Korean J Radiol.
2015 Dec;16(6):1266-1275. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1266.
Are Irregular Hypoechoic Breast Masses on Ultrasound Always Malignancies?: A Pictorial Essay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan 54538, Korea. khw@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Wonkwang University Hospital, Iksan 54538, Korea.
- KMID: 2344281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1266
Abstract
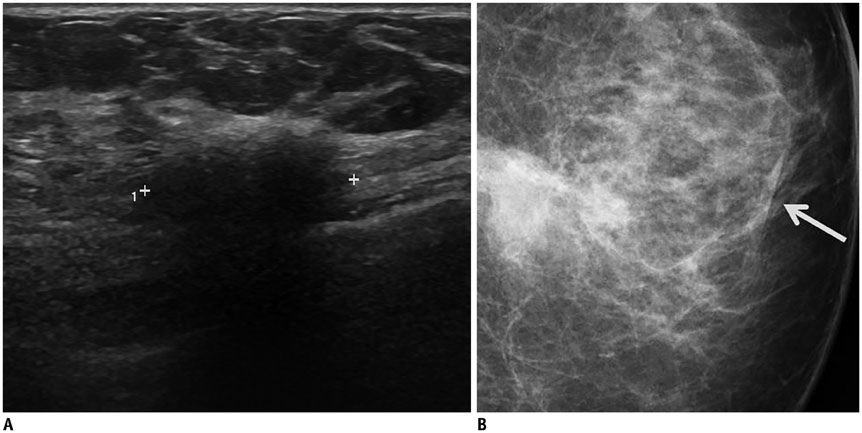
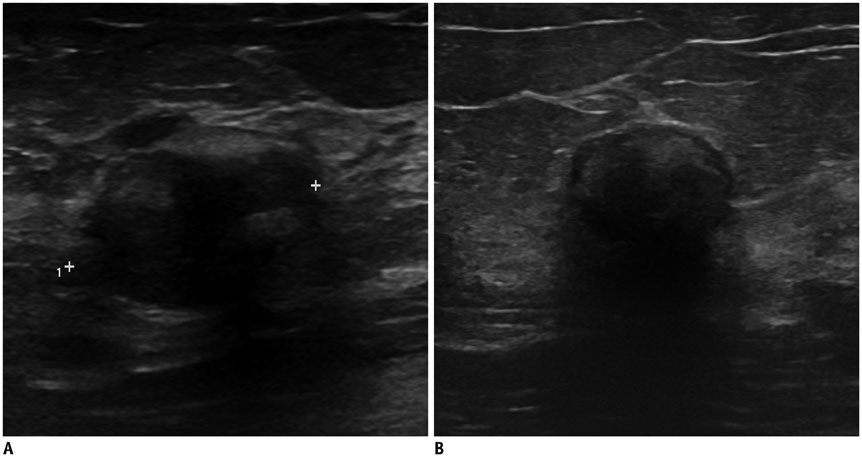
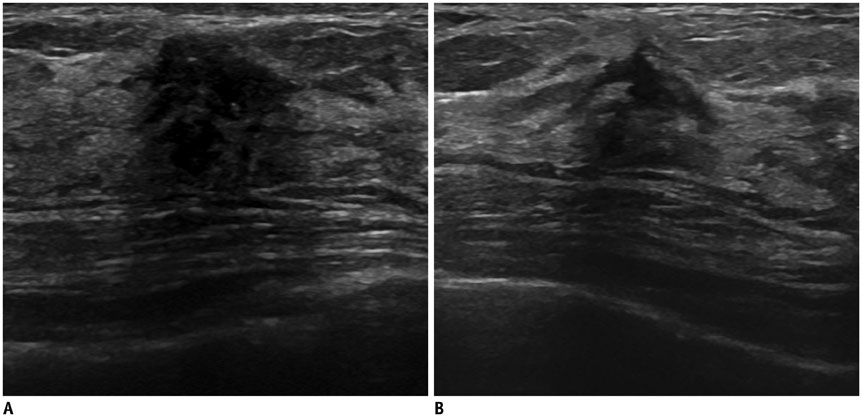
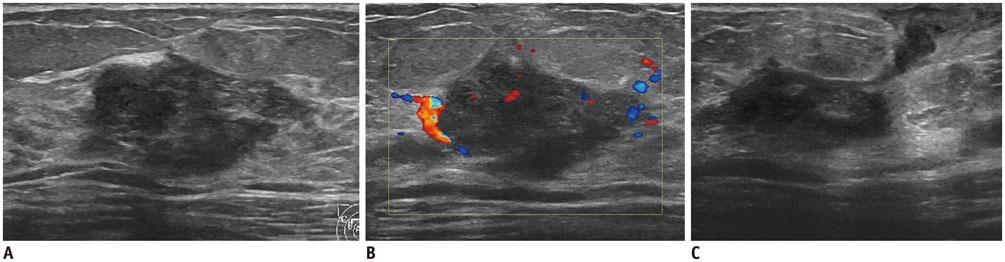
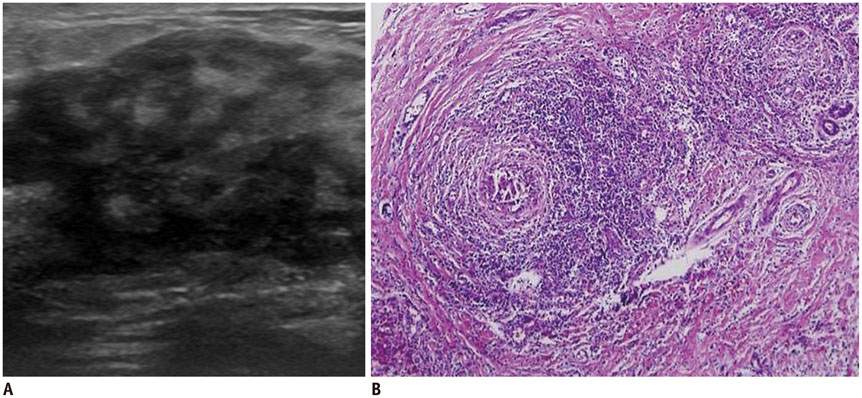
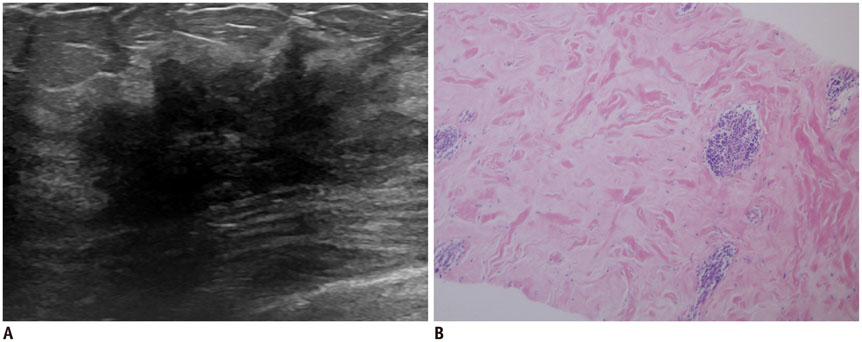
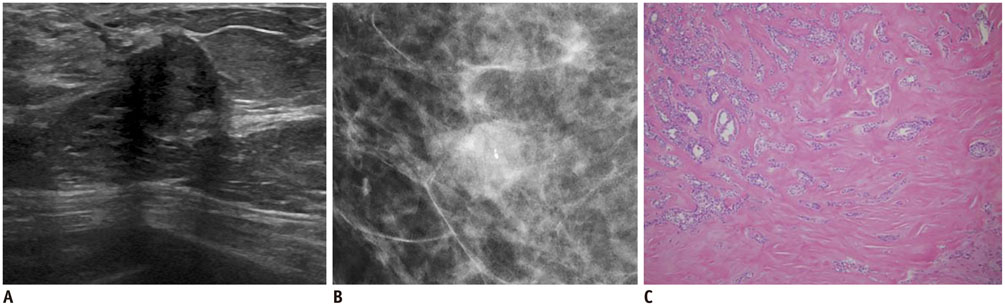
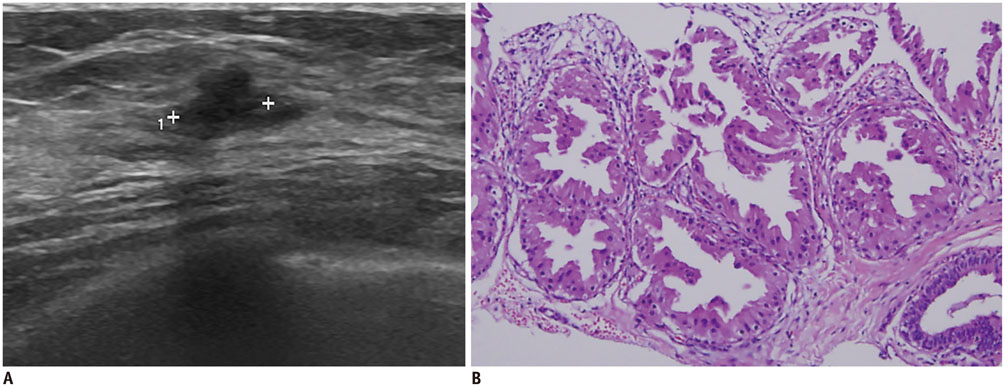
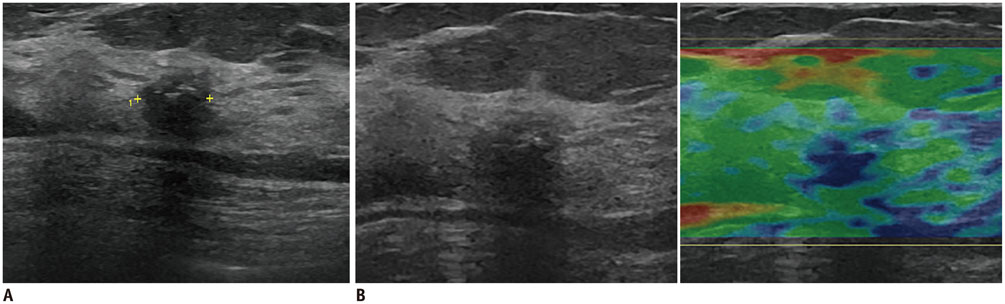
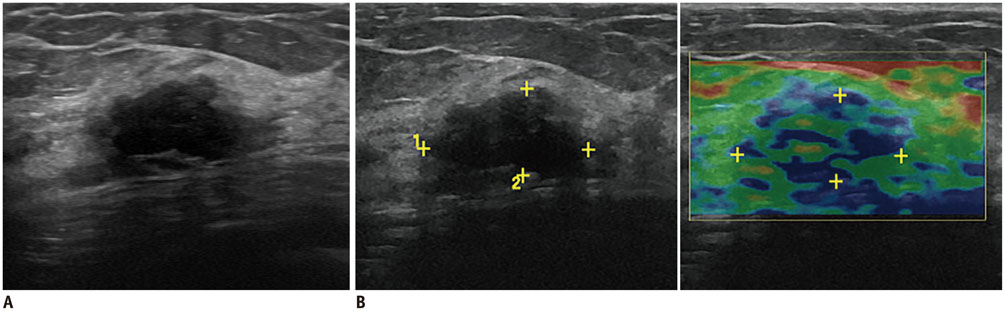
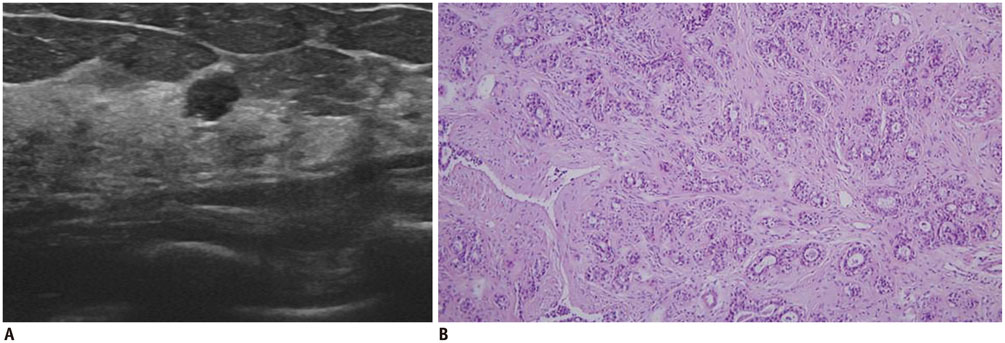
- Irregular hypoechoic masses in the breast do not always indicate malignancies. Many benign breast diseases present with irregular hypoechoic masses that can mimic carcinoma on ultrasonography. Some of these diseases such as inflammation and trauma-related breast lesions could be suspected from a patient's symptoms and personal history. Careful ultrasonographic examination and biopsy could help to differentiate these from malignancies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess/ultrasonography
Breast Diseases/pathology
Breast Neoplasms/pathology/*ultrasonography
Carcinoma/pathology/ultrasonography
Female
Fibroadenoma/pathology/ultrasonography
Fibrocystic Breast Disease/pathology/ultrasonography
Granulomatous Mastitis/pathology/ultrasonography
Humans
Ultrasonography, Mammary
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Imaging Features of Inflammatory Breast Disorders: A Pictorial Essay
Po Wey Leong, Niketa Chandrakant Chotai, Supriya Kulkarni
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(1):5-14. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.5.
Reference
-
1. Mendelson EB, Böhm-Vélez M, Berg WA, et al. ACR BIRADS® Ultrasound. ACR BI-RADS® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston, VA: American College of Radiology;2013.2. Raza S, Goldkamp AL, Chikarmane SA, Birdwell RL. US of breast masses categorized as BI-RADS 3, 4, and 5: pictorial review of factors influencing clinical management. Radiographics. 2010; 30:1199–1213.3. Taskin F, Koseoglu K, Ozbas S, Erkus M, Karaman C. Sonographic features of histopathologically benign solid breast lesions that have been classified as BI-RADS 4 on sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012; 40:261–265.4. Raza S, Chikarmane SA, Neilsen SS, Zorn LM, Birdwell RL. BI-RADS 3, 4, and 5 lesions: value of US in management--follow-up and outcome. Radiology. 2008; 248:773–781.5. Han BK, Choe YH, Ko YH, Nam SJ, Yang JH. Foreign body granulomas of the breast presenting as bilateral spiculated masses. Korean J Radiol. 2001; 2:113–116.6. Tez S, Sen M, Yenidünya S, Tez M. Foreign body granuloma: a mimic of breast carcinoma. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2009; 110:366–367.7. Wakabayashi M, Reid JD, Bhattacharjee M. Foreign body granuloma caused by prior gunshot wound mimicking malignant breast mass. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 173:321–322.8. Taboada JL, Stephens TW, Krishnamurthy S, Brandt KR, Whitman GJ. The many faces of fat necrosis in the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:815–825.9. Crystal P, Bukhanov K. Sonographic findings of palpable isoechoic breast fat necrosis: look for skin integrity. J Ultrasound Med. 2005; 24:105–107.10. Soo MS, Kornguth PJ, Hertzberg BS. Fat necrosis in the breast: sonographic features. Radiology. 1998; 206:261–269.11. Chala LF, de Barros N, de Camargo Moraes P, Endo E, Kim SJ, Pincerato KM, et al. Fat necrosis of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004; 33:106–126.12. Franquet T, De Miguel C, Cozcolluela R, Donoso L. Spiculated lesions of the breast: mammographic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 1993; 13:841–852.13. Shaheen R, Schimmelpenninck CA, Stoddart L, Raymond H, Slanetz PJ. Spectrum of diseases presenting as architectural distortion on mammography: multimodality radiologic imaging with pathologic correlation. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2011; 32:351–362.14. An YY, Kim SH, Cha ES, Kim HS, Kang BJ, Park CS, et al. Diffuse infiltrative lesion of the breast: clinical and radiologic features. Korean J Radiol. 2011; 12:113–121.15. Dixon JM, Ravisekar O, Chetty U, Anderson TJ. Periductal mastitis and duct ectasia: different conditions with different aetiologies. Br J Surg. 1996; 83:820–822.16. Nicholson BT, Harvey JA, Cohen MA. Nipple-areolar complex: normal anatomy and benign and malignant processes. Radiographics. 2009; 29:509–523.17. Nguyen SL, Doyle AJ, Symmans PJ. Interstitial fluid and hypoechoic wall: two sonographic signs of breast abscess. J Clin Ultrasound. 2000; 28:319–324.18. Taylor GB, Paviour SD, Musaad S, Jones WO, Holland DJ. A clinicopathological review of 34 cases of inflammatory breast disease showing an association between corynebacteria infection and granulomatous mastitis. Pathology. 2003; 35:109–119.19. Gurleyik G, Aktekin A, Aker F, Karagulle H, Saglamc A. Medical and surgical treatment of idiopathic granulomatous lobular mastitis: a benign inflammatory disease mimicking invasive carcinoma. J Breast Cancer. 2012; 15:119–123.20. Cho SH, Park SH. Mimickers of breast malignancy on breast sonography. J Ultrasound Med. 2013; 32:2029–2036.21. Gautier N, Lalonde L, Tran-Thanh D, El Khoury M, David J, Labelle M, et al. Chronic granulomatous mastitis: imaging, pathology and management. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 82:e165–e175.22. Logan WW, Hoffman NY. Diabetic fibrous breast disease. Radiology. 1989; 172:667–670.23. Camuto PM, Zetrenne E, Ponn T. Diabetic mastopathy: a report of 5 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Surg. 2000; 135:1190–1193.24. Francisco C, Júlio C, Fontes AL, Silveira Reis I, Fernandes R, Valadares S, et al. Diabetic mastopathy: a case report. Clin Imaging. 2012; 36:829–832.25. Mak CW, Chou CK, Chen SY, Lee PS, Chang JM. Case report: diabetic mastopathy. Br J Radiol. 2003; 76:192–194.26. Tas¸kin F, Köseoğlu K, Unsal A, Erkus¸ M, Ozbas¸ S, Karaman C. Sclerosing adenosis of the breast: radiologic appearance and efficiency of core needle biopsy. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2011; 17:311–316.27. Westenend PJ, Liem SJ. Core biopsy of nodular adenosis of the breast can lead to underdiagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:1596.28. Liberman L. Clinical management issues in percutaneous core breast biopsy. Radiol Clin North Am. 2000; 38:791–807.29. Wellings SR, Alpers CE. Apocrine cystic metaplasia: subgross pathology and prevalence in cancer-associated versus random autopsy breasts. Hum Pathol. 1987; 18:381–386.30. Bussolati G, Cattani MG, Gugliotta P, Patriarca E, Eusebi V. Morphologic and functional aspects of apocrine metaplasia in dysplastic and neoplastic breast tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986; 464:262–274.31. Warner JK, Kumar D, Berg WA. Apocrine metaplasia: mammographic and sonographic appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:1375–1379.32. Drukker BH. Fibrocystic change of the breast. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1994; 37:903–915.33. Love SM, Gelman RS, Silen W. Sounding board. Fibrocystic "disease" of the breast--a nondisease? N Engl J Med. 1982; 307:1010–1014.34. Chen JH, Nalcioglu O, Su MY. Fibrocystic change of the breast presenting as a focal lesion mimicking breast cancer in MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 28:1499–1505.35. Foster ME, Garrahan N, Williams S. Fibroadenoma of the breast: a clinical and pathological study. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1988; 33:16–19.36. Masciadri N, Ferranti C. Benign breast lesions: ultrasound. J Ultrasound. 2011; 14:55–65.37. Goel NB, Knight TE, Pandey S, Riddick-Young M, de Paredes ES, Trivedi A. Fibrous lesions of the breast: imaging-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2005; 25:1547–1559.38. Fornage BD, Lorigan JG, Andry E. Fibroadenoma of the breast: sonographic appearance. Radiology. 1989; 172:671–675.39. Tarallo V, Canepari E, Bortolotto C. Intraductal papilloma of the breast: a case report. J Ultrasound. 2012; 15:99–101.40. Brookes MJ, Bourke AG. Radiological appearances of papillary breast lesions. Clin Radiol. 2008; 63:1265–1273.41. Chang JM, Cho N, Moon WK, Park JS, Chung SY, Jang M. Does ultrasound-guided directional vacuum-assisted removal help eliminate abnormal nipple discharge in patients with benign intraductal single mass? Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:575–580.42. Slawson SH, Johnson BA. Ductography: how to and what if? Radiographics. 2001; 21:133–150.43. Moross T, Lang AP, Mahoney L. Tubular adenoma of breast. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983; 107:84–86.44. Soo MS, Dash N, Bentley R, Lee LH, Nathan G. Tubular adenomas of the breast: imaging findings with histologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 174:757–761.45. Lee SH, Chang JM, Cho N, Koo HR, Yi A, Kim SJ, et al. Practice guideline for the performance of breast ultrasound elastography. Ultrasonography. 2014; 33:3–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast lesions during pregnancy and lactation: a pictorial essay
- Imaging Features of Inflammatory Breast Disorders: A Pictorial Essay
- Sonographic Features of Palpable Breast and Axillary Lesions in Adult Male Patients: A Pictorial Essay
- Resolution of Hypoechoic Mass by Fine-Needle Aspiration
- Imaging Spectrum of Augmented Breast and Post-Mastectomy Reconstructed Breast with Common Complications: A Pictorial Essay