J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2014 Dec;55(12):1779-1786. 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1779.
Clinical Results and Optical Quality of Diffractive Multifocal IOL Implantation after Myopic Refractive Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Busan Sungmo Eye Hospital, Busan, Korea. pinmed@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2338960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2014.55.12.1779
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the visual outcome and optical quality in eyes with diffractive multifocal intraocular lens (DMIOL) implantation after myopic refractive surgery.
METHODS
Nineteen eyes (15 patients) were implanted with AcriSof ReSTOR(R) SN6AD1, the aspheric DMIOL after myopic refractive surgery (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis [LASIK] 14 eyes, photorefractive keratectomy [PRK] 4 eyes, laser-assisted subepithelial keratomileusis [LASEK] 1 eye). Preoperative and postoperative visual acuities and manifest refraction were measured. Preoperative corneal higher-order aberrations (HOAs) were measured using Hartmann-Shack (H-S) aberrometer in dilated pupils, and optical qualities were measured 1 month postoperatively using H-S aberrometer and a double-pass system under mesopic conditions. Patient satisfaction was investigated using a questionnaire at 2 months postoperatively.
RESULTS
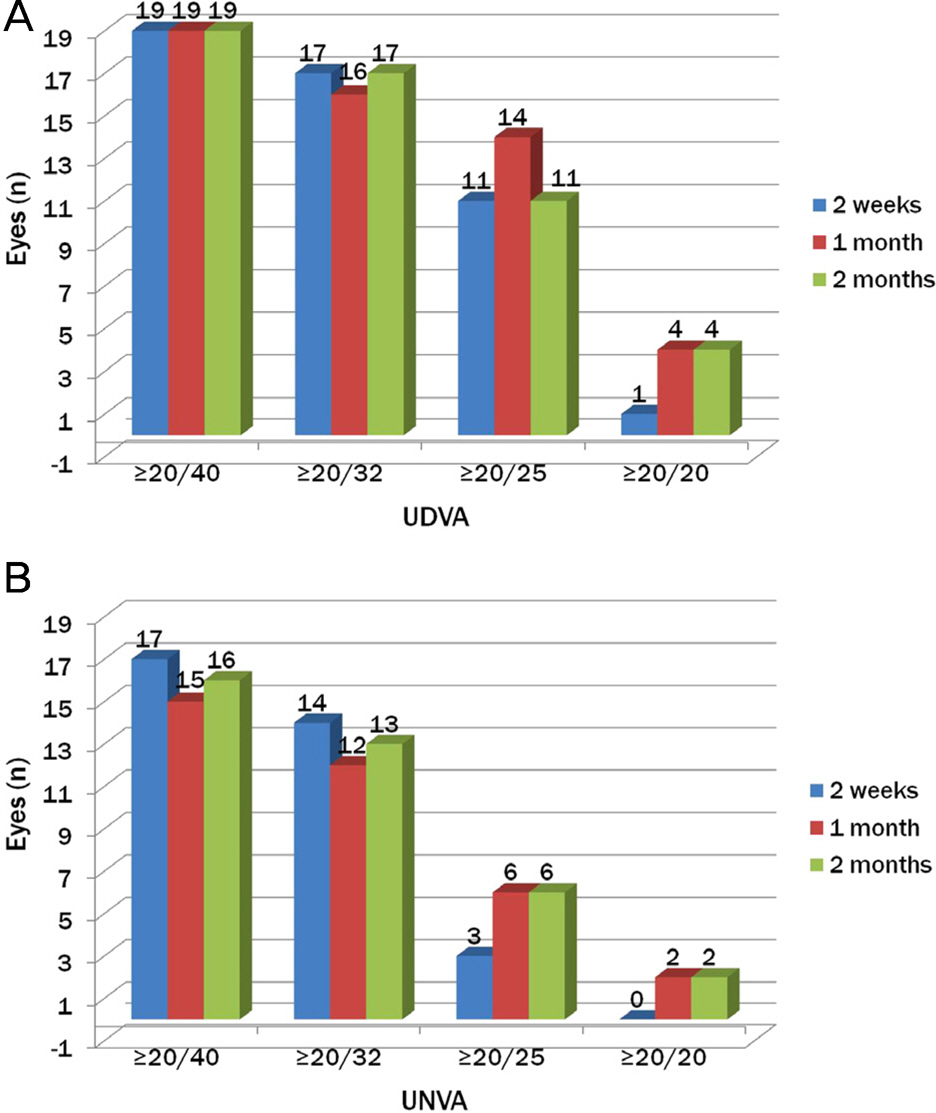
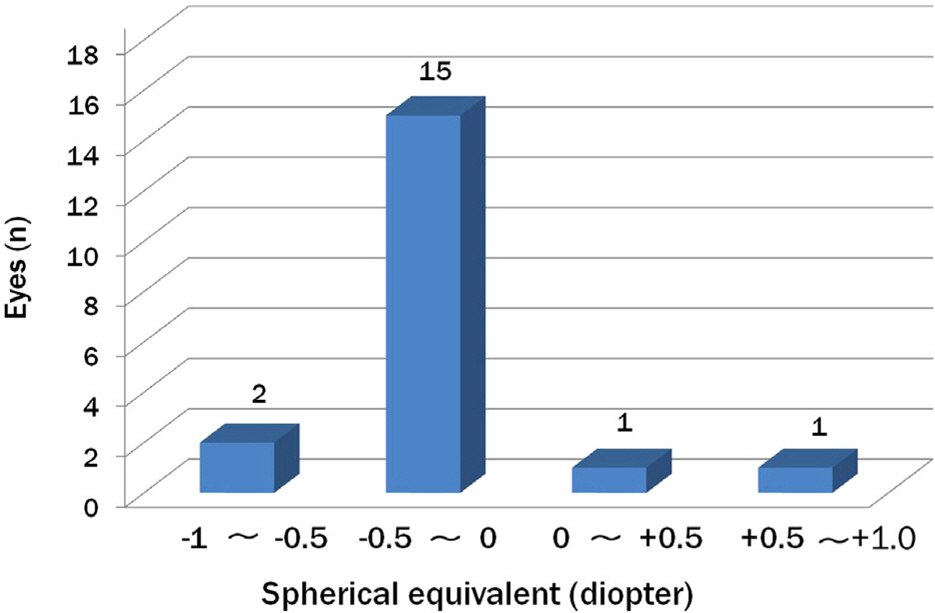
Uncorrected distant and near visual acuities at postoperative 2 months were 0.11 +/- 0.19, and 0.19 +/- 0.12 (log MAR), respectively. Postoperative spherical equivalent (SE) of 16 eyes (84.2%) was within +/-0.50 diopters (D) and all eyes were within +/-1.00 D from emmetropia. Preoperative corneal and postoperative ocular spherical aberrations in a 4.0 mm pupil diameter were 0.08 +/- 0.08 and 0.07 +/- 0.07 (microm), respectively. Objective scatter index was 3.42 +/- 1.71 and modulation transfer function (MTF) cut-off value was 21.03 +/- 12.37 cpd. General satisfaction score was 3.52 +/- 0.96 points out of 5, and 8 patients (11 eyes) were not satisfied with DMIOL implantation.
CONCLUSIONS
After DMIOL implantation in the eyes with previous myopic refractive surgery, postoperative SE was close to the target D, but optical qualities and patient satisfaction were poor.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. McCarthy M, Gavanski GM, Paton KE, Holland SP. Intraocular lens power calculations after myopic laser refractive surgery: a comparison of methods in 173 eyes. Ophthalmology. 2011; 118:940–4.
Article2. Wang L, Hill WE, Koch DD. Evaluation of intraocular lens power prediction methods using the American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgeons Post-Keratorefractive Intraocular Lens Power Calculator. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1466–73.
Article3. Khor WB, Afshari NA. The role of presbyopia-correcting intraocular lenses after laser in situ keratomileusis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013; 24:35–40.
Article4. Kang JH, Park JI, Lee KH. A new method for measuring corneal refractive power after refractive surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:859–64.5. Lee WS, Moon SJ, Lee KH, Lee DJ. Comparison of four systems of IOL calculation after keratorefractive surgery in eyes requiring cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1810–7.
Article6. Lee AC, Qazi MA, Pepose JS. Biometry and intraocular lens power calculation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:13–7.
Article7. Aristodemou P, Knox Cartwright NE, Sparrow JM, Johnston RL. Formula choice: Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, or SRK/T and refractive outcomes in 8108 eyes after cataract surgery with biometry by partial coherence interferometry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011; 37:63–71.
Article8. Kim SY, Kim MS. The Study on target refraction to improve visual quality in patients implanted with multifocal IOL. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:223–9.
Article9. Chang M, Eom Y, Kang SY, et al. Clinical outcome of diffractive multifocal aspheric intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:529–36.
Article10. Gwak JY, Choi JS, Pak KH, Baek NH. Visual and optical functions after diffractive multifocal intraocular lens. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:396–402.
Article11. Lee HS, Park SH, Kim MS. Clinical results and some problems of multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1235–41.
Article12. Zelichowska B, Rekas M, Stankiewicz A, et al. Apodized diffractive versus refractive multifocal intraocular lenses: optical and visual evaluation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:2036–42.13. Castillo-Gómez A, Carmona-González D, Martínez-de-la-Casa JM, et al. Evaluation of image quality after implantation of 2 diffractive multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:1244–50.
Article14. de Vries NE, Franssen L, Webers CA, et al. Intraocular straylight after implantation of the multifocal AcrySof ReSTOR SA60D3 diffractive intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:957–62.
Article15. López-Miguel A, Martínez-Almeida L, González-García MJ, et al. Precision of higher-order aberration measurements with a new Placido-disk topographer and Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2013; 39:242–9.
Article16. Park YL, Hwang GY, Joo CK. Comparative study of clinical outcomes between 2 types of multifocal aspheric intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:1199–207.
Article17. Kim SM, Kim CH, Chung ES, Chung TY. Visual outcome and patient satisfaction after implantation of multifocal IOLs: three-month follow-up results. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:230–7.
Article18. Muftuoglu O, Dao L, Mootha VV, et al. Apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation after laser in situ keratomileusis with or without subsequent excimer laser enhancement. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:1815–21.
Article19. Fernández-Vega L, Madrid-Costa D, Alfonso JF, et al. Optical and visual performance of diffractive intraocular lens implantation after myopic laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009; 35:825–32.
Article20. Yoon JU, Chung JL, Hong JP, et al. Comparison of wavefront analysis and visual function between monofocal and multifocal aspheric intraocular lenses. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2009; 50:195–201.
Article21. Alfonso JF, Madrid-Costa D, Poo-López A, Montés-Micó R. Visual quality after diffractive intraocular lens implantation in eyes with previous myopic laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:1848–54.
Article22. Alió JL, Piñero D, Muftuoglu O. Corneal wavefront-guided retreatments for significant night vision symptoms after myopic laser refractive surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008; 145:65–74.
Article23. Bühren J, Martin T, Kühne A, Kohnen T. Correlation of aberrometry, contrast sensitivity, and subjective symptoms with quality of vision after LASIK. J Refract Surg. 2009; 25:559–68.24. van Gaalen KW, Koopmans SA, Jansonius NM, Kooijman AC. Clinical comparison of the optical performance of aspheric and spherical intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010; 36:34–43.
Article25. Gatinel D. Limited accuracy of Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensing in eyes with diffractive multifocal IOLs. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:528. author reply 528-9.
Article26. Díaz-Doutón F, Benito A, Pujol J, et al. Comparison of the retinal image quality with a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor and a double-pass instrument. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:1710–6.27. Toto L, Falconio G, Vecchiarino L, et al. Visual performance and biocompatibility of 2 multifocal diffractive IOLs: six-month comparative study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:1419–25.28. Alfonso JF, Fernández-Vega L, Baamonde MB, Montés-Micó R. Correlation of pupil size with visual acuity and contrast sensitivity after implantation of an apodized diffractive intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007; 33:430–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Outcomes of Diffractive Multifocal Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Diffractive and Refractive Multifocal Intraocular Lens with Same Near Added
- Comparison of the Visual Outcomes after Cataract Surgery with Implantation of a Bifocal and Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens
- Effects of Bifocal versus Trifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lens Implantation on Visual Quality after Cataract Surgery
- Comparison of Optical Aberrations and Contrast Sensitivity between Monofocal and Multifocal Intraocular Lens