J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc.
2012 Jul;51(4):192-201.
A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study of Cognitive Behavioral Social Skills Training (Korean version) for Middle- or Older-Aged Patients with Schizophrenia : A Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Psychiatry, St. Andrew's Neuropsychiatric Hospital, Icheon, Korea. hansonpark@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Anthropology, Seoul National University College of Social Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Cognitive behavioral therapy and social skills training have been proposed as a promising modality for treatment of patients with schizophrenia. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Social Skill Training (CBSST) in patients with chronic schizophrenia.
METHODS
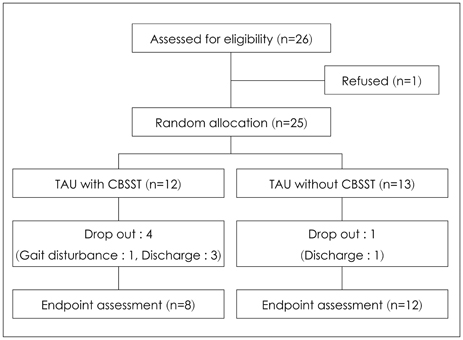
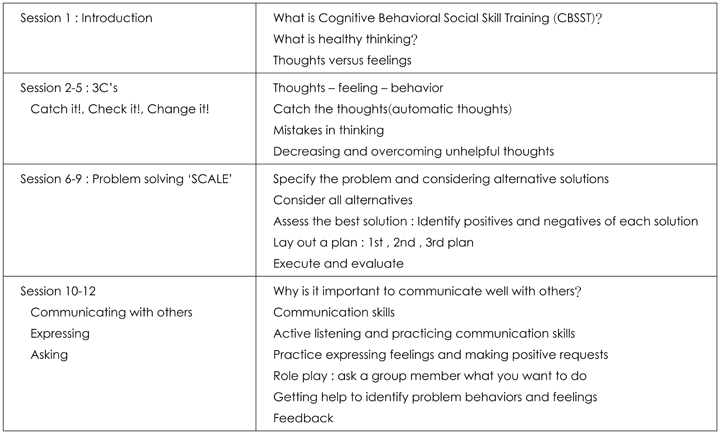
Twenty six middle- or older-aged hospitalized patients with schizophrenia were selected in a mental hospital. Eleven participants were randomly assigned to undergo treatment with CBSST and 15 participants were assigned to receive the usual treatment. CBSST was administered in a single group over 12 sessions for a period of weeks, and the participants were assessed by blinded raters at base line and end point, and end of treatment.
RESULTS
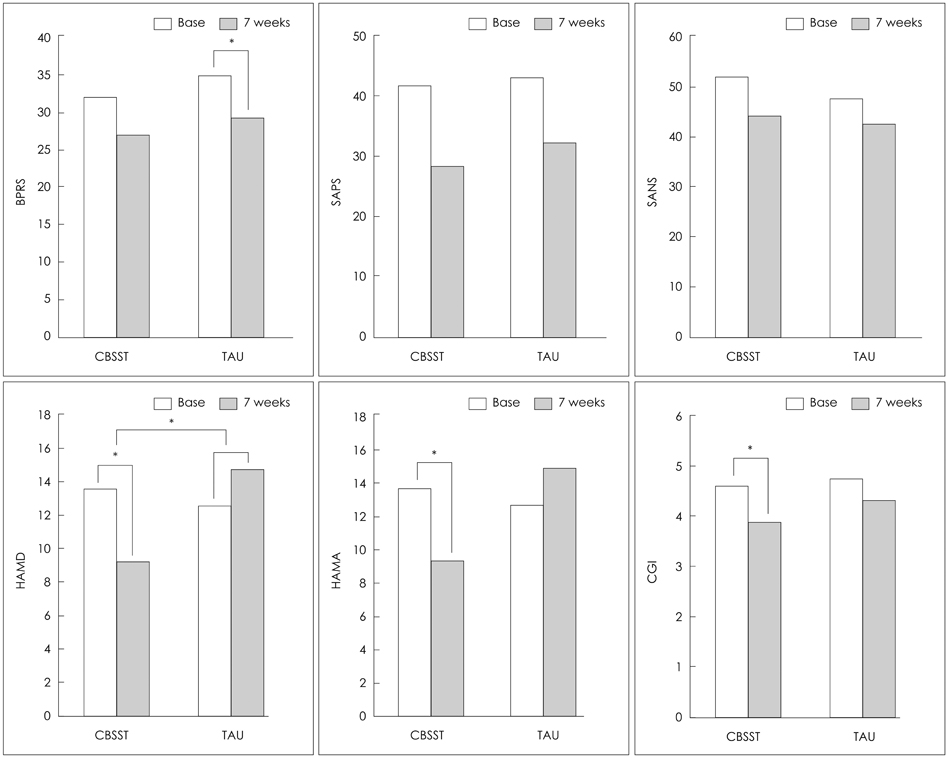
Compared to patients who received the usual treatment, those who received treatment with CBSST showed a significant reduction of Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression score, however, scores for other psychiatric symptoms did not differ significantly. In terms of Quality of life (QoL) analysis, scores for overall quality of life showed a more significant increase in the CBSST group, compared with the group of patients who received the usual treatment. According to results of the Independent Living Skill Survey, patients receiving CBSST showed significantly greater involvement in social activities than patients receiving usual treatment group.
CONCLUSION
Psychosocial intervention for patients with chronic schizophrenia is very important, not only for management of primary psychiatric symptoms, but also for QoL and social rehabilitation. The results of this study, showing improvement of depressive mood, overall life quality, and social activities, suggest that CBSST could be an effective treatment for these patients. This study is a pilot study performed in an inpatient treatment setting. Further studies are required in order to clarify the advantage of CBSST in treatment of patients with chronic schizophrenia, esp. under outpatient settings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. McGrath J, Saha S, Welham J, El Saadi O, MacCauley C, Chant D. A systematic review of the incidence of schizophrenia: the distribution of rates and the influence of sex, urbanicity, migrant status and methodology. BMC Med. 2004. 2:13.2. Kane JM, Correll CU. Past and present progress in the pharmacologic treatment of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010. 71:1115–1124.3. Bustillo JR, Lauriello J, Keith SJ. Schizophrenia: improving outcome. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 1999. 6:229–240.4. Swartz MS, Perkins DO, Stroup TS, Davis SM, Capuano G, Rosenheck RA, et al. Effects of antipsychotic medications on psychosocial functioning in patients with chronic schizophrenia: findings from the NIMH CATIE study. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. 164:428–436.5. Liberman RP. Psychiatric rehabilitation of chronic mental patients. 1988. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press Inc.6. Kopelowicz A, Liberman RP, Zarate R. Recent advances in social skills training for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2006. 32:Suppl 1. S12–S23.7. Penn DL, Corrigan PW, Bentall RP, Racenstein JM, Newman L. Social cognition in schizophrenia. Psychol Bull. 1997. 121:114–132.8. Corrigan PW. Social skills training in adult psychiatric populations: a meta-analysis. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 1991. 22:203–210.9. Pilling S, Bebbington P, Kuipers E, Garety P, Geddes J, Martindale B, et al. Psychological treatments in schizophrenia: II. Meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials of social skills training and cognitive remediation. Psychol Med. 2002. 32:783–791.10. Glynn SM, Marder SR, Liberman RP, Blair K, Wirshing WC, Wirshing DA, et al. Supplementing clinic-based skills training with manual-based community support sessions: effects on social adjustment of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2002. 159:829–837.11. Liberman RP. Psychosocial treatments for schizophrenia. Psychiatry. 1994. 57:104–141.12. Robinson DG, Woerner MG, McMeniman M, Mendelowitz A, Bilder RM. Symptomatic and functional recovery from a first episode of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2004. 161:473–479.13. Green MF. What are the functional consequences of neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia? Am J Psychiatry. 1996. 153:321–330.14. Wykes T, Steel C, Everitt B, Tarrier N. Cognitive behavior therapy for schizophrenia: effect sizes, clinical models, and methodological rigor. Schizophr Bull. 2008. 34:523–537.15. Medalia A, Aluma M, Tryon W, Merriam AE. Effectiveness of attention training in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1998. 24:147–152.16. Wexler BE, Bell MD. Cognitive remediation and vocational rehabilitation for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2005. 31:931–941.17. Lee DE, Choi YS. The history and achievement of psychosocial treatment for patients with schizophrenia. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2009. 48:411–422.18. Green MF. Cognitive remediation in schizophrenia: is it time yet? Am J Psychiatry. 1993. 150:178–187.19. Bellack AS, Gold JM, Buchanan RW. Cognitive rehabilitation for schizophrenia: problems, prospects, and strategies. Schizophr Bull. 1999. 25:257–274.20. Ostrom TM. The sovereignty of social cognition. Handbook of Social Cognition. 1984. Hillsdale, NJ, USA: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.;1–38.21. Hogarty GE, Flesher S. Developmental theory for a cognitive enhancement therapy of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1999. 25:677–692.22. Stanghellini G. Vulnerability to schizophrenia and lack of common sense. Schizophr Bull. 2000. 26:775–787.23. Frith CD, Corcoran R. Exploring 'theory of mind' in people with schizophrenia. Psychol Med. 1996. 26:521–530.24. Turkington D, Sensky T, Scott J, Barnes TR, Nur U, Siddle R, et al. A randomized controlled trial of cognitive-behavior therapy for persistent symptoms in schizophrenia: a five-year follow-up. Schizophr Res. 2008. 98:1–7.25. Grant PM, Huh GA, Perivoliotis D, Stolar NM, Beck AT. Randomized trial to evaluate the efficacy of cognitive therapy for low-functioning patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012. 69:121–127.26. McGurk SR, Twamley EW, Sitzer DI, McHugo GJ, Mueser KT. A meta-analysis of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2007. 164:1791–1802.27. Twamley EW, Jeste DV, Bellack AS. A review of cognitive training in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2003. 29:359–382.28. Granholm E, McQuaid JR, McClure FS, Pedrelli P, Jeste DV. A randomized controlled pilot study of cognitive behavioral social skills training for older patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2002. 53:167–169.29. McQuaid JR, Granholm E, McClure FS, Roepke S, Pedrelli P, Patterson TL, et al. Development of an integrated cognitive-behavioral and social skills training intervention for older patients with schizophrenia. J Psychother Pract Res. 2000. 9:149–156.30. Granholm E, McQuaid JR, McClure FS, Auslander LA, Perivoliotis D, Pedrelli P, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of cognitive behavioral social skills training for middle-aged and older outpatients with chronic schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2005. 162:520–529.31. Association AP, DSM-IV APATFo. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. 2000. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing Inc..32. Choi YS. Group Cognitive-Behaviora Social Skill Trainig Program Manual. 2010. Suwon: Gyeonggi Mental Health Support Teams.33. Overall JE, Beller SA. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS) in geropsychiatric research: I. Factor structure on an inpatient unit. J Gerontol. 1984. 39:187–193.34. Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS). 1984. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa.35. Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms. 1984. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa.36. Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1967. 6:278–296.37. Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959. 32:50–55.38. Spearing MK, Post RM, Leverich GS, Brandt D, Nolen W. Modification of the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Scale for use in bipolar illness (BP): the CGI-BP. Psychiatry Res. 1997. 73:159–171.39. Min SK, Lee CI, Kim KI, Suh SY, Kim DK. Development of Korean version of WHO Quality of Life Scale abbreviated version (WHOQOL-BREF). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000. 39:571–579.40. Wallace CJ, Liberman RP, Tauber R, Wallace J. The independent living skills survey: a comprehensive measure of the community functioning of severely and persistently mentally ill individuals. Schizophr Bull. 2000. 26:631–658.41. Woods SW. Chlorpromazine equivalent doses for the newer atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003. 64:663–667.42. Atkins M, Burgess A, Bottomley C, Riccio M. Chlorpromazine equivalents: a consensus of opinion for both clinical and research applications. Psychiatr Bull. 1997. 21:224–226.43. Adair JG. The Hawthorne effect: a reconsideration of the methodological artifact. J Applied Psychology. 1984. 69:334–345.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effects of Social Skills Training vs. Psychoeducation on Negative Attitudes of Mothers of Persons with Schizophrenia: A Pilot Study
- The Effects of Cognitive Behavioral Group Therapy Improving Social Cognition on the Self efficacy, Relationship Function and Social Skills for Chronic Schizophrenia
- Efficacy of Computerized Cognitive Rehabilitation Training for Inpatients with Schizophrenia : A Pilot Study
- Development of a Cognitive Rehabilitation Program for Patients with Schizophrena
- The History and Achievement of Psychosocial Treatment for Patients with Schizophrenia