Korean Circ J.
2016 May;46(3):374-383. 10.4070/kcj.2016.46.3.374.
Inter-Arm Difference in Brachial Blood Pressure in the General Population of Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Public Health, Yonsei University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hckim@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4National Academy of Agricultural Science, Rural Development Administration, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2344450
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.3.374
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES
We investigated the inter-arm difference in blood pressure of the general Korean population to identify associated factors.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
A total of 806 participants aged 30 to 64 years without history of major cardiovascular disease were analyzed in this cross-sectional study. They participated in the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Etiology Research Center cohort study that began in 2013. Brachial blood pressure was measured simultaneously for both arms using an automated oscillometric device equipped with two cuffs in seated position. After five minutes of rest, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were measured three times. The average of the three measurements was used for analysis. Multivariate logistic regression models were used to identify factors associated with inter-arm differences in blood pressure.
RESULTS
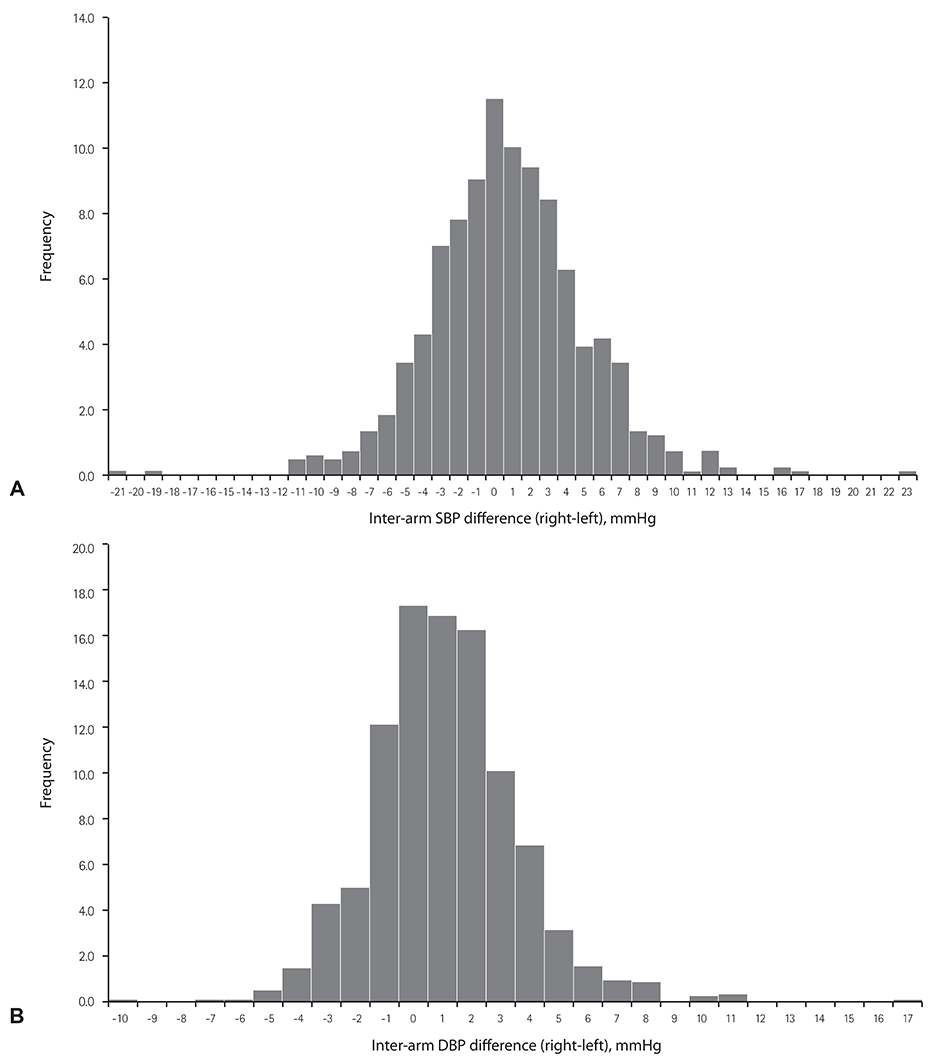
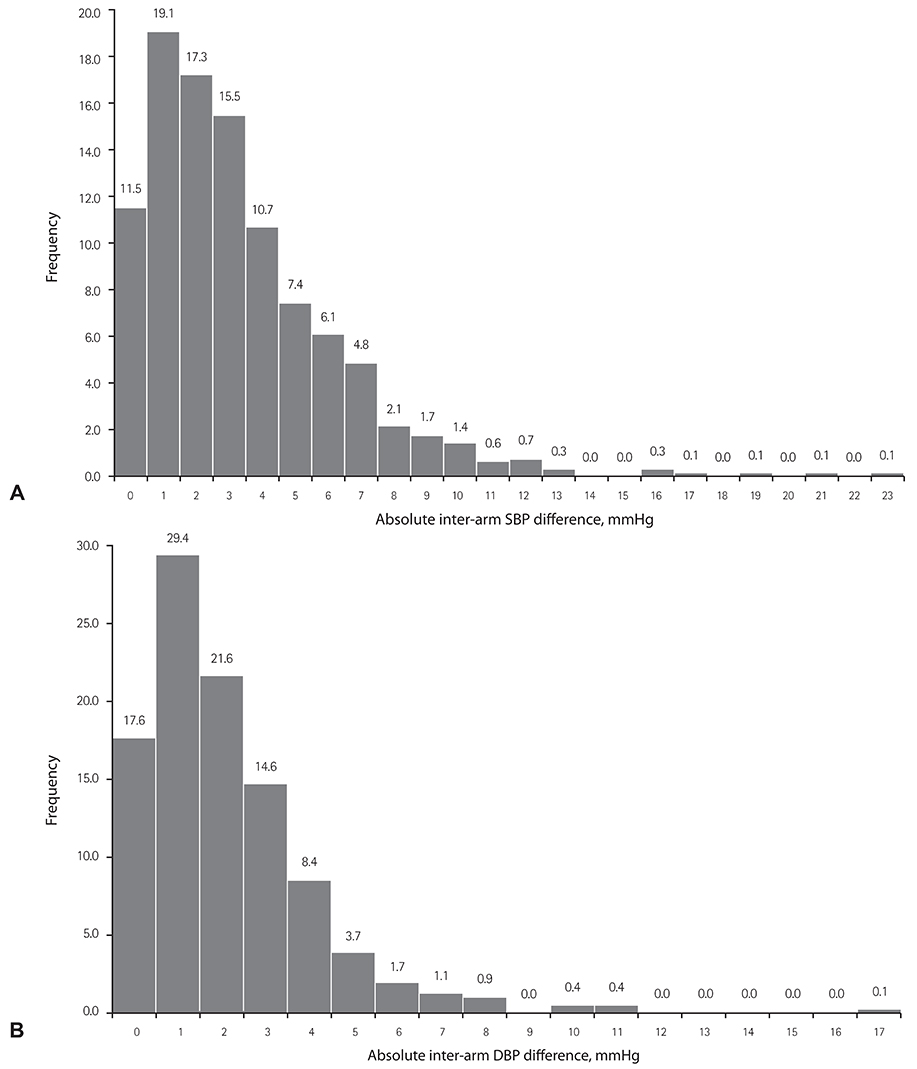
The mean inter-arm difference was 3.3 mmHg for SBP and 2.0 mmHg for DBP. Large inter-arm differences (≥10 mmHg) in SBP and in DBP were found in 3.7% and 0.9% of subjects, respectively. A large inter-arm difference in SBP was associated with mean SBP (p=0.002) and C-reactive protein (p=0.014) while a large inter-arm different in DBP was only associated with body mass index (p=0.015). Sex, age, and anti-hypertensive medication use were not associated with differences in inter-arm blood pressure.
CONCLUSION
Large inter-arm difference in blood pressure is only present in a small portion of healthy Korean adults. Our findings suggest that high SBP, chronic inflammation, and obesity may be associated with larger difference in inter-arm blood pressure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Implications of Simultaneously Measured Inter-Arm Difference
Jinho Shin
Korean Circ J. 2019;49(3):278-279. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2018.0416.Cohort Profile: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort in Korea
Jee-Seon Shim, Bo Mi Song, Jung Hyun Lee, Seung Won Lee, Ji Hye Park, Dong Phil Choi, Myung Ha Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungha Park, Won-Woo Lee, Yoosik Youm, Eui-Cheol Shin, Hyeon Chang Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(8):804-810. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.8.804.
Reference
-
1. Clark CE, Campbell JL, Evans PH, Millward A. Prevalence and clinical implications of the inter-arm blood pressure difference: a systematic review. J Hum Hypertens. 2006; 20:923–931.2. Clark CE, Taylor RS, Shore AC, Ukoumunne OC, Campbell JL. Association of a difference in systolic blood pressure between arms with vascular disease and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012; 379:905–914.3. Weinberg I, Gona P, O’Donnell CJ, Jaff MR, Murabito JM. The systolic blood pressure difference between arms and cardiovascular disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Med. 2014; 127:209–215.4. Tak YJ, Kim YJ, Lee SY, et al. Association of inter-arm blood pressure difference with atherosclerosis in patients without cardiovascular diseases. J Korean Soc Hypertens. 2013; 19:71–80.5. Clark CE, Campbell JL, Powell RJ. The interarm blood pressure difference as predictor of cardiovascular events in patients with hypertension in primary care: cohort study. J Hum Hypertens. 2007; 21:633–638.6. Clark CE, Taylor RS, Shore AC, Campbell JL. The difference in blood pressure readings between arms and survival: primary care cohort study. BMJ. 2012; 344:e1327.7. Arnett DK, Tang W, Province MA, et al. Interarm differences in seated systolic and diastolic blood pressure: the Hypertension Genetic Epidemiology Network study. J Hypertens. 2005; 23:1141–1147.8. Clark CE, Steele AM, Taylor RS, Shore AC, Ukoumunne OC, Campbell JL. Interarm blood pressure difference in people with diabetes: measurement and vascular and mortality implications a cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1613–1620.9. Johansson JK, Puukka PJ, Jula AM. Interarm blood pressure difference and target organ damage in the general population. J Hypertens. 2014; 32:260–266.10. Su HM, Lin TH, Hsu PC, et al. Association of interarm systolic blood pressure difference with atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e41173.11. Kim J, Song TJ, Song D, et al. Interarm blood pressure difference and mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2013; 80:1457–1464.12. Clark CE, Campbell JL, Powell RJ, Thompson JF. The inter-arm blood pressure difference and peripheral vascular disease: cross-sectional study. Fam Pract. 2007; 24:420–426.13. Agarwal NK, Agarwal SK. Inter-arm systolic blood pressure difference of 15 mm Hg and its relationship to CRP and other cardiovascular risk markers. History (Lond). 2013; 7:9–12.14. Kimura A, Hashimoto J, Watabe D, et al. Patient characteristics and factors associated with inter-arm difference of blood pressure measurements in a general population in Ohasama, Japan. J Hypertens. 2004; 22:2277–2283.15. Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R. Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation. 1986; 74:1399–1406.16. Cho HM, Kang DR, Kim HC, Oh SM, Kim BK, Suh I. Association between fibrinogen and carotid atherosclerosis according to smoking status in a Korean male population. Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56:921–927.17. Petrie JC, O’Brien ET, Littler WA, de Swiet M. Recommendations on blood pressure measurement. [Clin Res Ed]. BMJ. 1986; 293:611–615.18. Eguchi K, Yacoub M, Jhalani J, Gerin W, Schwartz JE, Pickering TG. Consistency of blood pressure differences between the left and right arms. Arch Intern Med. 2007; 167:388–393.19. Fonseca-Reyes S, Forsyth-MacQuarrie AM, García de Alba-García JE. Simultaneous blood pressure measurement in both arms in hypertensive and nonhypertensive adult patients. Blood Press Monit. 2012; 17:149–154.20. Cassidy P, Jones K. A study of inter-arm blood pressure differences in primary care. J Hum Hypertens. 2001; 15:519–522.21. Maeda S. Blood pressure differences between arms and association of dominant hands with blood pressure differences and carotid atherosclerosis. Blood Press Monit. 2013; 18:133–137.22. Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, et al. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals part: 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension. 2005; 45:142–161.23. Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2007; 28:1462–1536.24. Verberk WJ, Kessels AG, Thien T. Blood pressure measurement method and inter-arm differences: a meta-analysis. Am J Hypertens. 2011; 24:1201–1208.25. Reeves RA. The rational clinical examination. Does this patient have hypertension? How to measure blood pressure. JAMA. 1995; 273:1211–1218.26. Wingfield D, Freeman GK, Bulpitt CJ; General Practice Hypertension Study Group (GPHSG). Selective recording in blood pressure readings may increase subsequent mortality. QJM. 2002; 95:571–577.27. Harrison EG Jr, Roth GM, Hines EA Jr. Bilateral indirect and direct arterial pressures. Circulation. 1960; 22:419–436.28. Amsterdam B, Amsterdam AL. Disparity in blood pressures in both arms in normals and hypertensives and its clinical significance. N Y State J Med. 1943; 43:2294–2300.29. Pepys MB. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981; 1:653–657.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessment of Disparity in the Blood Pressure of Both Arms
- Association of Inter-arm Blood Pressure Difference with Atherosclerosis in Patients without Cardiovascular Diseases
- Comparison between Right and Left Upper Arms in Detection of Hypertension
- Ankle-brachial blood pressure differences in the beach-chair position of the shoulder surgery
- Ankle-brachial blood pressure differences before and during anesthesia