J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2013 Aug;54(8):1199-1207.
Comparative Study of Clinical Outcomes Between 2 Types of Multifocal Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ckjoo@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of the OptiVis(TM) Multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) and compare the clinical outcome between OptiVis(TM) and AcrySof(R) ReSTOR(R) D1.
METHODS
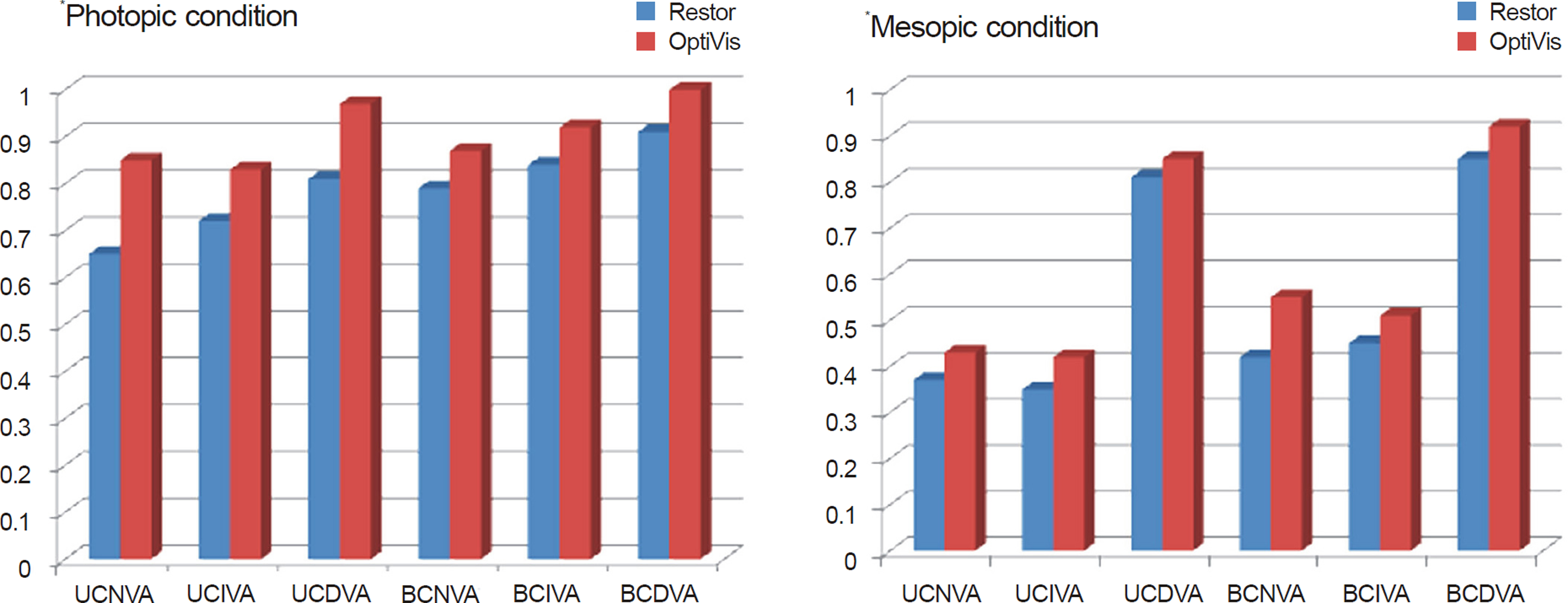
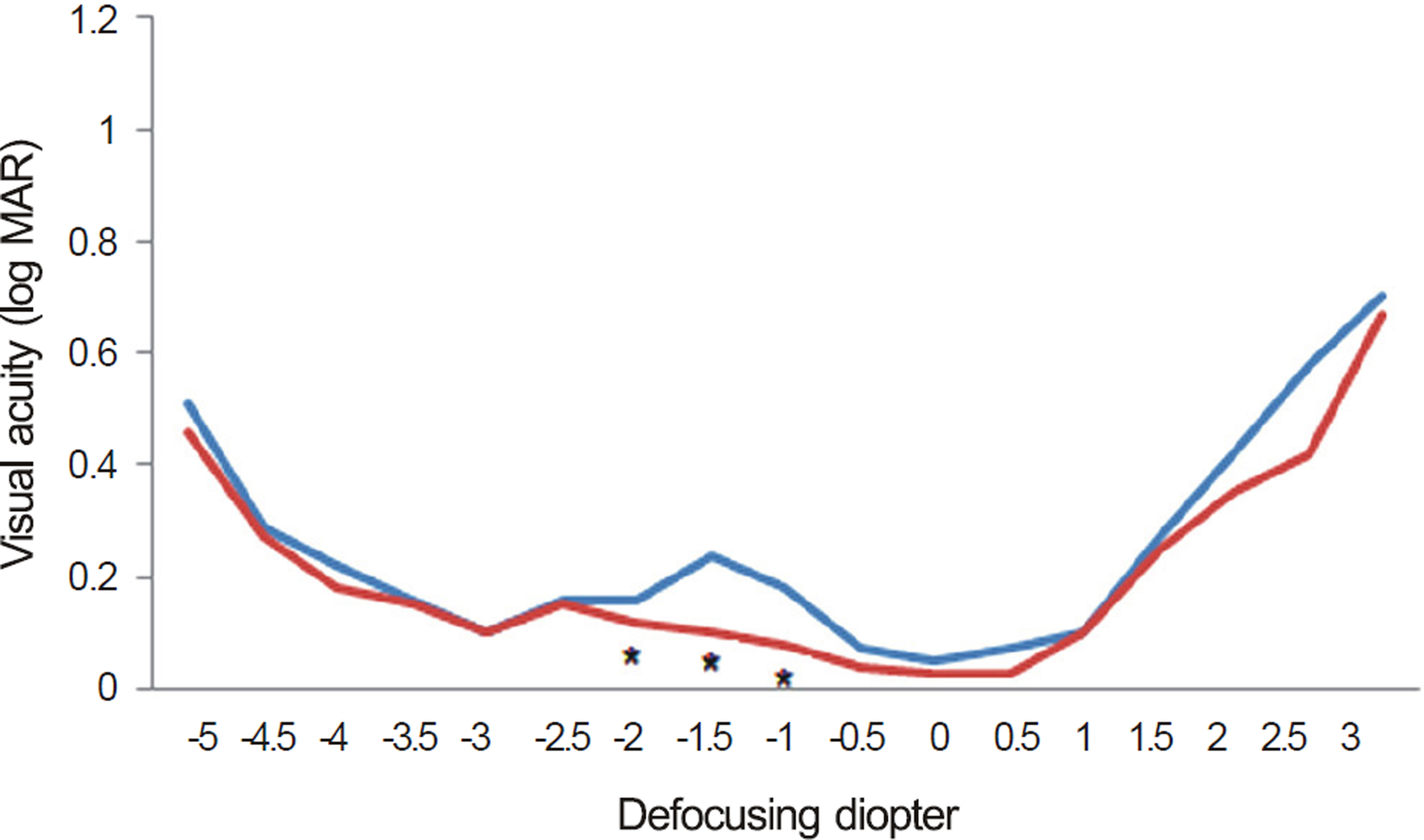
We reviewed 20 eyes of 11 patients implanted with OptiVis(TM) and 20 eyes of 10 patients implanted with AcrySof(R) ReSTOR(R) D1. The clinical outcomes of the 2 IOLs were evaluated 1 and 2 months postoperatively and consisted of distant, intermediate, and near visual acuity, depth of focus, contrast sensitivity, wavefront aberration, patient satisfaction, decentration and IOL tilt.
RESULTS
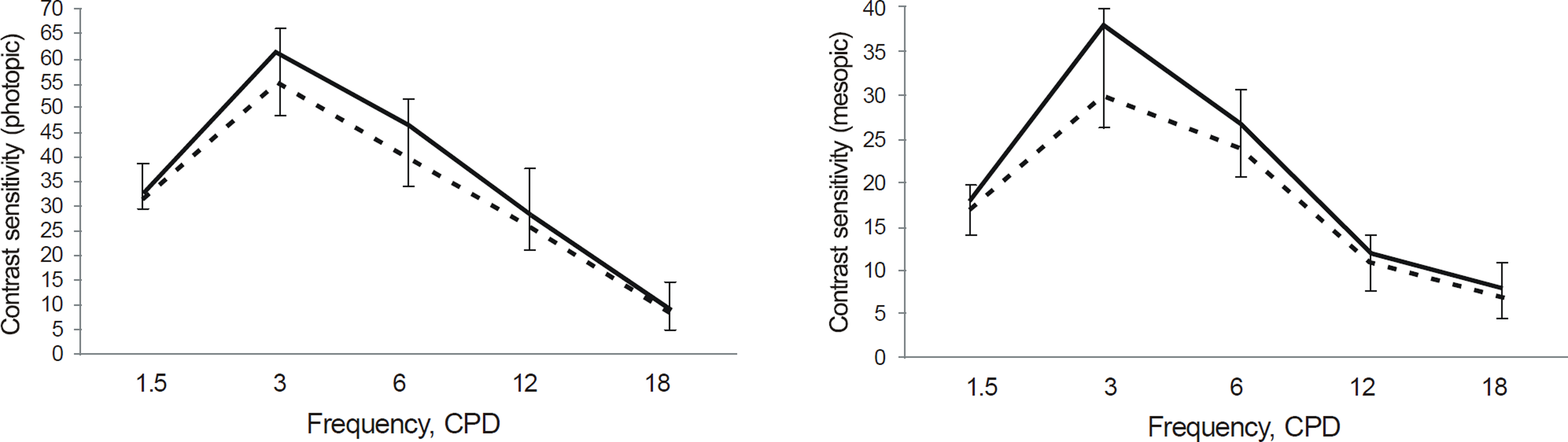
Intermediate vision was better in the OptiVis(TM) group. There were no statistical differences between the 2 groups with respect to distant vision, near vision and wavefront aberration, contrast sensitivity, decentration and IOL tilt. Depth of focus was deeper in the OptiVis(TM) group at the intermediate visual acuity zone. There were no statistically significant result differences between postoperative 1 and 2 months.
CONCLUSIONS
The OptiVis(TM) multifocal IOL provided satisfactory visual acuity at distance, near, and intermediate with no apparent reduction in contrast sensitivity. The IOL can be effective for improving patient satisfaction after cataract surgery as well as correcting presbyopia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Martínez Palmer A, Gómez Faiña P, España Albelda A. . Visual function with bilateral implantation of monofocal and multifocal intraocular lenses: a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:257–64.
Article2. Goes FJ. Refractive lens exchange with the diffractive multifocal tecnis ZM900 intraocular lens. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:243–50.
Article3. Fernández-Vega L, Alfonso JF, Rodríguez PP, Montés-Micó R. Clear lens extraction with multifocal apodized intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:1491–8.4. Fernández-Vega L, Alfonso JF, Montés-Micó R, Amhaz H. Visual acuity tolerance to residual refractive errors in patients with an apodized diffractive intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008; 34:199–204.
Article5. Lee DY, Roh JH, Shyn KH. 2005 Survey for KSCRS members: current trends in cataract surgery in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:485–92.6. Lane SS, Morris M, Nordan L. . Multifocal intraocular lenses. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2006; 19:89–105.7. Hütz WW, Eckhardt HB, Röhrig B, Grolmus R. Reading ability with 3 multifocal intraocular lens models. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:2015–21.
Article8. Kohnen T, Allen D, Boureau C. . European multicenter study of the AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive intraocular lens. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:584–e1.
Article9. Blaylock JF, Si Z, Vickers C. Visual and refractive status at differ-ent focal distances after implantation of the ReSTOR multifocal in-traocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1464–73.
Article10. Chiam PJ, Chan JH, Aggarwal RK, Kasaby S. ReSTOR intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery: quality of vision. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:1459–63.
Article11. Sallet G. Refractive outcome after bilateral implantation of an apo-dized diffractive intraocular lens. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 2006; 299:67–73.12. Souza CE, Muccioli C, Soriano ES. . Visual performance of AcrySof ReSTOR apodized diffractive IOL: a prospective com-parative trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 141:827–32.
Article13. Cumming JS, Colvard DM, Dell SJ. . Clinical evaluation of the Crystalens AT-45 accommodating intraocular lens: results of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration clinical trial. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006; 32:812–25.14. Gunenc U, Celik L. Long-term experience with mixing and matching refractive Array and diffractive CeeOn multifocal intraocular lenses. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:233–42.
Article15. Goes FJ. Visual results following implantation of a refractive mul-tifocal IOL in one eye and a diffractive multifocal IOL in the con-tralateral eye. J Refract Surg. 2008; 24:300–5.
Article16. Bi H, Cui Y, Ma X. . Early clinical evaluation of Acrysof ReSTOR multifocal intraocular lens for treatment of cataract. Ophthalmologica. 2008; 222:11–6.
Article17. Pepose JS, Qazi MA, Davies J. . Visual performance of patients with bilateral vs combination Crystalens, Rezoom, and ReSTOR in-traocular lense implants. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 144:347–57.18. Apple DJ, Sims J. Harold Ridley and the invention of the intra-ocular lens. Surv Ophthalmol. 1996; 40:279–92.
Article19. Piovella M, Bosc JM. Clinical evaluation of the OptiVis™ multi-focal intraocular lens. Adv Ther. 2011; 28:1012–20.
Article20. Lee HS, Park SH, Kim MS. Clinical results and some problems of multifocal apodized diffractive intraocular lens implantation. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:1235–41.
Article21. Caballero A, Losada M, Lopez JM. . Decentration of intra-ocular lenses implanted after intercapsular cataract extraction (enveloped technique). J Cataract Refract Surg. 1991; 17:330–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical outcomes of currently available multifocal intraocular lenses
- Comparison of Nd:YAG Capsulotomy Rates between Spherical and Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Comparative Study of Clinical Outcomes between 2 Types of 3-Piece Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Comparison of Wavefront Analysis and Visual Function Between Monofocal and Multifocal Aspheric Intraocular Lenses
- Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Refractive Aspheric Multifocal IOL Implantation