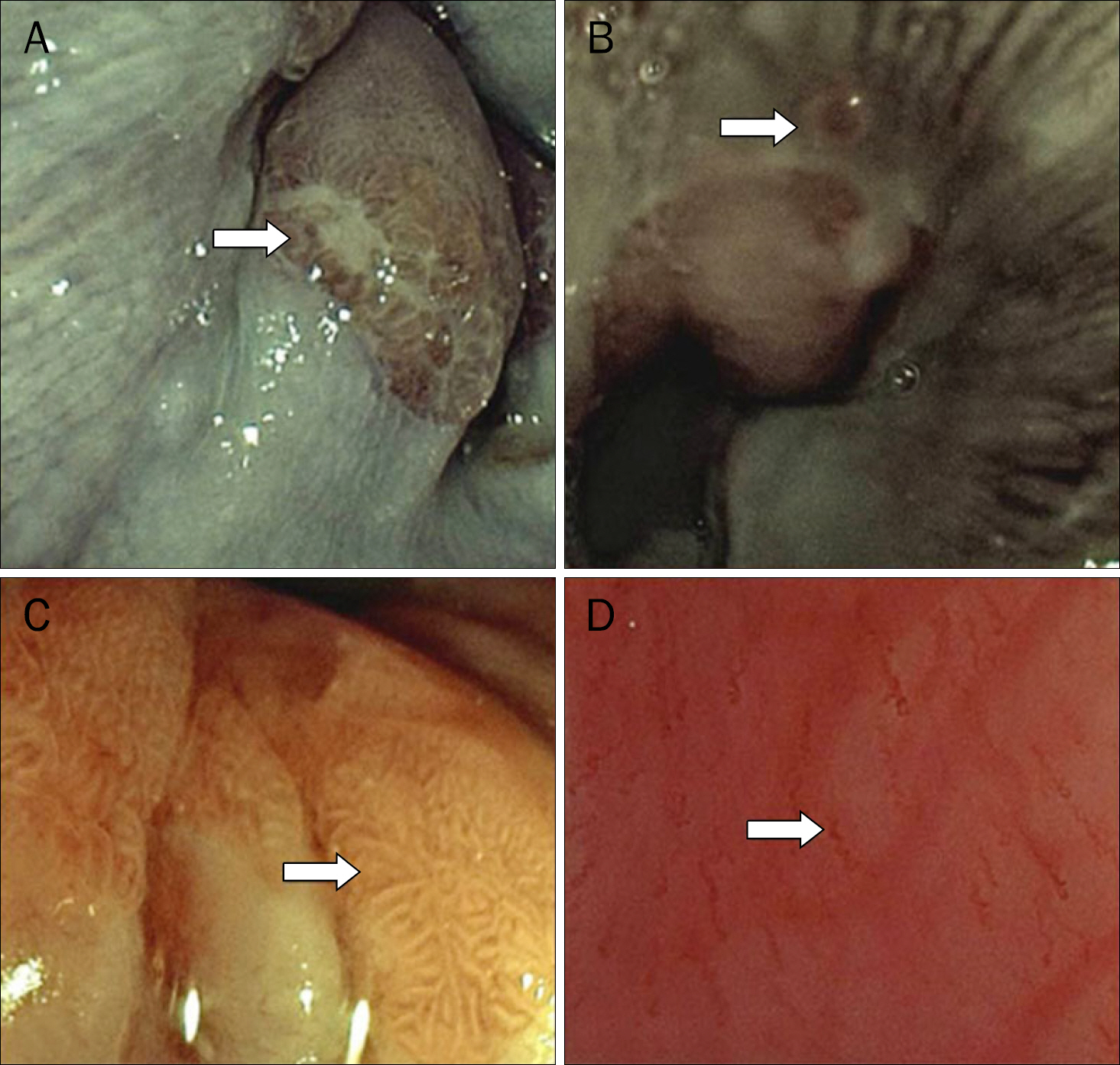
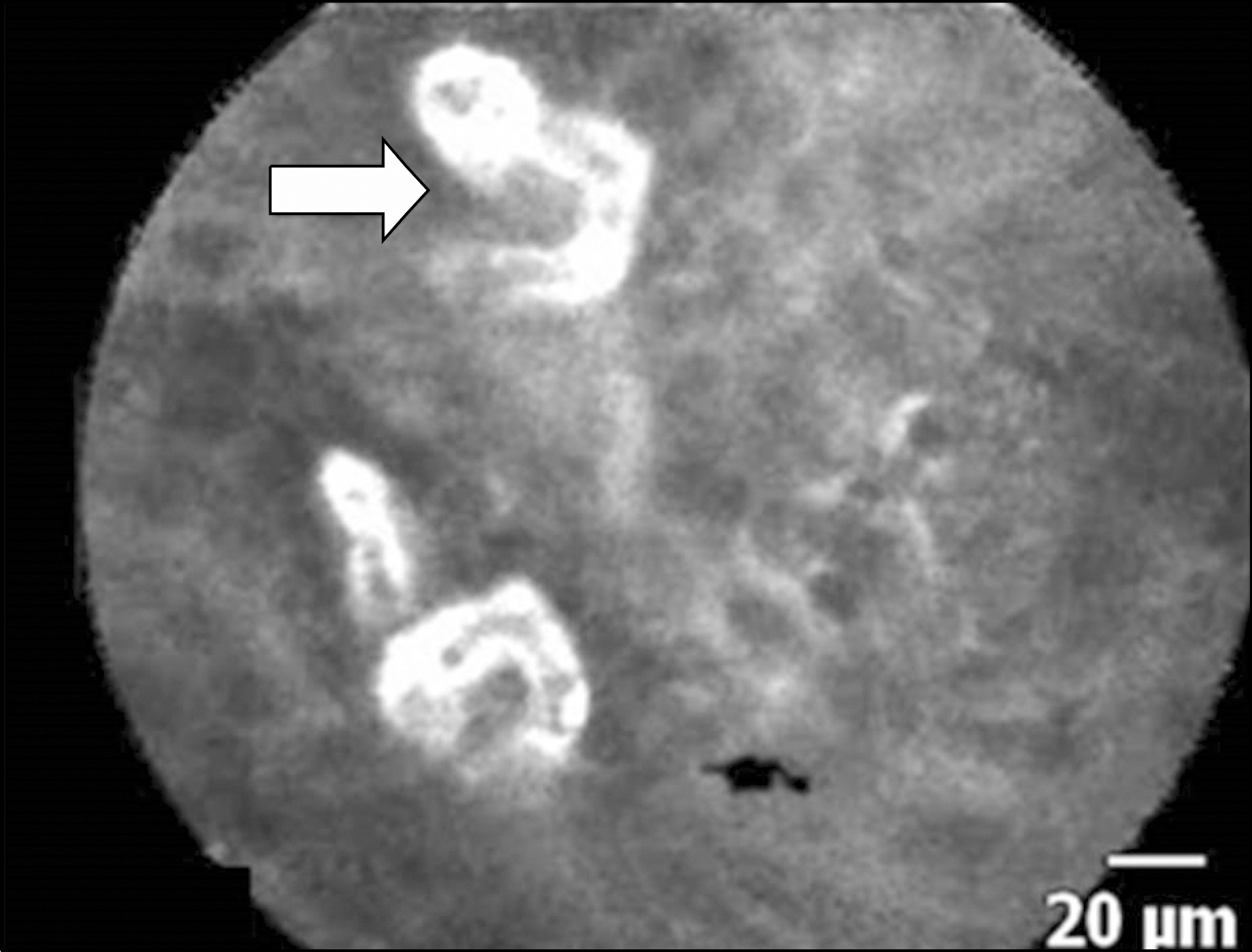
Flexible Spectral Imaging Color Enhancement and Probe-based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy in Minimal Change Esophageal Reflux Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand. Cholangiogram@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand.
- 3Thai Red Cross, Bangkok, Thailand.
- KMID: 2344489
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2016.68.1.29
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Although flexible spectral imaging color enhancement (FICE) can facilitate the diagnosis of minimal change esophageal reflux disease (MERD), the complicated diagnostic criteria cause suboptimal inter-observer agreement. Confocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) yields good diagnostic results but its inter-observer agreement has never been explored. This study compares the diagnostic value of magnifying FICE and probe-based CLE (pCLE) for MERD and evaluates the inter-observer agreement of both techniques.
METHODS
Thirty-six patients with suspected MERD and 18 asymptomatic controls were recruited. Magnifying FICE was used for evaluation of distal esophagus. pCLE counted the number of intrapapillary capillary loops (IPCLs) using more than five IPCLs in 500×500 micron area as a criterion for MERD diagnosis. The validity scores and interobserever agreement of both FICE and pCLE were assessed.
RESULTS
For FICE vs. pCLE, the accuracy was 79% vs. 87%, sensitivity 94% vs. 97%, specificity 50% vs. 66%, positive predictive value 79% vs. 85%, and negative predictive value 82% vs. 92%. Interobserver agreement of FICE was fair to substantial, whereas pCLE had substantial to almost perfect agreement.
CONCLUSIONS
Both FICE and pCLE have good operating characteristics and can facilitate the MERD diagnosis. However, among different observers, pCLE is more consistent on MERD diagnosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. El-Serag HB. Time trends of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:17–26.2. Ho KY, Chan YH, Kang JY. Increasing trend of reflux esophagitis and decreasing trend of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients from a multiethnic Asian country. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:1923–1928.
Article3. Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidencebased consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1900–1920. quiz 1943.
Article4. Moayyedi P, Talley NJ. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Lancet. 2006; 367:2086–2100.
Article5. Dent J. Microscopic esophageal mucosal injury in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:4–16.
Article6. Fass R, Fennerty MB, Vakil N. Nonerosive reflux disease–current concepts and dilemmas. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:303–314.7. Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA, Johansson S. Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut. 2005; 54:710–717.
Article8. Kiesslich R, Kanzler S, Vieth M, et al. Minimal change esophagitis: prospective comparison of endoscopic and histological markers between patients with nonerosive reflux disease and normal controls using magnifying endoscopy. Dig Dis. 2004; 22:221–227.
Article9. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999; 45:172–180.
Article10. Hoshihara Y, Hashimoto M. Endoscopic classification of reflux esophagitis. Nihon Rinsho. 2000; 58:1808–1812.11. Miwa H, Yokoyama T, Hori K, et al. Interobserver agreement in endoscopic evaluation of reflux esophagitis using a modified Los Angeles classification incorporating grades N and M: a validation study in a cohort of Japanese endoscopists. Dis Esophagus. 2008; 21:355–363.
Article12. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Mastracci L, et al. Microscopic esophagitis distinguishes patients with nonerosive reflux disease from those with functional heartburn. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:473–482.
Article13. Falk GW. Is conventional endoscopic identification of nonerosive reflux disease adequate? Digestion. 2008; 78(Suppl 1):17–23.
Article14. Osawa H, Yamamoto H. Present and future status of flexible spectral imaging color enhancement and blue laser imaging technology. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26(Suppl 1):105–115.
Article15. Miyasaka M, Hirakawa M, Nakamura K, et al. The endoscopic diagnosis of nonerosive reflux disease using flexible spectral imaging color enhancement image: a feasibility trial. Dis Esophagus. 2011; 24:395–400.
Article16. Kiesslich R, Lammersdorf K, Goetz M, et al. Microscopic changes in Non Erosive Reflux Disease (NERD) can be diagnosed during ongoing endoscopy by Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE). Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2006; 63:AB243.
Article17. Chu CL, Zhen YB, Lv GP, et al. Microalterations of esophagus in patients with nonerosive reflux disease: in-vivo diagnosis by confocal laser endomicroscopy and its relationship with gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:864–874.
Article18. Chaiteerakij R, Geratikornsupuk N, Tangmankongworakoon N, et al. Efficacy of intelligent chromo endoscopy for detection of minimal mucosal breaks in patients with typical reflux symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2008; 67:AB86.19. Ismail-Beigi F, Horton PF, Pope CE 2nd. Histological consequences of gastroesophageal reflux in man. Gastroenterology. 1970; 58:163–174.
Article20. Gaddam S, Mathur SC, Singh M, et al. Novel probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy criteria and interobserver agreement for the detection of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1961–1969.
Article21. Yoshida Y, Matsuda K, Sumiyama K, et al. A randomized crossover open trial of the adenoma miss rate for narrow band imaging (NBI) versus flexible spectral imaging color enhancement (FICE). Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013; 28:1511–1516.
Article22. Quang T, Schwarz RA, Dawsey SM, et al. A tablet-interfaced high-resolution microendoscope with automated image interpretation for real-time evaluation of esophageal squamous cell neoplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016. DOI: doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.03.1472. [Epub ahead of print].
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy and Molecular Imaging in Barrett Esophagus and Stomach
- Recent Advances in Image-enhanced Endoscopy
- High-Resolution Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Diagnosing Biliary Diseases
- Role of endoscopy in gastroesophageal reflux disease
- A Review of Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Pancreaticobiliary Disease