J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Jun;56(6):931-937. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.6.931.
Combined Phacoemulsification, Synechiolysis without Gonioprism Lens and Intracameral Tissue Plasminogen Activator Injection for Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckee@skku.edu
- KMID: 2339160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.6.931
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this study we evaluated the safety and efficacy of combined phacoemulsification and synechiolysis without aid of gonioprism lens and intraoperative intracameral tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) injection for angle-closure glaucoma.
METHODS
The method used in this study was synechiolysis with Kuglen hook without aid of gonioprism lens and intraoperative intracameral tPA injection following cataract surgery.
RESULTS
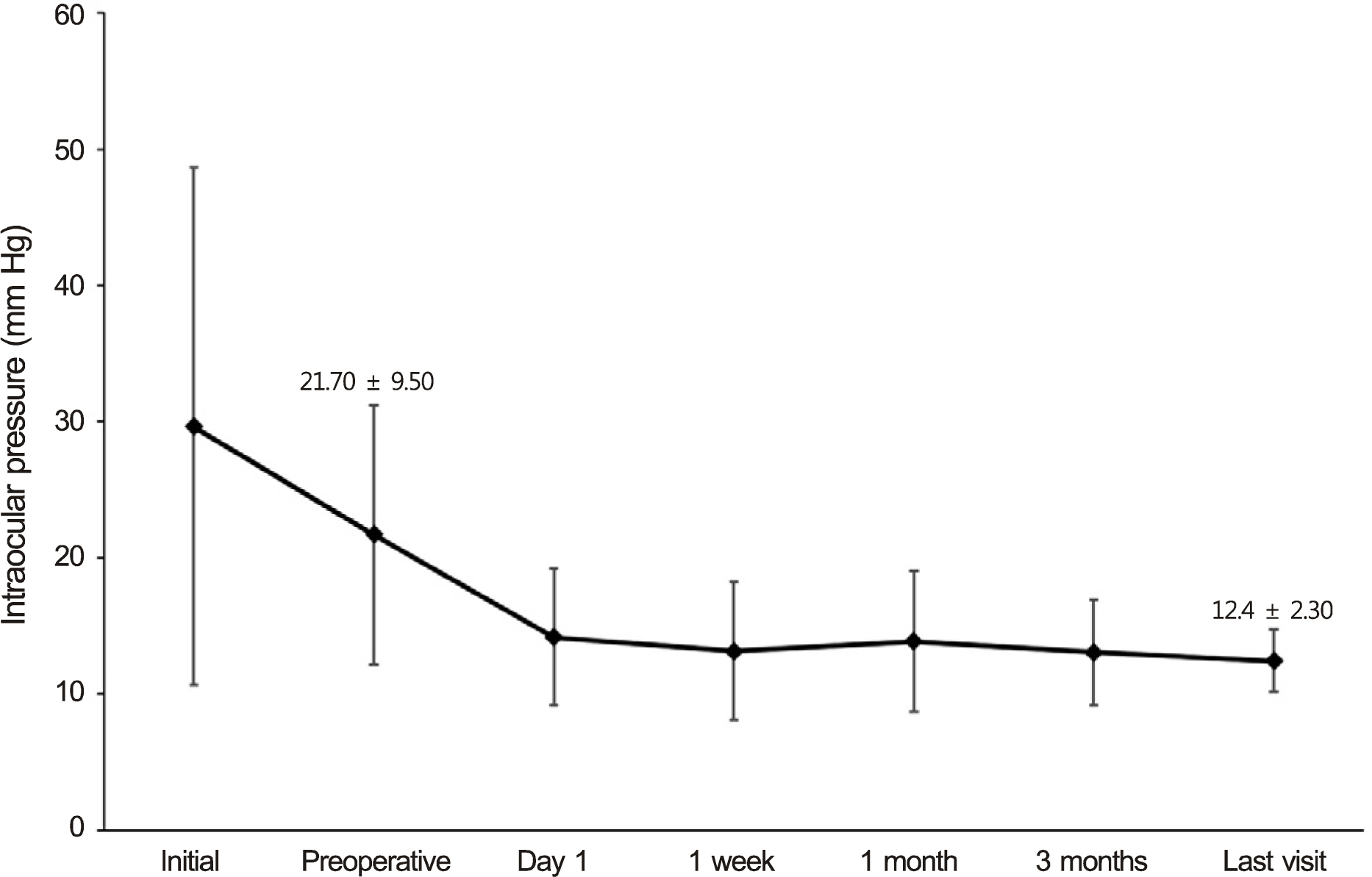
A total of 20 patients with a mean age of 71.4 +/- 5.4 years were treated. Mean follow-up time was 31.3 +/- 24.3 months. Mean preoperative and last visit intraocular pressures (IOPs) were 21.70 +/- 9.50 mm Hg and 12.40 +/- 2.30 mm Hg, respectively (p < 0.0001). The mean number of glaucoma medications decreased from 2.40 to 0.30 (p < 0.0001). IOP was maintained below 16 mm Hg in all cases. No significant intraoperative and postoperative complications, hyphema, or fibrin reaction occurred.
CONCLUSIONS
Combined phacoemulsification and peripheral anterior synechiolysis with Kuglen hook without aid of gonioprism lens and intraoperative intracameral tPA injection is an effective and safe surgical procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ritch R, Loe RF. Angle-closure glaucoma: clinical types. Ritch R, Shields MB, Krupin T, editors. The Glaucomas. 2d ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1996. v. 2:chap. 38.2. Lowe RF. Aetiology of the anatomical basis for primary angle-clo-sure glaucoma. Biometrical comparisons between normal eyes and eyes with primary angle-closure glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1970; 54:161–9.
Article3. Lowe RF. Anterior lens curvature. Comparisons between normal eyes and those with primary angle-closure glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972; 56:409–13.
Article4. Campbell DG, Vela A. Modern goniosynechialysis for the treatment of synechial angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1984; 91:1052–60.
Article5. Shingleton BJ, Chang MA, Bellows AR, Thomas JV. Surgical goniosynechialysis for angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97:551–6.
Article6. Tanihara H, Nagata M. Argon-laser gonioplasty following goniosynechialysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1991; 229:505–7.
Article7. Tanihara H, Nishiwaki K, Nagata M. Surgical results and complications of goniosynechialysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1992; 230:309–13.
Article8. Fang AW, Yang XJ, Nie L, Qu J. Endoscopically controlled goniosynechialysis in managing synechial angle-closure glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2010; 19:19–23.
Article9. Fakhraie G, Vahedian Z, Moghimi S, et al. Phacoemulsification and goniosynechialysis for the management of refractory acute angle closure. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2012; 22:714–8.
Article10. Teekhasaenee C, Ritch R. Combined phacoemulsification and goniosynechialysis for uncontrolled chronic angle-closure glaucoma after acute angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:669–75.
Article11. Imaizumi M, Takaki Y, Yamashita H. Phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation for acute angle closure not treated or previously treated by laser iridotomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:85–90.
Article12. Ming Zhi Z, Lim AS, Yin Wong T. A pilot study of lens extraction in the management of acute primary angle-closure glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:534–6.
Article13. Jacobi PC, Dietlein TS, Lüke C, et al. Primary phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation for acute angle-closure glaucoma. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1597–603.14. Hayashi K, Hayashi H, Nakao F, Hayashi F. Effect of cataract surgery on intraocular pressure control in glaucoma patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2001; 27:1779–86.
Article15. Maeda M, Watanabe M, Ichikawa K. Goniosynechialysis using an ophthalmic endoscope and cataract surgery for primary angle-clo-sure glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2014; 23:174–8.
Article16. Lai JS, Tham CC, Chan JC. The clinical outcomes of cataract extraction by phacoemulsification in eyes with primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG) and co-existing cataract: a prospective case series. J Glaucoma. 2006; 15:47–52.
Article17. White AJ, Orros JM, Healey PR. Outcomes of combined lens extraction and goniosynechialysis in angle closure. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2013; 41:746–52.
Article18. Yun YM, Yim JH, Kim CS. Clinical factors that influence intraocular pressure change after cataract surgery in primary open-angle glaucoma and angle-closure glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:85–96.19. Liu CJ, Cheng CY, Wu CW, et al. Factors predicting intraocular pressure control after phacoemulsification in angle-closure glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:1390–4.
Article20. Wishart PK, Atkinson PL. Extracapsular cataract extraction and posterior chamber lens implantation in patients with primary chronic angle-closure glaucoma: effect on intraocular pressure control. Eye (Lond). 1989; 3(Pt 6):706–12.
Article21. Harasymowycz PJ, Papamatheakis DG, Ahmed I, et al. Phacoemulsification and goniosynechialysis in the management of un-responsive primary angle closure. J Glaucoma. 2005; 14:186–9.
Article22. Liu CJ, Cheng CY, Ko YC, Lau LI. Determinants of long-term intraocular pressure after phacoemulsification in primary angle-clo-sure glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2011; 20:566–70.
Article23. Hamanaka T, Kasahara K, Takemura T. Histopathology of the trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal in primary angle-closure glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:8849–61.
Article24. Sihota R, Lakshmaiah NC, Walia KB, et al. The trabecular meshwork in acute and chronic angle closure glaucoma. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2001; 49:255–9.25. Wedrich A, Menapace R, Mühlbauer-Ries E. The use of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for intracameral fibrinolysis following cataract surgery. Int Ophthalmol. 1994-1995; 18:277–80.
Article26. Moon J, Chung S, Myong Y, et al. Treatment of postcataract fi-brinous membranes with tissue plasminogen activator. Ophthalmology. 1992; 99:1256–9.
Article27. Heiligenhaus A, Steinmetz B, Lapuente R, et al. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in cases with fibrin formation after cataract surgery: a prospective randomised multicentre study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:810–5.
Article28. Tripathi RC, Tripathi BJ, Park JK, et al. Intracameral tissue plasminogen activator for resolution of fibrin clots after glaucoma filtering procedures. Am J Ophthalmol. 1991; 111:247–8.
Article29. Laatikainen L, Mattila J. The use of tissue plasminogen activator in post-traumatic total hyphaema. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1996; 234:67–8.
Article30. Bennett SR, Folk JC, Blodi CF, Klugman M. Factors prognostic of visual outcome in patients with subretinal hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990; 109:33–7.
Article31. Sanders D, Peyman GA, Fishman G, et al. The toxicity of intravitreal whole blood and hemoglobin. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1975; 197:255–67.
Article32. Toth CA, Morse LS, Hjelmeland LM, Landers MB 3rd. Fibrin di-rects early retinal damage after experimental subretinal hemorrhage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991; 109:723–9.
Article33. Razeghinejad MR, Rahat F. Combined phacoemulsification and viscogoniosynechialysis in the management of patients with chronic angle closure glaucoma. Int Ophthalmol. 2010; 30:353–9.
Article34. Varma D, Adams WE, Phelan PS, Fraser SG. Viscogonioplasty in patients with chronic narrow angle glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:648–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phacoemulsification Alone versus Phacoemulsification Combined with Trabeculectomy for Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- The Change of Intraocular Pressure after Extracapsular Cataract Extraction in Patients with Angle-closure Glaucoma
- Phacoemulsification using Iris Hook in Patients with Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma Associated with Lens Subluxation
- Biometric Comparisons between Acute and Chronic Angle Closure Glaucoma
- Intravitreal Tissue Plasminogen Activator and Gas Injection in Submacular Hemorrhage