Clin Endosc.
2023 Nov;56(6):681-692. 10.5946/ce.2023.182.
Role of endoscopy in gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA
- 2Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
- 3Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, USA
- KMID: 2547888
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.182
Abstract
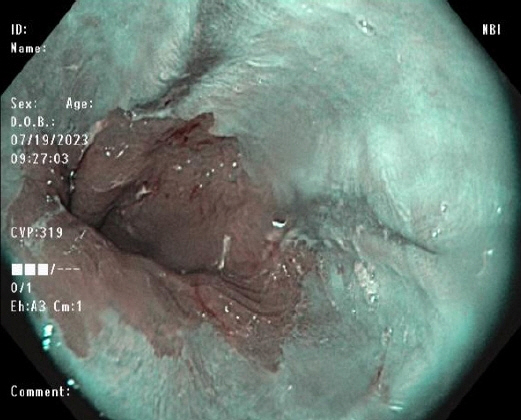
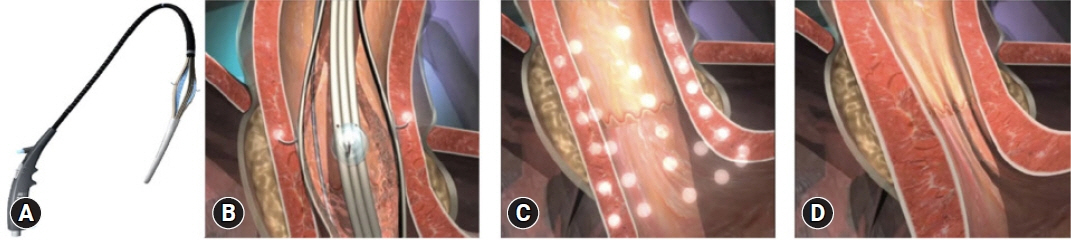
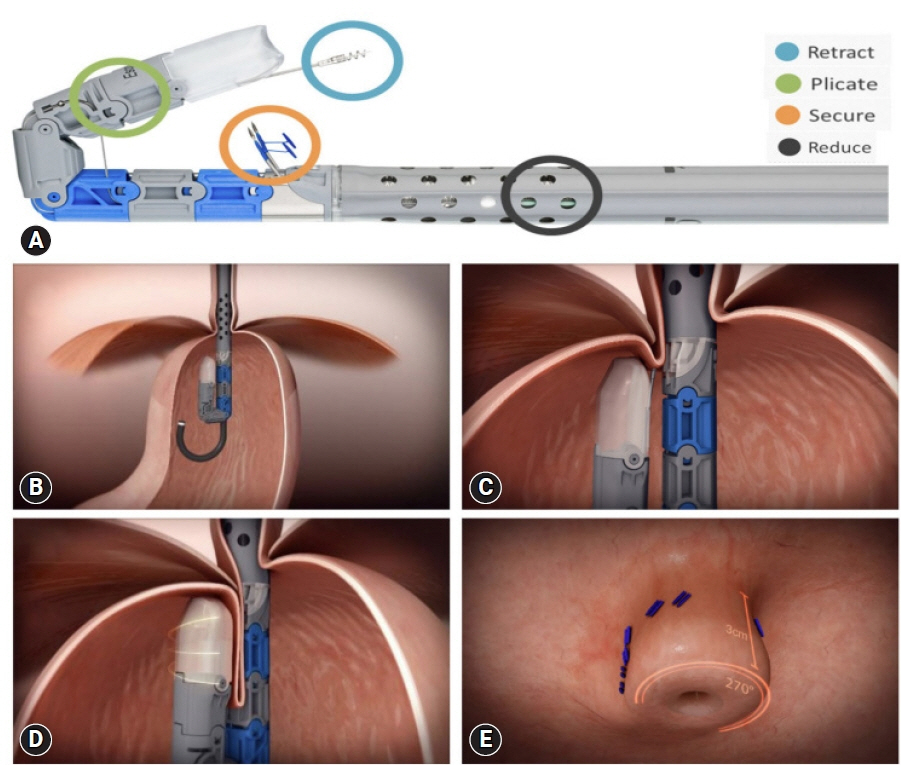
- In general, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is diagnosed clinically based on typical symptoms and/or response to proton pump inhibitor treatment. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is reserved for patients presenting with alarm symptoms, such as dysphagia, odynophagia, significant weight loss, gastrointestinal bleeding, or anorexia; those who meet the criteria for Barrett’s esophagus screening; those who report a lack or partial response to proton pump inhibitor treatment; and those with prior endoscopic or surgical anti-reflux interventions. Newer endoscopic techniques are primarily used to increase diagnostic yield and provide an alternative to medical or surgical treatment for GERD. The available endoscopic modalities for the diagnosis of GERD include conventional endoscopy with white-light imaging, high-resolution and high-magnification endoscopy, chromoendoscopy, image-enhanced endoscopy (narrow-band imaging, I- SCAN, flexible spectral imaging color enhancement, blue laser imaging, and linked color imaging), and confocal laser endomicroscopy. Endoscopic techniques for treating GERD include esophageal radiofrequency energy delivery/Stretta procedure, transoral incisionless fundoplication, and endoscopic full-thickness plication. Other novel techniques include anti-reflux mucosectomy, peroral endoscopic cardiac constriction, endoscopic submucosal dissection, and endoscopic band ligation. Currently, many of the new endoscopic techniques are not widely available, and their use is limited to centers of excellence.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1900–1920.
Article2. Nirwan JS, Hasan SS, Babar ZU, et al. Global prevalence and risk factors of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD): systematic review with meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:5814.
Article3. Delshad SD, Almario CV, Chey WD, et al. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and proton pump inhibitor-refractory symptoms. Gastroenterology. 2020; 158:1250–1261.
Article4. Tack J, Becher A, Mulligan C, et al. Systematic review: the burden of disruptive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease on health-related quality of life. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 35:1257–1266.
Article5. Ghoneim S, Wang J, El Hage Chehade N, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the proton pump inhibitor test in gastroesophageal reflux disease and noncardiac chest pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2023; 57:380–388.
Article6. Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: the Lyon Consensus. Gut. 2018; 67:1351–1362.
Article7. Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH, et al. ACG clinical guideline for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022; 117:27–56.
Article8. Poh CH, Gasiorowska A, Navarro-Rodriguez T, et al. Upper GI tract findings in patients with heartburn in whom proton pump inhibitor treatment failed versus those not receiving antireflux treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:28–34.
Article9. Qumseya BJ, Bukannan A, Gendy S, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence and risk factors for Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019; 90:707–717.
Article10. Fass R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. N Engl J Med. 2022; 387:1207–1216.
Article11. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999; 45:172–180.
Article12. Hoshihara Y, Hashimoto M. Endoscopic classification of reflux esophagitis. Nihon Rinsho. 2000; 58:1808–1812.13. Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, et al. The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for Barrett's esophagus: the Prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1392–1399.
Article14. Visaggi P, Del Corso G, Gyawali CP, et al. Ambulatory pH-impedance findings confirm that grade B esophagitis provides objective diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023; 118:794–801.
Article15. Bond A, Burkitt MD, Cox T, et al. Dual-focus magnification, high-definition endoscopy improves pathology detection in direct-to-test diagnostic upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2017; 26:19–24.
Article16. Chaiteerakij R, Rerknimitr R, Kullavanijaya P. Role of digital chromoendoscopy in detecting minimal change esophageal reflux disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 2:121–129.
Article17. Qumseya BJ, Wang H, Badie N, et al. Advanced imaging technologies increase detection of dysplasia and neoplasia in patients with Barrett's esophagus: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1562–1570.
Article18. East JE, Vleugels JL, Roelandt P, et al. Advanced endoscopic imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology Review. Endoscopy. 2016; 48:1029–1045.
Article19. Tseng PH, Chen CC, Chiu HM, et al. Performance of narrow band imaging and magnification endoscopy in the prediction of therapeutic response in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011; 45:501–506.
Article20. Mannath J, Subramanian V, Hawkey CJ, et al. Narrow band imaging for characterization of high grade dysplasia and specialized intestinal metaplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:351–359.
Article21. Hajelssedig OE, Zorron Cheng Tao Pu L, Thompson JY, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of narrow-band imaging endoscopy with targeted biopsies compared with standard endoscopy with random biopsies in patients with Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021; 36:2659–2671.
Article22. Sharma P, Hawes RH, Bansal A, et al. Standard endoscopy with random biopsies versus narrow band imaging targeted biopsies in Barrett's oesophagus: a prospective, international, randomised controlled trial. Gut. 2013; 62:15–21.
Article23. Netinatsunton N, Sottisuporn J, Attasaranya S, et al. i-Scan detection of minimal change esophagitis in dyspeptic patients with or without gastroesophageal reflux disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016; 16:4.
Article24. Kim MS, Choi SR, Roh MH, et al. Efficacy of I-scan endoscopy in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease with minimal change. Clin Endosc. 2011; 44:27–32.
Article25. Hoffman A, Basting N, Goetz M, et al. High-definition endoscopy with i-Scan and Lugol's solution for more precise detection of mucosal breaks in patients with reflux symptoms. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:107–112.
Article26. Negreanu L, Preda CM, Ionescu D, et al. Progress in digestive endoscopy: flexible spectral imaging colour enhancement (FICE). Technical review. J Med Life. 2015; 8:416–422.27. Lee SP, Kae SH, Jang HJ, et al. Inter-observer variability of experts and trainees for the diagnosis of reflux esophagitis: comparison of linked color imaging, blue laser imaging, and white light imaging. J Dig Dis. 2021; 22:425–432.
Article28. Takeda T, Nagahara A, Ishizuka K, et al. Improved visibility of Barrett's esophagus with linked color imaging: inter- and intra-rater reliability and quantitative analysis. Digestion. 2018; 97:183–194.
Article29. Takeda T, Asaoka D, Abe D, et al. Linked color imaging improves visibility of reflux esophagitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020; 20:356.
Article30. Borovicka J, Fischer J, Neuweiler J, et al. Autofluorescence endoscopy in surveillance of Barrett's esophagus: a multicenter randomized trial on diagnostic efficacy. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:867–872.
Article31. ASGE Technology Committee. Confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80:928–938.32. Kiesslich R, Gossner L, Goetz M, et al. In vivo histology of Barrett's esophagus and associated neoplasia by confocal laser endomicroscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006; 4:979–987.
Article33. Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Di Lorenzo C, et al. The spectrum of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis beyond infancy: a clinical series of 30 children. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95:1422–1430.
Article34. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Mastracci L, et al. Microscopic esophagitis distinguishes patients with non-erosive reflux disease from those with functional heartburn. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:473–482.
Article35. Kandulski A, Jechorek D, Caro C, et al. Histomorphological differentiation of non-erosive reflux disease and functional heartburn in patients with PPI-refractory heartburn. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 38:643–651.
Article36. Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, et al. Diagnosis and management of Barrett's esophagus: an updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022; 117:559–587.
Article37. Fass R. Endoscopic approaches for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2019; 15:555–557.38. Pearl J, Pauli E, Dunkin B, et al. SAGES endoluminal treatments for GERD. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:3783–3790.
Article39. Triadafilopoulos G. Stretta: a valuable endoscopic treatment modality for gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:7730–7738.
Article40. Shibli F, Fass R. Endoscopic anti-reflux procedures: ready for clinical use? Curr Treat Options Gastro. 2021; 19:399–420.
Article41. Mann R, Gajendran M, Perisetti A, et al. Advanced endoscopic imaging and interventions in GERD: an update and future directions. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:728696.
Article42. Fass R, Cahn F, Scotti DJ, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled and prospective cohort efficacy studies of endoscopic radiofrequency for treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc. 2017; 31:4865–4882.
Article43. American Foregut Society Clinical Practice Committee TIF Working Group, Brewer Gutierrez OI, Choi D, et al. American Foregut Society white paper on transoral incisionless fundoplication. Foregut. 2023; 26345161231170788.44. Ihde GM. The evolution of TIF: transoral incisionless fundoplication. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020; 13:1756284820924206.
Article45. Chang KJ. Endoscopic foregut surgery and interventions: the future is now. The state-of-the-art and my personal journey. World J Gastroenterol. 2019; 25:1–41.
Article46. Håkansson B, Montgomery M, Cadiere GB, et al. Randomised clinical trial: transoral incisionless fundoplication vs. sham intervention to control chronic GERD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 42:1261–1270.
Article47. Hunter JG, Kahrilas PJ, Bell RC, et al. Efficacy of transoral fundoplication vs omeprazole for treatment of regurgitation in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015; 148:324–333.
Article48. Trad KS, Barnes WE, Simoni G, et al. Transoral incisionless fundoplication effective in eliminating GERD symptoms in partial responders to proton pump inhibitor therapy at 6 months: the TEMPO Randomized Clinical Trial. Surg Innov. 2015; 22:26–40.
Article49. Trad KS, Barnes WE, Prevou ER, et al. The TEMPO trial at 5 years: transoral fundoplication (TIF 2.0) is safe, durable, and cost-effective. Surg Innov. 2018; 25:149–157.
Article50. NCT04457193. Outcomes after transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) following successful endoscopic ablation for Barrett's esophagus [Internet]. Bethesda: Clinical Trial.gov;2020. [cited 2023 Jul 24]. Available from: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04457193.51. Kalapala R, Karyampudi A, Nabi Z, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of PPI-dependent GERD: results from a randomised, sham controlled trial. Gut. 2022; 71:686–694.
Article52. Zacherl J, Roy-Shapira A, Bonavina L, et al. Endoscopic anterior fundoplication with the Medigus Ultrasonic Surgical Endostapler (MUSE™) for gastroesophageal reflux disease: 6-month results from a multi-center prospective trial. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:220–229.
Article53. Peng L, Wan R, Chen S, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic anterior fundoplication with a novel ultrasonic surgical endostapler for gastroesophageal reflux disease: six-month results from a multicenter prospective trial. Endosc Ultrasound. 2023; 12:128–134.
Article54. Testoni PA, Testoni S, Mazzoleni G, et al. Transoral incisionless fundoplication with an ultrasonic surgical endostapler for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: 12-month outcomes. Endoscopy. 2020; 52:469–473.
Article55. Han J, Chin M, Fortinsky KJ, et al. Endoscopic augmentation of gastroesophageal junction using a full-thickness endoscopic suturing device. Endosc Int Open. 2018; 6:E1120–E1125.
Article56. Inoue H, Ito H, Ikeda H, et al. Anti-reflux mucosectomy for gastroesophageal reflux disease in the absence of hiatus hernia: a pilot study. Ann Gastroenterol. 2014; 27:346–351.57. Kuribayashi S, Hosaka H, Nakamura F, et al. The role of endoscopy in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. DEN Open. 2022; 2:e86.
Article58. Yoo IK, Ko WJ, Kim HS, et al. Anti-reflux mucosectomy using a cap-assisted endoscopic mucosal resection method for refractory gastroesophageal disease: a prospective feasibility study. Surg Endosc. 2020; 34:1124–1131.59. Hedberg HM, Kuchta K, Ujiki MB. First experience with banded anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) for GERD: feasibility, safety, and technique (with video). J Gastrointest Surg. 2019; 23:1274–1278.60. Garg R, Mohammed A, Singh A, et al. Anti-reflux mucosectomy for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open. 2022; 10:E854–E864.61. Hu HQ, Li HK, Xiong Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic cardial constriction in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e0169.62. Li ZT, Ji F, Han XW, et al. Endoscopic cardial constriction with band ligation in the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: a preliminary feasibility study. Surg Endosc. 2021; 35:4035–4041.63. Ota K, Takeuchi T, Harada S, et al. A novel endoscopic submucosal dissection technique for proton pump inhibitor-refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2014; 49:1409–1413.64. Ota K, Takeuchi T, Kojima Y, et al. Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastroesophageal reflux disease (ESD-G) for medication-refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: 35 cases underwent ESD-G including 15 cases followed more than 5 years. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021; 21:432.65. Seleem WM, Hanafy AS, Mohamed SI. Endoscopic management of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018; 53:390–397.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiologic studies on gastroesophageal reflux
- Nonerosive Reflux Disease
- Incidence of Esophagitis in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- How Is the Autonomic Nerve Function Different Between Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Alone and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease With Diabetes Mellitus Neuropathy?
- Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer and Reflux Disease